* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Show all work on a separate sheet of work paper
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
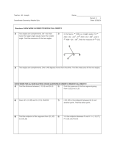
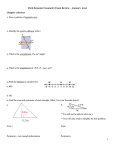
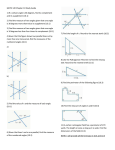
Geometry Unit 2 Worksheet Show all work on a separate sheet of work paper. Remember to follow the criteria for credit. Use the following diagram for problems 1 – 3. Use the following diagram for problems 7 – 9. 1. Identify a pair of complementary angles. 7. Identify a pair of complementary angles. 2. Identify a pair of supplementary angles. 8. Identify a pair of supplementary angles. 3. Identify a pair of vertical angles. 9. Identify a pair of vertical angles. 4. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 5. 6. 10. Use the following diagram to solve for x. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 11. Use the following diagram to solve for x. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. 12. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. Page 1 of 10 © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry Unit 2 Use the following diagram for problems 13 – 15. Worksheet Use the following diagram for problems 19 – 21. 13. Identify a pair of complementary angles. 19. Identify a pair of complementary angles. 14. Identify a pair of supplementary angles. 20. Identify a pair of supplementary angles. 15. Identify a pair of vertical angles. 21. Identify a pair of vertical angles. 16. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 22. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 17. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 23. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 24. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. 18. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. Page 2 of 10 © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 25. 26. Unit 2 Use the following diagram to solve for x. Worksheet 30. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. 31. Find the circumference to the nearest tenth. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 1 dm 32. Find the circumference to the nearest tenth. 3 hm 27. Use the following diagram to solve for x and y. 28. Use the following diagram to solve for x. 29. Use the following diagram to solve for x. Page 3 of 10 33. Find the circumference to the nearest tenth. 34. Find the circumference to the nearest tenth. © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry Unit 2 35. Find the circumference to the nearest tenth. 36. Find the perimeter. 11 mm 4 mm Worksheet 41. Find the perimeter. 42. Find the perimeter. 43. Find the area. 6 mm 15 mm 37. Find the perimeter. 6m 3m 10 m 15 m 38. 3 km Find the perimeter. 18 hm 5 hm 8 hm 12 hm 44. 39. Find the area. Find the perimeter. 8 hm 3 dm 4 dm 40. Find the perimeter. 45. Find the area. 4 km 4 cm 6 km Page 4 of 10 5 cm © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 46. Unit 2 Find the area. Worksheet 51. Find the area. 52. Find the area. 53. Find the area. 54. Find the area of a square whose perimeter is 12 m. 55. Find the area of a square whose perimeter is 8 cm. 56. Find the area of a square whose perimeter is 32 m. 57. Find the area of a square whose perimeter is 36 cm. 6 dm 3 dm 47. Find the area. 6 mm 7 mm 5 mm 11 mm 48. Find the area. 5 km 16 km 8 km 12 km 49. 50. Find the area. Find the area. Page 5 of 10 © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 58. 59. 60. 61. Unit 2 Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 6π cm. Leave your answer in terms of π. Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 8π cm. Leave your answer in terms of π. Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 10π cm. Leave your answer in terms of π. Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 12π cm. Leave your answer in terms of π. For problems 62 – 67, rewrite the given statement in if-then form. Underline the hypothesis once and the conclusion twice. 62. An object weighs 16 ounces if it weighs one pound. 63. Three points are collinear if they lie on the same line. 64. Blue trunkfish live in the waters of a coral reef. 65. The measure of a right angle is 90˚. 66. 67. A line contains at least two points. Constrictors, such as pythons, are not poisonous. Page 6 of 10 Worksheet Use the following statement for problems 68 – 74. If an angle is a right angle, then it has a measure of 90˚. 68. Classify the statement as true or false. 69. Write the converse of the given statement. 70. Classify the converse as true or false. 71. Write the inverse of the given statement. 72. Classify the inverse as true or false. 73. Write the contrapositive of the given statement. 74. Classify the contrapositive as true or false. Use the following statement for problems 75 – 81. If two angles are supplementary, then the sum of the angle measures is 180˚. 75. Classify the statement as true or false. 76. Write the converse of the given statement. 77. Classify the converse as true or false. 78. Write the inverse of the given statement. 79. Classify the inverse as true or false. 80. Write the contrapositive of the given statement. 81. Classify the contrapositive as true or false. © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry Unit 2 Use the following statement for problems 82 – 88. Worksheet 92. If an angle is bisected, then it is divided into two congruent parts. 82. 83. Classify the statement as true or false. If an angle is acute, then its measure is 36˚. 93. Write the converse of the given statement. 84. Classify the converse as true or false. 85. Write the inverse of the given statement. 86. Classify the inverse as true or false. 87. Write the contrapositive of the given statement. 88. Classify the contrapositive as true or false. If you have a job, then you work only on Saturday. Page 7 of 10 Points A, B and C are on plane X. q: Point D is on plane Y. 97. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. Using p and q, write q p in words. p: Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. If you are in a math class, then you have math first hour. 91. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. If x > y, then x2 > y2 96. 90. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. If x2 = 25, then x = 5. 95. If you live in a state east of Arizona, then you live in Texas. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. If you own an automobile, then you own a Chevy. 94. 89. Prove that the following conditional statement is false by providing a counterexample. 98. Using p and q, write ~q ~p in words. p: Points X, Y and D are on the same line. q: Point W is on the same line as X and Y. Using p and q, write p q in words. p: intersects at a point. q: Point P is the point of intersection. © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 99. 100. Unit 2 Using p and q, write q p in words. 106. A and B are supplementary. q: John has the fastest time for the 100 butterfly. Therefore, mA mB 180 ˚. Using p and q, write ~p ~q in words. 107. q: Sarah went to the movies. Using p and q, write in words. q: Freshmen want to be like sophomores. 108. For problems 102 – 106, state whether the given argument is valid or invalid. If it is invalid, briefly explain why. An isosceles triangle has at least two sides with the same length. ∆XYZ has three sides with the same length. If the following two premises (statements) are true, what conclusion can you reach? Points Q, R, S lie within plane P. Points Q, S lie on line k. If it is raining, then my dog gets wet. It is raining. 109. Therefore, my dog is wet. 103. If the following two premises (statements) are true, what conclusion can you reach? ~q p: Sophomores are the smartest students on campus. 102. If two angles are supplementary, then their sum is 180˚. p: John is a good swimmer. p: Sarah went to the mall. 101. Worksheet If mA = 90˚, then A is not acute. If the following two premises (statements) are true, what conclusion can you reach? A square has four sides with the same length and four angles with the same measure. ABCD has four sides with the same length. A is not acute. Therefore, mA = 90˚. 104. If it is a cat, then it is an animal. Whiskers is an animal. Therefore, Whiskers is a cat. 105. If M is the midpoint of AC, then AM = MC M is the midpoint of AC. 110. Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, … Therefore, AM = MC. Page 8 of 10 © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 111. Unit 2 Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 120. Find the distance between the point A( 5, 8 ) and point B( -2, 3 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 121. Find the distance between the point E( -3.5, -2 ) and point F( 3.5, 6 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 122. Find the distance between the point B( 3, -1 ) and point C( 0, 3 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 123. Find the distance between the point E( 3, -3 ) and point D( -2, -1 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 124. Find the distance between the point J( 1, 4 ) and point K( -2, 3 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 125. Find the midpoint of the segment formed by point X( 4, 5 ) and point Y( -1, 3 ). 1, 6, 11, 16, 21, … 112. Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, … 113. Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 0, 3, 8, 15, … 114. Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 1, 2, 5, 10, 17, 26, … 115. Worksheet Find the next two terms for the given sequence and describe the pattern for the sequence. 3, -12, 48, -192, … 116. Sketch the points M, N and P such that M and P are collinear and N is non-collinear. 126. Find the midpoint of the segment formed by point A( 5, 8 ) and point B( -2, 3 ). 117. Sketch the points T, U and V such that T and U are collinear and V is non-collinear. 127. Find the midpoint of the segment formed point E( -3.5, -2 ) and point F( 3.5, 6 ). 118. Sketch the points P, Q and R such that Q and R are collinear and P is non-collinear. 128. Find the midpoint of the segment formed by point B( 3, -1 ) and point C( 0, 3 ). 129. Find the midpoint of the segment formed by point E( 3, -3 ) and point D( -2, -1 ). 130. Find the midpoint of the segment formed by point J( 1, 4 ) and point K( -2, 3 ). 119. Find the distance between the point X( 4, 5 ) and point Y( -1, 3 ). Round your answer to the nearest tenth. Page 9 of 10 © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01 Geometry 131. Unit 2 In the diagram below, bisects ABC . If mDBC = 32˚ and mABC = (6x + 4)˚, find x. 135. Worksheet In the diagram below, bisects LMN . If mLMP = (2x – 27)˚ and mNMP = (5x – 45)˚, find x. A L M B D P C 132. In the diagram below, bisects XYZ . If mXYZ = (2x + 24)˚ and mXYW = 30˚, find x. 136. N In the diagram below, bisects KAR . If mTAK = 27 ˚ and mKAR = (7x – 9)˚, find x. Y X Z W 133. In the diagram below, bisects QRS . If mQRT = (4x – 28)˚ and mSRT = (12x – 36)˚, find x. Q T R S 134. In the diagram below, bisects MAT . If mMAT = (8x – 6)˚ and mMAH = 45˚, find x. H M A Page 10 of 10 T © Mastery Mathematics 8/11/01