* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download O`Neill`s Math
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
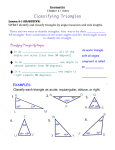
2009-2010 11th Grade Client-based Project: Phase I & Phase II ROP Graphic Design/Multimedia Production: making W.A.V.E.S School of Digital Media & Design Inter Algebra/Pre Calculus – O’Neill 1st SEMESTER Timeline Units of Study Essential Questions? Applied Learning Projects September October November December January Chapter 5 Quadratic Functions 5.1 Introduction to Quadratic Functions 5.2 Introduction to Solving Quadratic Equations 5.3 Factoring Quadratic Expressions 5.4 Completing the Square 5.5 The Quadratic Formula 5.6 Quadratic Equations and Complex Numbers 5,7 Curve Fitting with Quadratic Models 5.8 Solving Quadratic Inequalities What is a system of linear equations, and what do they represent? Out of This World After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Use the function to model the vertical motion of a basketball. Compare and contract algebraic models of Chapter 6 Chapter 1 Data and Linear Representations 1.1 Tables and Graphs of Linear Equations 1.2 Slopes and Intercepts 1.3 Direct Variation 1.4 Scatter Plots and Least-Squares Lines 1.5 Intro to Solving Equations 1.6 Intro to Solving Inequalities 1.7 Solving Absolute Value Chapter 2 Numbers and Functions 2.1 Operations with numbers 2.2 Properties of exponents 2.3 Introduction to functions 2.4 Operations with functions 2.5 Inverses of Functions 2.6 Special Functions 2.7 A Preview of Transformations Chapter 3 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 3.1 Solving Systems by Graphing or Substitution 3.2 Solving Systems by Elimination 3.3 Linear Inequalities in Two variables 3.4 Systems of Linear Equations 3.5 Linear Programming 3.6 Parametric Equations What are the different ways linear data can be represented? Correlation Exploration After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: What are the operations that can be performed on numbers and functions? Space Trash After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Use a table to represent the relationship between time in years and the number of space debris objects, and What is a system of linear equations, and what do they represent? Maximum Profit/Minimum Cost After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Represent real-world data by using scatter plots. Find and use linear models to predict Set up and solve linearprogramming problems that involve finding maximums Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 6.1 Exponential Growth and Decay 6.2 Exponential Functions 6.3 Logarithmic Functions 6.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions 6.5 Applications of Common Logarithmic 6.6 The Natural Base, e 6.7 Solving Equations and Modeling What are exponential and logarithmic functions and what do they represent? Warmups After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Collect real-world data on the heating and cooling of an object, and determine an appropriate other possible data values. Making W.A.V.E.S. Project Integration Resources Assessment Content Standards Students introduced to client *understand project scope *begin research EQ: How can students develop professional work for an authentic client? Identification of the roles, processes, and documentation that are inherent in the production of client based media projects *Graphing data - linear using data from WAVES Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects 1.0, 9.0, 21.0,24.0, 25.0 show that an appropriate function models this relationship. Find and discuss models for accumulation of space debris. Determine the piecewise function that describes the relationship between altitude and number of orbital objects. Production research: Research current solutions and problems vs. proposed solutions WS 1.7; WA 2.4 EQ: How do graphic designers communicate a written idea visually? *Graphing using transformations *Inductive & Deductive Reasoning using data from WAVES Digital Portfolio upload Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Benchmark 11.1, 12.0, 21.0, 24.0, 25.0 and minimums. Investigate how changes in the objective function or in the constraint inequalities affect the outcome. the form for the vertical motion of the basketball on different planets. exponential function to model the heating and cooling of an object. Make predictions about the temperature of an object that is heating or cooling to a constant surrounding temperature. Verify Newton’s law of cooling. Production assimilation and Video Production: EQ: What elements contribute to a wellorganized media project? Synthesize what has been learned in production applications to support a production process. Digital Portfolio upload *Graphing System of Equations using data from WAVES EQ: How does one determine the effectiveness of a product? Fine tuning oratory skills for media presentation SA 2.4 Digital Portfolio upload *Graph data - quadratics Final Media Package Showcase to client EQ: In what ways has the research and production process influenced the final Media Package? Developing an understanding of the production process and its relationship to a future project *Graphing Exponential Functions using data from WAVES Digital Portfolio upload Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects 2.0, 21.0 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 16.0, 21.0 11.1, 11.2, 15.0, 21.0 2nd SEMESTER Timeline Units of Study Essential Question Applied Learning February Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions 7.1 An Introduction to Polynomials 7.2 Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs 7.3 Products and Factors of Polynomials 7.4 Solving Polynomial Equations 7.5 Zeros of Polynomials Functions What are polynomial functions and what do they represent? Fill It Up! After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Collect and organize data. March April May June Chapter 8 Rational Functions and Radical Functions: 8.1 Inverse, Joint, and Combined Variation 8.2 Rational Functions and Their Graphs 8.3 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 8.4 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 8.5 Solving Rational expressions and Inequalities 8.6 Radical Expressions and Radical Functions 8.7 Simplifying Radical Expressions 8.8 Solving Radical Equations and Inequalities What are rational and radical functions and what do they represent? Chapter 10 Counting Principles and Probability 10.1 Introduction to Probability 10.2 Permutations 10.3 Combinations 10.4 Using Addition with Probability 10.5 Independent Events 10.6 Dependent Events and Conditional Probability 10.7 Experimental Probability and Simulation Chapter 9 Conic Sections 9.1 Introduction to Conic Sections 9.2 Parabolas 9.3 Circles 9.4 Ellipses 9.5 Hyperbolas 9.6 Solving Nonlinear Systems Chapter 11 & Chapter 12 Sequences and Series 11.1 Sequences and Series 11.2 Arithmetic Series 11.3 Arithmetic Sequences 11.4 Geometric Sequences 11.5 Geometric Series and Mathematical Induction 12.4 Measures of Dispersion What are permutations and combination and what do they represent? What are conic sections and what do they represent? Means to an End After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Find the arithmetic mean and the harmonic mean of a “Next, Please…” After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Focus on This! What is the difference between an Arithmetic and Geometric series or sequence and what can they represent? Over the Edge After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Set up models that simulate random After completing the Chapter Project, the student will be able to do the following: Describe the properties Experimentally determine the center Determine a polynomial model that best fits a data set. Test your polynomials model. Making W.A.V.E.S.English/Language Arts Phase II Project Integration Resources Assessment Content Standards EQ: What elements are necessary to produce a countywide youth event? Advertising Campaign production-print materials, website, email communications psa production to expand the client’s market Students are grouped according to career pathway interestdivided into pre-, during, and post-production components Digital Portfolio upload *Graph polynomials using data from WAVES Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 Pr Calculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Benchmark 5.0, 6.0, 21.0, 25.0 set of data. Determine the relationship between the arithmetic and harmonic mean. Determine which of the averages - arithmetic mean, harmonic mean, or weighted harmonic mean - best represents a data set. EQ: What elements are necessary to produce a countywide youth event? Advertising Campaign production-print materials, website, email communications psa production to expand the client’s market Students are grouped according to career pathway interestdivided into pre-, during, and post-production components Digital Portfolio upload *Explore geometric representation using data from WAVES Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects 7.0, 21.0, 25.0 events. Use data from simulations to estimate probabilities. of ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. Create ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas by using an alternative method of graphing. of gravity of an object. Model data from our experiments with sequence and series Determine whether your model gives predictions that are consistent with observations. EQ: What actions can students take to affect change in their community? Finalize production process SDGS Forum last week of April Student presentations at forum which include light presentation materials Day of forum photo and video documentation Digital Portfolio upload * Determine probability of events using data from WAVES EQ: How can a political message be effectively communicated through the combination of text, images, sound and rhetorical strategies? DMD Earth Day-student presentations of research Post-production of forum video Digital Portfolio Upload and finalized * Graph using data from WAVES EQ: How can a political message be effectively communicated through the combination of text, images, sound and rhetorical strategies? DMD Earth Day-student presentations of research Post-production of forum video Digital Portfolio Upload and finalized * Graph using data from WAVES Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects 18.0, 19.0, 20.0, 21.0, 24.0, 25.0, PS1, PS2 16.0, 17.0 Textbooks: Algebra 2 - Holt 2004 PreCalculus -Pearson 2004 Class work Homework Quizzes Tests Chapter Projects Benchmark 21.0, 22.0, PS3 Geometry Standards Correlation to Chapter and Section Section Chapter 1- Foundations for Geometry Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Measuring and Constructing Segments Measuring and Constructing Angles Pairs of Angles Using Formulas in Geometry Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Content Standard Vocabulary 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning. 8.0 Know, derive, and solve problems involving perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric figures. 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straightedge and compass, such as angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors, and the line parallel to a given line through a point off the line. 22.0 Know the effects of rigid motion on figures in the coordinate plane and space, including rotations, translations, and reflections. 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms. Academic Vocabulary demonstrate show identifying seeing and being able to name what something is solve find the value of a variable that makes the left side of an equation equal to the right side of the equation basic most important pr fundamental; used as a starting point effect outcome rigid motion movements of a figure that do not change its shape undefined terms segment point endpoint line ray plane opposite rays collinear postulate coplanar 1.2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Use length and midpoint of a segment Construct midpoints and congruent segments 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straightedge and compass. 1.3 Measuring and Constructing Angles Name and classify angles Measure and construct angles and angle bisectors 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straightedge and compass, such as angle bisectors. 1.4 Pairs of Angles Identify adjacent, vertical, complementary, and supplementary angles Find measures of pairs of angles 1.5 Using Formulas in Geometry Apply formulas for perimeter, area, and circumference Preparation for 13.0 Prove relationships between angles in polygons by using properties of complementary, supplementary and vertical angles. coordinate distance length congruent segments construction angle vertex interior of an angle exterior of an angle measure degree adjacent angles linear pair vertical angles 1.1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Identify, name and draw points, lines, segments, rays, and planes Apply basic facts about points, lines, and planes 8.0 Know and solve problems involving perimeter, circumference, area of common geometric figures. perimeter area base height between midpoint bisect segment bisector acute angle right angle obtuse angle straight angle congruent angles angle bisector complementary angles supplementary angle diameter radius circumference pi 1.6 Midpoint and Distance Formula in the Coordinate Plane Develop and apply the formula for a midpoint Use the distance formula and the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points Preparation for 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry, including the midpoint of a line segment and the distance formula coordinate plane leg hypotenuse 1.7 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Identify reflections, rotations, and translations Graph transformations in the coordinate plane Chapter 2 Geometric Reasoning Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Conditional Statements Using Deductive Reasoning to Verify Conjectures Biconditional Statements and Definitions Algebraic Proof Geometric Proof Flowchart and Paragraph Proofs 22.0 Know the effects of rigid motion on figures in the coordinate plane, including rotations, translations, and reflections. 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning. 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 3.0 Construct and judge the validity of a logical argument and give counterexamples to disprove a statement. transformation reflection preimage rotation image translation Academic Vocabulary inductive reach a conclusion based on examples deductive reach a conclusion based on laws geometric relating to the laws and methods of geometry valid(ity) legal argument statements that support or are against something 2.1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Use inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures Find counterexamples to disprove conjectures 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of inductive reasoning. Also covered: 3.0 Construct and judge the validity of a logical argument and give counterexamples to disprove a statement. inductive reasoning conjecture counterexample 2.2 Conditional Statements Identify, write and analyze the truth value of conditional statements Write the inverse, converse and contrapositive of a conditional statement 3.0 Construct and judge the validity of a logical argument and give counterexamples to disprove a statement. conditional statement hypothesis conclusion truth value negation converse inverse contrapositive logically equivalent statements 2.3 Using Deductive Reasoning to Verify Conjectures App;y the Law of Detachment and the Law of Syllogism in Logical Reasoning 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of inductive and deductive reasoning. deductive reasoning 2.4 Biconditional Statements and Definitions Write and analyze biconditional statements 3.0 Construct and judge the validity of a logical argument and give counterexamples to disprove a statement. biconditional statement polygon quadrilateral 2.5 Algebraic Proofs Review properties of equality and use them to write algebraic proofs Identify properties of equality and congruence Preparation for 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction Proof Also covered 15.0 definition triangle 2.6 Geometric Proof Write two-column proofs Prove geometric theorems by using deductive reasoning 2.0 Write geometric proofs theorem two-column proof 2.7 Flow Chart and Paragraph Proofs Write flowchart and paragraph proofs Prove geometric theorems by using deductive reasoning 2.0 Write geometric proofs flow chart proofs paragraph proofs Chapter 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Lines and Angles Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals Proving Lines Parallel Perpendicular Lines Slopes of Lines Lines in the Coordinate Plane 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning. 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal, the properties of quadrilaterals, and the properties of circles. 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straight edge and compass, such as angle bisector, perpendicular bisectors, and the line parallel to a given line through a point off the line. Academic Vocabulary demonstrate show identifying seeing and beong able to name what something is geometric relating to the laws and methods of geometry properties unique features cut to go across or through something basic most important or fundamental: used as a starting point bisector(s)a line that devidess and angle or another line into two equal parts 3.1 Lines and Angles Identify parallel, perpendicular and skew lines Identify the angles formed by two lines and a transversal Preparation for 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal parallel lines perpendicular lines skew lines parallel planes transversal corresponding angles alternate interior angles alternate exterior angles same-side interior angles 3.2 Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals Prove and use theorems about the angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal 3.3 Proving Lines Parallel Use the angles formed by a transversal to prove two lines are parallel 3.4 Perpendicular Lines Prove and apply theorems about perpendicular lines 3.5 Slopes of Lines Find slopes of lines Use slopes to identify parallel and perpendicular lines 3.6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane Graph lines and write their equations in slopeintercept and point-slope form 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal Also covered 16.0 2.0 Write geometric proofs Preparation for 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry Preparation for 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry perpendicular bisector distance from a point to a line rise run slope point-slope form slope-intercept form Classify lines as parallel, intersecting, or coinciding Chapter 4 Triangle Congruence Classifying Triangles Angle Relationships in Triangles Congruent Triangles Triangle Congruence: SSS and SAS Triangle Congruence: ASA, AAS, and HL Triangle Congruence: CPCTC Introduction to Coordinate Proof Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles 4.0 Prove basic theorems involving congruence 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent and use concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles to classify figures and solve problems 13.0 Prove relationships between angles in polygons by using properties of complementary and exterior angles 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry Academic Vocabulary involving relating to concept idea corresponding matching interior inside exterior outside relationships links coordinate geometry a form of geometry that uses a set of numbers to describe the exact position of a figure with reference to the x- and y-axes 4.1 Classifying Triangles Classify triangles by their angle measures and side lengths Use triangle classification to find angle measures and side lengths 4.2 Angle Relationships in Triangles Find the measures of interior and exterior angles of triangles Apply theorems about the interior and exterior angles of triangles 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of triangles to classify figures and solve problems 4.3 Congruent Triangles Use properties of congruent triangles Prove triangles congruent by using the definition of congruence 4.4 Triangle Congruence: SSS and SAS Apply SSS and SAS to construct triangles and solve problems Prove triangles congruent by using SSS and SAS 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent and use concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles acute triangle equiangular triangle right triangle obtuse triangle equilateral triangle auxiliary line corollary interior exterior interior angle exterior angle corresponding angles corresponding sides congruent polygons 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent and use concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles triangle rigidity included angle 4.5 Triangle Congruence: ASA, AAS, and HL Apply ASA, AAS, and HL to construct triangles and to solve problems Prove triangles congruent by using ASA, AAS, and HL 4.6 Triangle Congruence: CPCTC Use CPCTC to prove parts of triangles are congruent 4.7 Introduction to Coordinate Proof Position figures in the coordinate plane for use in 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent and use concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles included side 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent and use concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles CPCTC 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry coordinate proof 12.0 Find and use measures of interior and exterior angles of triangles to solve problems 13.0 Prove relationships between angles in polygons by using properties of complementary and exterior angles isosceles triangle scalene triangle remote interior angle coordinate proof Prove geometric concepts by using coordinate proof 4.8 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Prove Theorems about isosceles and equilateral triangles Apply properties of isosceles and equilateral triangles Chapter 5 Properties and Attributes of Triangles Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors Bisectors of Triangles Medians and Altitudes of Triangles The Triangle Midsegment Theorem Indirect Proof and Inequalities in One Triangle Inequalities in Two Triangles The Pythagorean Theorem Applying Special Right Triangles 5.1 Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors Prove and apply theorems about perpendicular bisectors Prove and apply theorems about angle bisectors 5.2 Bisectors of Angles Prove and apply properties of perpendicular bisectors of a triangle Prove and apply properties of angle bisectors of a triangle 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of triangles to classify figures and solve problems legs of an isosceles triangle vertex angle base base angles 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction 6.0 Know and be able to use the triangle inequality theorem 14.0 Prove the Pythagorean theorem 15.0 Use Pythagorean theorem to determine distance and find missing lengths of sides of right triangles 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straight edge and a compass 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 20.0 Know and be able to use angle and side relationships in problems with special right triangles, such as 30, 60, 90 triangles and 45, 45, 90 triangles 2.0 Write geometric proofs Academic Vocabulary contradiction a statement that disagrees or conflicts with a know fact able to use have the skills you need prove explain why something is true determine find relationships connections special particular 2.0 Write geometric proofs concurrent point of concurrency circumcenter of a triangle circumscribed incenter of a triangle inscribed median of a triangle centroid of a triangle altitude of a triangle orthocenter of a triangle midsegment of a triangle 5.3 Medians and Altitudes of Triangles Apply properties of medians of a triangle Apply properties of altitudes of a triangle 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straight edge and a compass 5.4 The Triangle Midsegment Theorem Prove and use properties of triangle midsegments 5.5 Indirect Proof and Inequalities in One Triangle Write indirect proofs Apply inequalities in one triangle 5.6 Inequalities in Two Triangles Apply inequalities in two triangles 5.7 Pythagorean Theorem Use Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems Use Pythagorean inequalities to classify triangles 5.8 Applying Special Right Triangles 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction 6.0 Know and be able to use the triangle inequality theorem equidistant locus indirect proof 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction 14.0 Prove the Pythagorean theorem 15.0 Use Pythagorean theorem to determine distance and find missing lengths of sides of right triangles Also covered 6.0 and 12.0 20.0 Know and be able to use angle and side relationships in Pythagorean triple Justify and apply properties of 45-45-90 triangles Justify and apply properties of 30-60-90 triangles Chapter 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Properties and Attributes of Polygons Properties of Parallelograms Conditions of Parallelograms Properties for Special Parallelograms Conditions for Special Parallelograms Properties of Kites and Trapezoids problems with special right triangles, such as 30, 60, 90 triangles and 45, 45, 90 triangles 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems 15.0 Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine distance and find missing lengths of sides of right triangles 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 6.1 Properties and Attributes of Polygons Classify polygons based on their sides and angles Find and use the measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons 6.2 Properties of Parallelograms Prove and apply properties of parallelograms Use properties of parallelograms to solve problems 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems 6.3 Conditions for Parallelograms Prove that a given quadrilateral is a parallelogram 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of polygons to solve problems 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of polygons to solve problems also covered 17.0 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems also covered 15.0 5.0 Prove that triangles are similar 7.0 Use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut 6.4 Properties of Special Parallelograms Prove and apply properties of rectangles, rhombuses, and squares Use properties of rectangles, rhombuses, and squares to solve problems 6.5 Conditions for Special Parallelograms Prove that a given quadrilateral is a rectangle, rhombus, or square 6.6 Properties of Kites and Trapezoid Use properties of kites to solve problems Use properties of trapezoids to solve problems Chapter 7 Similarity Ratio and Proportions 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of quadrilaterals 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of polygons to solve problems Academic Vocabulary involving relating to properties unique features interior inside exterior outside determine find length(s) distance from end to end coordinate geometry a form geometry that uses a set of numbers to describe the exact position of a figure with reference to the x- and y- axes side of a polygon concave vertex of a polygon convex diagonal regular polygon parallelogram rectangle rhombus square kite trapezoid base of a trapezoid leg of a trapezoid base angle of a trapezoid isosceles trapezoid midsegment of a trapezoid Academic Vocabulary similar alike by a transversal 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of triangles and polygons to solve problems 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry determine find out dimensions size of objects interior inside coordinate geometry a form of geometry that uses a set of numbers to describe the exact position of a figure with reference to the x- and y-axes 7.1 Ratio and Proportions Write and simplify ratios Use proportions to solve problems Preparation for 5.0 Prove that triangles are similar ratio proportion extremes 7.2 Ratios in Similar Polygons Identify similar polygons Apply properties of similar polygons to solve problems 7.3 Triangle Similarity: AA, SSS, and SAS Prove certain triangles are similar by using AA, SSS, and SAS Use triangle similarity to solve problems 7.4 Applying Properties of Similar Triangles Use properties of similar triangles to find segment length Apply proportionality and triangle angle bisector theorems 5.0 Prove that triangles are similar similar similar polygons similarity ratio 7.5 Using Proportional Relationships Use ratios to make indirect measurements Use scale drawings to solve problems 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 12.0 Find and use measures of sides of triangles and polygons to solve problems 5.0 Prove that triangles are similar 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry indirect measurement scale drawing scale 4.0 Prove basic theorems involving similarity 15.0 Use the Pythagorean theorem to find missing lengths of sides of right triangles 18.0 Know the definitions of the basic trigonometric functions defined by the angles of a right triangle 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle, given an angle and a length of a side Academic Vocabulary involving relating to Pythagorean mathematics that relate to ancient Greek mathematician, Pythagoras lengths distances along the side of a right triangle form end to end trigonometric mathematics that uses the proportional relationships between the sides and angles of right triangles functions quantities used to show the relationship between the parts of a triangle Ratios in Similar Polygons Triangles Similarity: AA, SSS, and SAS Applying Properties of Similar Triangles Using Proportional Relationships Dilations and Similarity in the Coordinate Plane 7.6 Dilations and Similarity in the Coordinate Plane Apply similarity properties in the coordinate plane Use coordinate proof to prove figures similar Chapter 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Similarity in Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios Solving Right Triangles Angles of Elevation and Depression Law of sines and law of cosines Vectors means cross products 5.0 Prove that triangles are similar 7.0 Use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior angles of triangles to solve problems dilation scale factor 8.1 Similarity in Right Triangles Use geometric mean to find segment lengths in right triangles Apply similarity relationships in right triangles to solve problems 8.2 Trigonometric Ratios Find the sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle Use trigonometric ratios to find side lengths in right triangles and to solve real-world problems 4.0 Prove basic theorems involving similarity geometric mean 18.0 Know the definitions of the basic trigonometric functions defined by the angles of a right triangle 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle, given an angle and a length of a side trigonometric ratio sine cosine tangent 8.3 Solving Right Triangles Use trigonometric ratios to find angle measures in right triangles and to solve real-world problems 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle, given an angle and a length of a side Also covered:15.0 18.0 8.4 Angles of Elevation and Depression Solve problems involving angles of elevation and angles of depression 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle, given an angle and a length of a side 8.5 Law of Sines and Law of Cosines Use the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to solve triangles 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle 8.6 Vectors Find the magnitude and direction of a vector Use vectors and vector addition to solve real-world problems 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle vector component form magnitude direction Chapter 9 Extending Perimeter, Circumference, and Area Developing Formulas for Triangles and Quadrilaterals Developing Formulas for Circles and Regular Polygons Composite Figures Perimeter and Area in the Coordinate Plane Effects of Changing Dimensions Proportionality Geometric Probability 8.0 Know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, and area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, equilateral triangles, rhombi, parallelograms, and trapezoids 11.0 determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 12.0 Find and use measures of sides of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems Academic Vocabulary derive develop a conclusion about something using a different method solve find the value of a variable that makes the left side of the equation equal to the right side of the equation compute calculate of work out a problem rhombi plural of rhombus, a parallelogram with four sides of equal length determine find out dimensions sizes of objects classify assign polygons to groups according to their features 9.1 Developing Formulas for Triangles and Quadrilaterals 8.0 Know, derive, and solve problems involving the area of angle of elevation angle of depression equal vectors parallel vectors resultant vectors Develop and apply the formulas for the areas of triangles and special quadrilaterals Solve problems involving perimeters and areas of triangles and special quadrilaterals 9.2 Developing Formulas for Circles and Regular Polygons Develop and apply the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle Develop and apply the formula for the area of a regular polygon 9.3 Composite Figures Use the Area Addition Postulate to find the areas of composite figures Use composite figures to estimate the area of irregular shapes 9.4 Perimeter and Area in the Coordinate Plane Find the perimeters and areas if figures in a coordinate plane common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, rhombi, parallelograms, and trapezoids 9.5 Effects of Changing Dimensions Proportionally Describe the effect on perimeter and area when one or more dimensions of a figure are changed Apply the relationship between perimeter and area in problem solving 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, and area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, and parallelograms 11.0 determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures Geometric Probability Calculate geometric probability Use geometric probability to predict results in realworld situations 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, equilateral triangles, and trapezoids geometric probability 1.0 Demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of inductive reasoning 8.0 Know and solve problems involving perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric figures 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres; and commit to memory the formulas for prisms, pyramids, and cylinders 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the area and volume of solids Academic Vocabulary demonstrate show identifying seeing and being able to name what something is common geometric figures figures formed with straight lines and/or simple shapes, for example, rectangles, squares, and circles commit keep in mind information so it can be recalled later determine find out 9.6 Chapter 10 Spatial Reasoning Solid Geometry Representation of Three-Dimensional Figures Formulas in Three Dimensions Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Volume of Pyramids and Cones Spheres 8.0 Know, derive, and solve problems involving the circumference, and area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, equilateral triangles 8.0 Know and solve problems involving area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids circle center of a circle center of a regular polygon apothem central angle of a regular polygon composite figure 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 10.0 Compute area of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles 12.0 Find and use measures of sides of polygons to classify figures and solve problems dimensions size of objects face cone edge cube vertex net prism cross section cylinder pyramid orthographic drawing isometric drawing perspective drawing vanishing point horizon 10.1 Solid Geometry Classify three-dimensional figures according to their properties Use nets and cross sections to analyze threedimensional figures Preparation for 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, 10.2 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures Draw representations of three-dimensional figures Recognize a three-dimensional figure from a given representation Preparation for 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface area of prisms, pyramids, 10.3 Formulas in Three Dimensions Apply Euler’s formula to find the number of vertices, edges, and faces of a polyhedron Develop and apply the distance and midpoint formulas in three dimensions Preparation for 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres polyhedron space 10.4 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Learn and apply the formula foe the surface area of a prism Learn and apply the formula foe the surface area of a cylinder 9.0 Compute surface area of prisms, cylinders, commit to memory the formulas for prisms and cylinders 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the area of solids lateral face lateral edge right prism oblique prism altitude 10.5 Surface Area of Pyramid and Cones Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a pyramid Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a cone 9.0 Compute the surface area of pyramids, cones, and commit to memory the formulas for pyramids vertex of a pyramid axis of a cone regular pyramid right cone altitude of a pyramid oblique cone vertex of a cone altitude of a cone slant height of a regular pyramid slant height of a right cone 10.6 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learn and apply the formula foe the volume of a prism Learn and apply the formula for the volume of a cylinder 10.7 Volume of Pyramids and Cones Learn and apply the formula for the volume of a pyramid Learn and apply the formula for the volume of a cone 10.8 Spheres 9.0 Compute the volumes of prisms, cylinders, and commit to memory the formulas for prisms, and cylinders 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the area and volume of solids Also covered: 8.0, 11.0 volume 9.0 Compute the volumes of pyramids, cones and commit to memory the formulas for pyramids 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the volume of solids 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface area spheres sphere surface area lateral surface axis of a cylinder right cylinder oblique cylinder Learn and apply the formula for the volume of a sphere Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a sphere Chapter 11 Circles Lines That Intersect Circles Arcs and Chords Sector Area and Arc Length Inscribed Angles Angle Relationships in Circles Segment Relationships in Circles Circles in the Coordinate Plane 11.1 Lines That Intersect Circles Identify tangents, secants, and chords Use properties of tangents to solve problems 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the area and volume of solids 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 21.0 Solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents of circles interior of circle exterior of a circle chord secant tangent of a circle point of tangency congruent circles concentric circles tangent circles common tangent 11.2 Arcs and Chords Apply properties of arcs Apply properties of chords 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 21.0 Solve problems regarding relationships among chords of circles central angle arc minor arc major arc semicircle adjacent arcs congruent arcs 11.3 Sector Area and Arc Length Find the area of sectors Find arc lengths 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the circumference and area of common geometric figures 21.0 Solve problems regarding relationships among chords of circles sector of a circle segment of a circle arc length 11.4 Inscribed Angles Find the measure of an inscribed angles Use inscribed angles and their properties to solve problems 11.5 Angle Relationships in Circles Find the measures of angles formed by lines that intersect circles Use angle measures to solve problems 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 21.0 Prove and solve problems regarding relationships among inscribed angles, and inscribed polygons of circles inscribed angle intercepted arc subtend 11.6 Segment Relationships in Circles Find the lengths of segments formed by lines that intersect circles Use lengths of segments in circles to solve problems 11.7 Circles in the Coordinate Plane 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 21.0 Prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents of circles 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the circumference and area of common geometric figures 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straightedge and compass 21.0 Prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents, inscribed angles, and inscribed polygons of circles center of a sphere radius of a sphere hemisphere great circle Academic Vocabulary involving relating to properties unique features basic most important or fundamental; used as a starting point regarding about relationships connections 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles 21.0 Prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents, inscribed angles of circles 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of circles secant segment external secant segment tangent segment Write equations and graph circles in the coordinate plane Use the equation and graph of a circle to solve problems Chapter 12 Extending Transformational Geometry Reflections Translations Rotations Compositions of Transformations Symmetry Tessellations Dilations 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane and space, including rotations, translations, and reflections 12.1 Reflections Identify and draw reflections 12.2 Translations Identify and draw translations 12.3 Rotations Identify and draw rotations 12.4 Compositions of Transformations Apply theorems about isometries Identify and draw compositions of transformations, such as glide reflections 12.5 Symmetry Identify and describe symmetry in geometric figures 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane, including reflections 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane including translations 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane, including rotations 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane including rotations, translations, and reflections 12.6 Tessellations Use transformations to draw tessellations Identify regular and semiregular tessellations and figures that will tessellate 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in space, including rotations, translations, and reflections 12.7 Dilations Identify and draw dilations 8.0 Know and solve problems involving the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures 22.0 Know the effect of rigid motions on figures in space, including rotations and reflections Academic Language common geometric figures figures formed with straight lines and/or simple shapes, fro example, rectangles, squares, and circles determine find out dimensions sizes of objects effect outcome rigid motion movements of a figure that do not change its shape or size isometry composition of transformations glide reflection symmetry line symmetry line of symmetry rotational symmetry translation symmetry frieze pattern glide reflection symmetry tessellation regular tessellation semiregular tessellation center of dilation enlargement reduction