* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 09-TempControls
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Thermal comfort wikipedia , lookup
Underfloor heating wikipedia , lookup
Radiator (engine cooling) wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypothermia wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
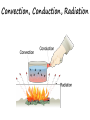
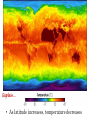
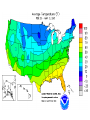
The Atmosphere: Heat overview Temperature v. Heat • Temperature: measurement of the motion of atoms or molecules faster motion = higher temp • Heat: the transfer of energy from one object to another flows from higher to lower temp • Heat fuels the weather, and temperature measures it! Temperature Temperature v. Heat • Temperature: measurement of the motion of atoms or molecules faster motion = higher temp • Heat: the transfer of energy from one object to another flows from higher to lower temp • Three main types of energy transfer: • Convection • Conduction • Radiation Heat Transfer in the Atmosphere Conduction Convection Radiation Mr. Fetch’s Earth Science Classroom Conduction The transfer of heat through direct touch/contact Convection • The circular transfer of heat through fluids (liquids & gases). – Warm air rising – Cold air sinking Radiation The transfer of energy in waves through space All objects, at any temperature, emit radiant energy Convection, Conduction, Radiation The Atmosphere: Temperature Controls Temperature Controls Temperature Controls: conditions that change temperature from one place to the next Example latitude Explain… • As latitude increases, temperature decreases Temperature Controls Temperature Controls: conditions that change temperature from one place to the next Examples: latitude altitude Average Monthly Temperatures for Guayaquil and Quito Explain… • As altitude increases, temperature decreases Temperature Controls Temperature Controls: conditions that change temperature from one place to the next Examples: latitude altitude cloud cover Cloud cover and temperature Explain… • Daytime: cloud cover reflects sunlight = colder • Nighttime: cloud cover traps energy = warmer Temperature Controls Temperature Controls: conditions that change temperature from one place to the next Examples: latitude altitude cloud cover land v. water Average monthly temperatures for Vancouver and Winnipeg Explain… • Land heats faster and to higher temp, cools faster and to lower temps (more extremes) • Coastal areas are more mild because of ocean influence Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere Explain… • Southern Hemisphere has less land than Northern, so more mild Land and Sea Breezes • Why is the beach warmer? • Cooler air is drawn on shore by what process? • Convection causes a cool wind to blow on shore Land and Sea Breezes • Which will cool off faster? Land or water? • Cooler air is drawn off land toward water • At the beach at night you will experience a breeze blowing toward water Isotherms Iso = therm = Isotherms are lines on a weather map that connect points where the temperature is equal. Isotherms show the effects of temperature controls, such as latitude, altitude, distribution of land and water, and ocean currents Write your summary box