* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download studt guide test 4 chapter 7
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
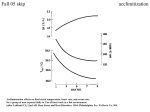
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive isolation wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
• • • • • • • 7.1 Darwin’s influences • Other scientists- Jean B. de Lamarck; Charles Lyell, Alfred Wallace, Thomas Malthus • His trip around the world, observations of different species, and fossils collected 7.2 Natural selection • Formulation of the idea is based on observations (large number of offspring, variation of individuals within the population, limited resources, natural selection pressures, reproductive fitness, descent with modification (adaptation) 7.3 Fossil record 7.4 Evidence for evolution • Geographical distribution of species • Comparative anatomy and comparative embryology • Homologues structures • Comparative studies on DNA from different organisms • DNA and bioinformatics -provide much evidence 7.5 Populations are the units which evolution acts on • Gene pool • Sources of genetic variation – mutations, independent assortment, and cross over • Natural select acts on the gene pool- changes in phenotype frequencies occurs when microevolution is occurring 7.6 Evolutionary mechanisms • Microevolution • Genetic drift • Bottleneck and founder effects- some genes are lost from the gene pool • Genetic variation is reduced • Gene flow • Migration – sometimes increases genetic variation in the gene pool • Natural selection • Types include predation selection and sexual selection 7.7 Macroevolution • Large changes have occurred overtime and speciation has occur • Speciation is the evolutionary formation of new species from the ancestral species • Patterns of Speciation • Non-branching, and branching speciation • Novel features a structure used for one function may evolve to having different functions • For examples feathers in dinosaur were for insulation and in birds they adapted for flight Rapid speciation and diversification follows mass extinctions • 7.8 Geological record ( note: bya billion years ago, mya million years ago) • Precambrian – • 4.6 bya earth forms, • 3.5 bya prokaryotes evolve, • 2.1 bya first eukaryotes evolve, • Paleozoic era • 541 mya: Explosion in animal diversity within the oceans • 420 mya: Plant life begins on land • 370 mya: Animals migrate to land • 251 mya: Mass extinction event • Mesozoic- Age of dinosaurs • 230 mya: First dinosaurs • 100 mya: Flowering plants begin to dominate the land • Cenozoic- Age of mammals • 65 mya: Extinction of dinosaurs and diversification of mammals • 200,000 years ago: Appearance of anatomically modern humans • 7.9 Reproductive barriers • What is a species? • Reproductive barriers maintain species- if there is a failure of reproductive barriers new species can result in new species formation • Pre zygotic barriers • Behavioral isolation • Temporal isolation ( mating times different) • Habitat isolation • Mechanical incompatibility • Gametic incompatibility • Post-zygotic barriers • Zygote mortality • Hybrid weakness ( hybrid sterility or reduced hybrid fertility, reduced hybrid viability, F2 breakdown • 7.10 Speciation • Patterns of speciation- gradualism and punctuated equilibrium • Allopatric speciation form after geographic isolation • Sympatric speciation without physical barriers often due polyploidy like in wheat • 7.11 Taxonomy • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species • Compare taxonomy of tiger and human • Human- Order Primate, family Hominids, Genus Homo species sapiens 7.12 Phylogenetic trees • Evolutionary relationships are shown by phylogenic trees • Compare bears 12.1 Ecology 12.2 The biosphere includes abiotic factors • Abiotic factors (energy, wind, temperature, fire, water, nutrients 12.3 Energy flows through ecosystem 12.4 Elements cycle through the biosphere • Carbon cycle • Nitrogen cycle 12.5 Water cycle Examples of biomes • 12.6 Aquatic biomes • 12.7 Terrestrial biomes 12.8 Species interactions • Competition • Mutualism • Predation • Parasites • symbiosis 12.9 Food webs 12.10 Species diversity • keystone species • succession 12.11 Invasive species • Examples 12.12 Biodiversity is measured on many levels • Causes of loss of diversity • Global climate changes 12.13 Population biology • Survivorship curses (type 1,2,3) • Dispersion patterns 12.14 Population growth models • Logistic and exponential 12.15 Human population growth is exponential 12.16 Humans cause ecological problems 12.17 Humans can solve ecological problems 12.18 Global climate change • greenhouse effect 12.19 Organisms adapt to their environments