* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations - WordPress.com
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
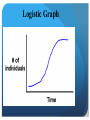
Populations Biology 2015-2016 Populations Objective: to understand the way that populations of different organisms grow and shrink, and what factors cause these changes in a population http://www.worldometers.inf o/world-population/ I. Describing a population 1. Geographic Distribution: the area inhabited by a population Map shows the Geographic Distribution of the California Quail 1994-2003 2. Population density: number of individuals per unit area Population Density: a. High density: lots of individuals in one area: example grass b. Low density: few individuals in a unit area: example: trees 3. Growth rate: how quickly a population changes in size Example: Some bacteria can double their population in minutes! 45 Minutes 3. Growth rate: how quickly a population changes in size Example 2: Trees can not double their population in 45 minutes. Its takes years and years for a population of trees to double in size. 45 years II. Factors affecting population growth 1. Birth rate 2. Death rate Birth = Death Stays the same 100 Born 100 Die b. Birth > Death Increases 150 Born 50 Die Birth < Death Decreases 50 Born 150 Die 3. Immigration: movement of individuals into an area Example: The Bison immigrates to a meadow full of grass because it provides a good source of food. 4. Emigration: movement of individuals out of an area Example: The Bison Emigrates away from a meadow without grass because it does not provide a good source of food. 5. You must emigrate from somewhere in order to immigrate to somewhere. Emigrate from.. Immigrate to.. III. Types of Growth 1. Exponential Growth: individuals reproduce at a constant rate a. Conditions necessary for exponential growth 1. Unlimited Resources b. Example: Bacteria c. Shape of graph J d. Graph 2. Absence of disease and parasites Exponential Graph 2. Logistic Growth: Population grows rapidly until some factor limits growth a. When does population growth slow or stop? 1. Birthrate: 1. Immigration: b. Example: Down Up 4. Emigration: Up Most animal populations in nature c. Shape of Graph d. Graph Down 3. Death rate: S Logistic Graph e. Carrying capacity: Maximum # of individuals that an area can support IV. Limits to Growth 1. Limiting Factor: Condition that controls population size ex: food, land Animals in a population may not have enough food to go around IV. Limits to Growth 2. Competition: Two or more species attempt to use same resource a. example: Bird and squirrel both eat berry b. Effect on evolution: b. Effect on evolution: both species under pressure to change in ways that decrease their competition Bird eat worm Squirrel eat nuts 3. Predation: one organism eats another a. example: Mouse and Snake b. predator: Hunter c. prey: Hunted 3. Predation: one organism eats another d. Effect on evolution: prey species evolve defenses against predators, predators evolve counter defenses Mouse: Camouflage Snake: forked tongue and heat vision 4. Parasitism: organisms live and feed inside/on a host organism a. examples: Fleas, ticks, leaches, tape worm 5. Random events: Unusual weather, human activities, natural disasters.