* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viability - Al-Sharqia Echo Club (AEC)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
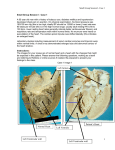
MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY & REVASCULARIZATION MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY & REVASCULARIZATION By AHMED M. MABROUK Consultant Interventioal Cardiologist KFMMC. Dhahran January 2010 Myocardial Perfusion Reserve Resting myocardial blood flow is normal until 85% stenosis Max myocardial blood flow begins to decline from 45% stenosis MBF hyperemia MPR rest 0 20 40 60 80 100 % diameter narrowing Gould KL et al., Am J Cardiol 1974; 34:48-55 Historical background : • Described by Rahimatolla & others in the last two decades of the last century viability ,the capacity of survival , is an active adaptive process of the myocardium to conditions of low energy supply , • The gold standard is improved contractile performance after revascularization. Definitions Viability : Myocardium that demonstrates abnormal function at rest and that improves with revascularization. Preserved cell membrane integrity, preserved glucose metabolism and inotropic reserve . Hibernation : Chronic condition of contractile dysfunction due to longstanding low perfusion in which restoration of myocardial blood flow results in recovery of function. Patients with evidence of viability treated medically had an annual mortality of 16% vs 3.2% in revascularized patients . Patients without viable myocardium have similar ,or better outcomes with medical therapy as compared with revascularization. Stunning : Transient loss or reduction in myocardial contractility resulting from transient reduction in blood flow ( in the absence of irreversible damage ) , it may remain hours, days, or months despite return of normal or near normal blood flow. Gold standard is recovery of function with time. Ischemia , stunning , hibernation , scarring, and normal myocardium may coexist in the same patient. In patients with viable myocardium , revascularization : has been shown to : Improve functional class. Reduce angina. Decrease mortality. ASSESSMENT DOBUTAMINE STRESS ECHO. Interpretation by regional wall motion (WM) analysis Interpretation Rest Stress Normal WM and contractility Hyperdynamic Normal Normal WM New WM abnormality or lack of hyperdynamic WM Ischemia WM abnormality Worsening ( hypokinesis , akinesis ) dyskinesis ) Ischemia WM abnormality Unchanged Infarct Akinetic WM Improved to hypokinetic or to normal WM, biphasic response Viable myocardium ( akinesis , Recovery of contractility of akinetic myocardium after revascularization is better predicted by increased contractility seen on dobutamine stress echocardiography than by thallium and PET. HOWEVER : Dobutamine is not as sensitive as thallium uptake or PET for detecting myocardial viability. NUCLEAR IMAGING Characterization of the defects : Fixed : - No uptake at rest & stress. Scar or severely ischemic viable myocardium. - How to differentiate ?! Reversible: - Ischemic myocardium. Partially reversible :- Mixture of scar and ischemic myocardium. Artifacts : - Breast attenuation. - Diaphragmatic attenuation. - More commonly seen with thallium. Stunned Myocardium LIMITED PERFUSION DEFECT& MORE EXTENSIVE RWMA. PET (Positron Emission Tomography) • Allows simultaneous evaluation of blood flow imaging (i.e. perfusion) and metabolic activity .(using FDG) . • It's now considered as the gold standard for identifying viable myocardium . • Patterns : • Normal - normal flow - normal metabolism. • Viable myocardium - reduced flow - normal or increased metabolism : (Mismatch). • Scar - reduced flow - reduced metabolism : (Match). VIABILITY by MRI GADOLINUM ENHANCEMENT sensitivity : 94 % specificity : 84 % DCE compares well with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET), the "gold standard" for myocardial viability imaging. DCE has a sensitivity of 94% and a specificity of 84% when compared with FDG-PET in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and LV dysfunction. DCE performs well as resting thallium201 myocardial perfusion imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) for detecting transmural infarctions (specificity 98% and 97%, respectively) but is more accurate in detecting regions of subendocardial infarction , which are missed by radionuclide techniques in 47% of myocardial segments and 13% of patients. Advantages of MRI Radionuclide techniques expose patients to a substantial amount of ionizing radiation, and PET is performed by relatively few specialized centers. examples Dark: viable Bright: non-viable Target: no re-flow Viability study Viability Study 4293701 Results of cardiovascular MRI with delayed contrast enhancement in myocardial infarction (MI) ACUTE MI OLD MI Marcu, C. B. et al. CMAJ 2006;175:911-917 AKINETIC NON- VIABLE DYSKINETIC VIABLE NONTRANSMURAL SUBENDOCARDIAL D.C.E. PRESUMABLY VIABLE Circulation 2003 108:116-117 Wall thinning Dyskinesia No systolic thickening Profound Microvascular obstruction Complete LAD obstruction Myocard. Rupture Microvasc. Obs. Platelet & fibrin. dobutamine 0 μg/kg/min 10 μg/kg/min 40 μg/kg/min Bellenger N et al. Heart 2006;92:1206. Segment No. Relationship between 201Tl uptake and delayed contrast enhancement in MRI 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 DC Score 0 1 2 3 4 Normal Mild decreased Moderate decreased Thallium Uptake Severe decreased Absent (A) 201Tl SPECT (B) Delayed enhanced MRI rest delay rest delay Mismatch between SPECT and MRI Mismatch between SPECT& MRI Influence of transmural extent of delayed contrast enhancement on recovery of regional function in 97 dysfunctional segments at baseline Systolic Wall Thickening Ratio (%) Transmurality Baseline Follow-Up Difference P 0 - 25% (n=52) 9.7 14.8 28.0 12.9 17.9 15.6 < 0.0001 26 - 50% (n=32) 6.2 13.9 15.2 15.3 9.0 18.6 0.01 51 - 75% (n=9) 0.1 6.0 3.7 19.0 3.6 17.9 0.56 76 -100% (n=4) -11.9 17.1% -1.8 22.8 10.2 29.7 0.56 How much viable myocardium predicts recovery ? • In a large study the average was found 22% . • Definite recovery is expected when we get > 4 viable segments CONCLUSION Delayed enhanced MRI has a better diagnostic power of myocardial viability and predictive value of functional recovery than 201-Tl SPECT REVASCULARIZATION for SCARRED MYOCARDIUM ? CASE PRESENTATION The enigma of Open artey hypothesis 65 years old lady referred to our hospital after thrombolysis for STEMI complicated by acute pulmonary edema. R.F. : DM , HTN , and DYSLIPIDEMIA On Ex. : She is sweating ,cyanosed , and in in respiratory distress, with no chest pain. V. S. : p : 115 bpm. RSR. B.p :161/89 mmHg. R.R.:42/m. O2 sat.:76% on O2 4L/m. by nasal mask. Cadiac auscultation : S1 ,S2 , S4 , and no murmurs. Chest auscultation :bilateral widespread rales, going with acute pulmonary oedema. ECG. : 5 mm. ST-seg. Elevation in V1-V6. Cardiac enzymes : normal. Echo. :Dilated mod. to severe LV impairment, dyskinetic ant. ,anteroseptal, and apical segments. Increased LV f.p. , and a large LV aneurysm , with no thrombus. Coronary angio. After stabilization. Showed : 100% LAD with prox. Calcium. 50 % prox. Dominant CX. Diffusely diseased small RCA. Large LV aneurysm Decision : Schedule for viability. A nuclear study ( ? ) showed no viability in LAD territory . Medical treatment :She improved , and successfully discharged home on maximal anti-failure medications. However, few weeks later she repeatedly presented with several episodes of severe SOB and after admission at the local Hospital, was referred back to us again with the diagnosis of recurrent A P O. At presentation to ER Again She was in Acute pulmonary edema. The case was discussed for possible : 1-Revascularization with LV aneurysmectomy ( SVR ). 2- Trial of PCI to CTO of LAD. PCI to LAD was attempted after stabilization. The patient was discharged home again after the procedure, and was electively admitted for control coronary and LV angio. after one year during which she remained asymptomatic on medical treatment. Repeat Echocardiography : showed mildly improved LV function . DOES SHE STILL NEED ANEURYSMECTOMY ? Yes if : Failure of medical treatment with : Persistent heart failure. Life threatening arrhythmia. Take Home Message Ischemia , stunning , hibernation , scarring, and normal myocardium may coexist in the same patient. In patients with viable myocardium , revascularization : has been shown to : Improve functional class. Reduce angina. Decrease mortality. Viability assessment : Not so accurate by Dobutamine Stress Echo. ( LOW SENSITIVITY ),unless we have a definite contractile reserve. Demanding and costing by Nuclear and MRI. However rewarding in terms of recovery after revascularization.