* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint 2.6Mb
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Antikythera mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
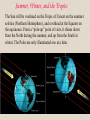
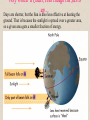
When does a “day” start? set Universal Time using the Greenwich Meridian (Britannia rules the waves...) since "noon" drifts around the Earth, need International Date Line to make the day change (avoid political boundaries for convenience) the Earth moves around the Sun at varying speeds, so let's use the "mean solar day" Timekeeping Fundamentally Based on the Sun : “Civil” or “solar” time Noon: the Sun is "overhead" (actually, on the meridian) but this is different at every longitude (that was OK until railroads) so let's have "time zones" (the Sun hits the meridian at noon only in the middle of a zone) use "daylight savings time" to make it get dark later (Sun hits meridian at 1pm) (but nothing astronomical happens; this is an arbitrary convention) Solar vs Sidereal Time The Solar day is not the same as the Sidereal day (“sidereal” means when a star crosses the meridian) A sidereal day is 4 minutes shorter (due to Earth's orbiting Sun), so stars come up 4 minutes sooner every (solar) day Month and Year the Moon does not go around its cycle in an exact number of days (synodic period = 29.5 days) months (from moon) vary between 30,31 days (use Feb. to fix year) lunar months will drift through the year (need extra month every so often if usually 12) lunar weeks will have drifting weekends (religious out of phase with civil calendar) the Year is not an exact number of solar days long (shorter than 365 1/4 by 11m 14s) we have leap years to cover the 1/4 day (otherwise the seasons will slip) we have more rules to cover the rest (no leap year every fourth century, etc.) the rotation of the Earth is slowing down, so need leap seconds too History of Calendars • The Week – 7 days : about the time between major moon phases • Sunday - Sun, Monday[Lundi] – Moon, Tuesday[Martedi] – Mars, • Wednesday[Mercoldi] – Mercury, Thursday[Giovedi] – Jupiter, • Friday[Venerdi] – Venus, Saturday – Saturn • The Month – – – – Early Roman – 12 lunar months = 354 days; every 3 years have a 13th month Julian Calendar – go to months of 30, 31days; have leap years to fix extra quarter day To fix drift of equinox, 46BC had 445 days (“year of confusion”) July and August named after Julius Caesar and Augustus Caesar • The Gregorian Calendar – Equinox had slipped again by 10 days in 16th century; Pope Gregory XIII fixed it in 1582 by dropping 10 days in Oct. – changed calendar rules (only century years divisible by 400 are leap years) – Protestants didn’t follow until later; 1752 for US & UK (can’t charge rent for missing days) – Year starts on Jan. 1 instead of Mar. 25 (so 1751 had no Jan., Feb., or Mar 1-24); Washington’s birthday not really on Washington’s birthday (born Feb. 11 but celebrated Feb. 22) – Russian didn’t change until 1917 revolution (losing 13 days) Summer, Winter, and the Tropics The Sun will be overhead on the Tropic of Cancer on the summer solstice (Northern Hemisphere), and overhead at the Equator on the equinoxes. From a “pole-up” point of view, it shines down from the North during the summer, and up from the South in winter. The Poles are only illuminated one at a time. The Reasons for Seasons The Midnight Sun Above the Arctic Circle, the Sun never sets during summer. It travels a tilted circle around the sky (at the Pole the circle is flat). Why Winter is Colder, even though the Sun is up… Days are shorter, but the Sun is also less effective at heating the ground. That is because the sunlight is spread over a greater area, so a given area gets a smaller fraction of energy. Just kidding…. Different Points of View You can choose to make the Ecliptic “horizontal” or you can make the Equator “horizontal”. You could also replace the Sun with the Earth in this picture (going “geocentric”) and then it would be clear why the Sun shines “down” or “up” on either pole during the solstices. Astro Quiz Suppose the Earth’s rotation axis was perpendicular to its orbital plane (so the celestial equator was on the ecliptic). Which statement below would be FALSE? 1) There would not be any real seasons. 2) All stars would be circumpolar. 3) The length of the day would not vary by month or latitude. What the seasons are NOT due to… NOT the ellipticity of the Earth’s orbit: Our ellipticity is very small, and we are closest to the Sun in January. You can most easily see this by remembering that at the same time it is Winter here, it is Summer in the Southern Hemisphere. NOT the fact that one pole is closer to the Sun because the Earth’s axis is tilted: The size of the Earth is miniscule compared with its distance to the Sun, so it doesn’t matter how things are oriented, they are all about the same distance from the Sun. Note: Summer is not warmest at the solstice (June) because it takes a while for the seasonal effects to really kick in, so we tend to be hottest a couple of months later (and coldest a couple of months after the winter solstice). Precession of the Earth’s Pole The changing tilt of the Earth’s pole slowly changes at what point in the orbit corresponds to a given season. Thirteen thousand years from now, winter will occur 6 months later. The calendar has to be adjusted to make winter stay in the. “winter months”. This has also caused the “Sun signs” to drift off from their original dates.