* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
Global serializability wikipedia , lookup
Commitment ordering wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
CIS 3052 [Part 2]
JDBC
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. This is an API for the Java programming
language that defines how a client may access a (relational oriented) database. It provides
methods for querying and updating data in a database. This API enables Java programs to
execute SQL statements and to interact with any SQL-compliant database. Since nearly all
relational database management systems (DBMSs) support SQL, and because Java itself runs
on most platforms, JDBC makes it possible to write a single database application that can
run on different platforms and interact with different DBMSs.
The MySQL Database Engine
MySQL is a relational database management system that runs as a server providing multiuser access to a number of databases. The MySQL development project has made its source
code available under the terms of the GNU General Public License, as well as under a variety
of proprietary agreements. MySQL was owned and sponsored by a single for-profit firm, the
Swedish company MySQL AB, now owned by Sun Microsystems, a subsidiary of Oracle
Corporation.
Free-software projects that require a full-featured database management system often use
MySQL. MySQL is also used in many high-profile, large-scale World Wide Web products
including Wikipedia, Google and Facebook.
The MySQL community server can be downloaded at no charge from
http://www.mysql.com/. A special interfacing file called the JDBC Driver for MySQL is
required to interface the MySQL database engine to JDBC. This file can be downloaded from
http://www.mysql.com/products/connector/.
Connecting to a database using Java via JDBC
There are three main steps required to use a database from a Java program. These are:
1. Connect to the data source (database)
2. Send queries and update statements to the database
3. Retrieve and process the results received from the database in answer to your query
In this section, examples of how to manipulate databases with JDBC are given. A students
table is used as a dummy for the code illustrated below. The database management system
that is used for this example is the MySQL Server. This table is illustrated below:
Id
Name
Surname
Tel
Address
Class
Subject1
1
Matthew
Xuereb
79888609
Mosta
3B
Italian
2
Joe
Borg
79123456
San Gwann
4B
French
3
Paul
Camilleri
99654321
Luqa
5B
Latin
Subject2
Computer
Studies
Biology
Computer
Studies
Subject3
Chemistry
Chemistry
Business
Studies
As the table is stored in a MySQL database server, the JDBC Driver for MySQL is required and
should be included in the Libraries section via the NetBeans IDE as explained below:
CIS 3052 [Part 2]
JDBC
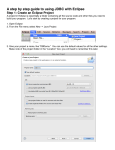
1. Right click on the Libraries icon under the Projects section an click on the Add
JAR/Folder option as shown in the screen shoot below:
2. Select the MySQL Connector driver and click on open as shown in the screen shoot
below:
Example
The following example illustrates how a database can be queried:
public class DBDemo {
/** The JDBC driver name */
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
/** The database URL */
static final String DATABASE_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/school";
/** The database username */
static final String DATABASE_USERNAME = "root";
/** The database password */
static final String DATABASE_PASSWORD = "letmein";
// The main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a reference to a connection
Connection connection = null;
CIS 3052 [Part 2]
JDBC
// Create a reference to a statement
Statement statement = null;
try{
//Load the database driver class
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
// Establish the connecion to the database
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(DATABASE_URL,
DATABASE_USERNAME,
DATABASE_PASSWORD);
// Create a statement for querying database
statement = connection.createStatement();
// Query the database
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(
"SELECT name,surname,class FROM students");
// Process the query results
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int numOfColumns = metaData.getColumnCount();
// Display the column names
for(int i = 1;i <= numOfColumns;i++){
System.out.printf("%-8s\t",metaData.getColumnName(i));
}
System.out.println();
// Display the data
while(resultSet.next()){
for(int i = 1;i <= numOfColumns;i++){
System.out.printf("%-8s\t",resultSet.getObject(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
// Close the connections
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();;
}
}
}
In order to add (update) records to a database, a statement as shown in the example below
should be used:
String updateStatement =
"(name,surname,tel,address,class,subject1,subject2,subject3) " +
"VALUES ('Joseph','Xuereb','79888609','Mosta','3B','Italian',” +
“'Computer Studies','Chemistry')");
statement.executeUpdate(updateStatement);