* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download power supply - IndiaStudyChannel.com
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
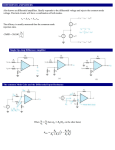
EMBEDDED MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEM FOR MEASUREMENT OF NEURO SENSORY HEARING LOSS ABSTRACT ABSTRACT Audiometry is the technique to identify & quantitatively determine the degree of hearing loss of a person by measuring his or her hearing sensitivity, so that suitable medical treatment or one of the appropriate hearing aids and assistive devices can be prescribed. In audiological investigations, the hearing sensitivity is tested for pure tones, speech or other sound stimuli. The result, when plotted graphically, is called an audiogram. The electronic instrument used for measuring the hearing threshold level is called an audiometer. Using it, the test tones of different frequencies and levels are generated and presented to the patient and hearing thresholds are determined on the basis of patient s response. The auditory system and its disorders are described. Audiometric test is discussed. INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Accurate assessment of hearing is vital to the diagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected otology disorders for the determination of the underlying process, as well as in the planning of rehabilitation of hearing loss. An audiometer essentially consists of a function generator, a stereo amplifier stage, an ear phone and a masking unit. The embedded microcontroller based system is more precise than the conventionally used audiometer. PHYSIOLOGY OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY OF AUDITORY SYSTEM THE ORGAN OF HEARING Parts of the Ear Outer Ear: It serves to collect and channel sound to the middle ear. Middle Ear: It serves to transform the energy of a sound wave into the internal vibrations of the bone structure of the middle ear and ultimately transform these vibrations into a compression wave in the inner ear. Inner Ear: It serves to transform the energy of a compression wave within the inner ear fluid into nerve impulses which can be transmitted to the brain. TESTING CARRIED IN HUMAN EAR TESTING CARRIED IN HUMAN EAR Pure tone air conduction threshold testing A series of 0.5 s bursts of single-frequency stimuli are presented to the subject through calibrated earphones worn on the head. The subject is requested to respond (by hand raising or button pushing) each time a beep is heard, even if it is faint. This testing is performed separately for each ear and for frequencies from 250 to 8000 Hz. The audiometer attenuator is adjusted until the person responds correctly to 50% of the test beeps presented. The threshold (50% correct responses) is recorded on the audiogram using a (red) “o” for the right ear and a (blue) “x” for the left ear. Any hearing loss measured may be due to pathology of one or more parts of the ear. Audiogram BLOCK DIAGRAM OF AUDIOMETER FUNCTION GENERATOR PRE AMPLIFIER CLAMPER OPERATOR SWITCH POWER AMPLIFIER A/D CONVERTER MICRO CONTROLLER 89C51 LCD DISPLAY -20DB TO 200DB HEARING LEVEL ATTENUATOR CONTROL HEADPHONE ON PATIENT PATIENT RESPONSE SWITCH HARDWARE POWER SUPPLY POWER SUPPLY 1. 2. Linear Mode Power Supply: ac/dc power supply convertor Switched Mode Power Suppy: a) dc/dc power supply convertor b) dc/ac power supply convertor LINEAR MODE POWER SUPPLY OPERATION OF POWER SUPPLY A transformer supplies ac voltage at the required level. This bidirectional ac voltage is converted into an unidirectional pulsating dc using a rectifier. The unwanted ripple contents of this pulsating dc are removed by a filter to get dc voltage. The output of the filter is fed to a regulator which gives a steady dc output independent of load variations and input supply fluctuations. POWER SUPPLY – CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FUNCTION GENERATOR FUNCTION GENERATOR A function generator is an instrument that generates signals for use in electronic test situations. A function generator generates signals. We may also find that another common name for the instrument is signal generator. The signal produced by the function generator can have many waveshapes. We may find • • • • • • • Sinusoidal signals Square wave signals Triangle signals Ramp signals Pulses Noise signals User-defined signals The frequency of the signals can be controlled. The amplitude of the signals can be controlled. Not all of the signals above are found on every function generator, and there are more specialized functions that can be performed. In general, a generator that produces the first three signals may be called a signal generator, and with more functions the generator may be called a function generator. There are three basic controls on a function generator. They are: • A control to set frequency • A control to set waveshape (sinusoid, triangle, square) • A control to set amplitude The function generator can be used to do the following adjustments: • To set the frequency to a value by using a pot. • To set the amplitude to a value by using another pot. • To change the wave shape with the help of a rotary switch. PRE-AMPLIFIER PRE AMPLIFIER An amplifier which amplifies the input without producing any phase shift between input and output is called non-inverting amplifier. The input is applied to the non-inverting input terminal of the op-amp. The op-amp always amplifies the difference input voltage Vd. This difference voltage is the difference between the voltages Vin and Vf where Vf is the feedback voltage. The feedback voltage opposes the input voltage that is, it is 180° out of phase with respect to the input. This indicates that the feedback is negative. When the input signal and part of the output signal are in phase, the feedback is called positive feedback. Use of positive feedback results in oscillations and hence not used. PRE AMPLIFIER – CIRCUIT DIAGRAM POWER AMPLIFIER POWER AMPLIFIER – CIRCUIT DIAGRAM In general, an amplifier receives an input signal from some transducer or other input source and provides a large amplified signal to some output device or another amplifier stage. The small signal amplifiers are basically voltage amplifiers, the voltage and current signal levels are small in such amplifiers. The output current capability of such amplifier is limited. The amount of power handling capacity and power efficiency are of little concern for the small signal amplifiers. The output current capability of such amplifier is limited. The amount of power handling capacity and power efficiency are of little concern for the small signal amplifiers The power amplifier is basically used to amplify an audio signal faithfully. The loads to such amplifiers are generally loud speakers, headphones and servomotors ATTENUATOR CONTROL ATTENUATOR CONTROL The attenuator control acts as a band pass filter. A band pass filter is basically a frequency selector. It allows one particular band of frequencies to pass. Thus, the pass band is between the two cut-off frequencies fH and fL where fH>fL. Any frequency outside this band gets attenuated. ATTENUATOR CONTROL – CIRCUIT DIAGRAM CLAMPER CIRCUIT CLAMPER CIRCUIT Clamper is a circuit that "clamps" a signal to a different dc level. The different types of clampers are positive negative and biased clampers. A clamping network must have a capacitor, a diode and a resistive element. The magnitude R and C must be chosen such that the time constant RC is large enough to ensure that the voltage across the capacitor does not discharge significantly during the interval the diode is non- conducting. CLAMPER CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER ADC Analog to digital converter are classified into two general groups based on the conversion techniques One technique involves comparing a given analog signal with the internally generated reference voltages. This group includes successive approximation, flash, delta modulated (DM), adaptive delta modulated and flash type converters. Another technique involves changing an analog signal into time or frequency and comparing these new parameters against known values. This group includes integrator converters and voltage-tofrequency converters. SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED SYSTEM INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED SYSTEM Microprocessors and microcontrollers are widely used in embedded system products. An embedded product uses a microprocessor or microcontroller to do one and task only. A printer is an example of embedded system since the processor inside it performs one task only ; namely, getting the data and printing it. In embedded system, there is only one application software that is typically built in ROM. IC 89C51 MICROCONTROLLER The AT89C51 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8bit Microcomputer with 4 Kbytes of Flash Programmable and Erasable Read Only Memory(PEROM). The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer. It is a powerful microcomputer which provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution to many embedded control applications. Details of IC89C51 ROM 4k RAM 128 I/O Pins 32 Timer 2 Interrupt 6 Vcc 5V Packaging 40 CONCLUSION CONCLUSION Thus the Embedded Microcontroller Based Audiometer is used to determine the sensitivity of the human ear. Accurate assessment of the hearing loss can be done using this device. The conventional audiometer is analog in nature. In this project the embedded micro-controller concepts are implemented to make audiometery more versatile, cost effective and simpler in design. In future, we can enhance the system by having additional graphic features, data storage and signal processing advantage of a PC based system, with the added benefit of economy and portability. The Kit designed by us