* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MS Word
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
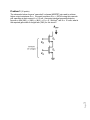
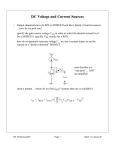
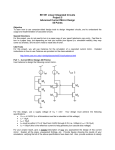
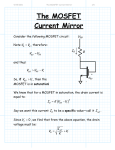
Name ______________________________ ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 6 (Fall 2016 – Due Monday, October 26, 2016) Problem 1 (18 points) You are given a common-emitter BJT and a common-source MOSFET (n-channel). Fill in the table below. Assume the BJT to be in the forward active mode and the nchannel MOSFET to be in the saturation region of operation. [The purpose of this exercise is to compare BJT and MOSFET parameters. Remember that A0 is the voltage gain without a separate load resistance RL.] NPN BJT Cell = 100, VA = 100 V and VTH = kT/q = 25 millivolt Bias Current is IC = 0.1 mA IC = 1 mA N-channel MOSFET Cell nCOX = 200 A/V2, (W/L) = 40 and VA = 10 V ID = 0.1 mA ID = 1 mA Page 1 gm (mA/V) r0 (k) A0 (V/V) RIN (k) Problem 2 (20 points) You are given the circuit drawn below. It is fabricated in a CMOS process for which nCOX = 2pCOX = 200 A/V2, V’An = |V’Ap| = 20 V/m, Vtn = -Vtp = 0.5 volt and VDD = 2.5 volts. The two transitor types have L = 0.5 m and are to be operated at |VOV | = 0.3 volt. Find the required gate node voltage VG, and the (W/L) ratios for both the n-channel and p-channel MOSFETs to meet the required conditions. VG = _________ volts (W/L)n = ________ Page 2 (W/L)p = ________ Problem 3 (12 points) Page 3 The schematic below shows a “cascoded” n-channel MOSFET pair used to achieve higher output resistance ROUT. We want to achieve ROUT = 200 k using this cascode pair operating at drain current ID = 0.5 mA. Assuming identical geometrical device layouts so that (W/L)1 = (W/L)2 = (W/L), nCOX = 0.1 mA/volt2, and VA = 10 volts; what is the required gate width-to-length ratio (W/L) for this circuit? Problem 4 (20 points) George Wilson (was an IC designer at Tektronix who lead a highly productive bipolar IC design group that made many contributions to Tektronix oscilloscope products in the 1980’s and 1990’s) proposed an improved current mirror over the basic current mirror using only two BJT transistors. What is now known as the “Wilson current mirror” adds transistor Q3 to the basic current mirror as is illustrated in the schematic below. (a) Derive an expression for the ratio of (IREF/IC). Page 4 (b) Compare the (IREF/IC) ratio for the Wilson current mirror to the (IREF/IC) ratio of the basic current mirror, that is, a current mirror without transistor Q3. What improvement in (IREF/IC) does the Wilson current mirror over the basic current mirror? Problem 5 (15 points) Page 5 Starting with the basic current mirror (with transistor Q1 and Q2 only), we place a small resistance RE in series with the emitter of transistor Q2 as shown in the schematic below. For this problem assume you can neglect base currents (that is, assume infinite ), the npn transistor saturation current IS is 1 10-15 A, and both transistors are identical. If resistor RE = 0, then IREF = IC. But the presence of RE reduces IC. Let IREF = 1 mA. If IC = 0.75 IREF, what is the value of RE? Page 6 Problem 6 (15 points) Current mirrors are often used for DC biasing in integrated circuits. But they can also be used as signal-current amplifiers. Consider the circuit schematic below for an example of a signal-current amplifier. Transistor Q1 acts as the input current source (driven by voltage VIN). Derive an expression for the small-signal current gain (I0 /ID1) and the small-signal voltage gain (vout /vin) with (W2 /L) and (W3 /L) being the primary variable parameters?