* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Electronics - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
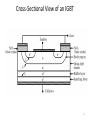
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
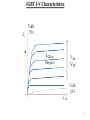
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
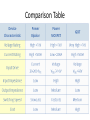
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
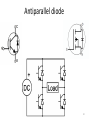
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
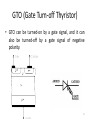
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
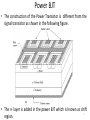
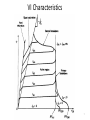
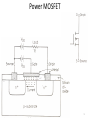
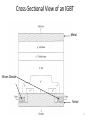
Power Electronics Lecture-9 Power Transistors & GTO Dr. Imtiaz Hussain Associate Professor email: [email protected] URL :http://imtiazhussainkalwar.weebly.com/ 1 Outline • Power Transistors – Power BJT – Power MOSFET – IGBT • GTO 2 Power Transistors • Power transistors are fully controlled semiconductor switches. • These are turned ON when the signal (voltage or current) is given to control terminal. • Types – Power BJT – Power MOSFET – Insulated Gate Bipolar Junction Transistor (IGBT) 3 Power BJT • The symbol of the Power BJT is same as signal level transistor. 4 Power BJT • The construction of the Power Transistor is different from the signal transistor as shown in the following figure. • The n- layer is added in the power BJT which is known as drift 5 region. Power BJT • A Power BJT has a four layer structure of alternating P and N type doping. • In most of Power Electronic applications, the Power Transistor works in Common Emitter configuration. • In power switches npn transistors are most widely used than pnp transistors. • The thickness of the dirft region determines the breakdown voltage of the Power transistor. 6 VI Characteristics 7 VI Characteristics • The VI characteristics of the Power BJT is different from signal level transistor. • The major differences are Quasi saturation region & secondary breakdown region. • The Quasi saturation region is available only in Power transistor characteristic not in signal transistors. It is because of the lightly doped collector drift region present in Power BJT. • The primary breakdown is similar to the signal transistor’s avalanche breakdown. • Operation of device at primary and secondary breakdown regions should be avoided as it will lead to the catastrophic failure of the device. 8 Power MOSFET 9 Power MOSFET 10 Power MOSFET 11 Power MOSFET 12 IGBT • IGBT is a new development in area of Power MOSFET technology. • This device combines into it the advantages of both MOSFET and BJT. • So an IGBT has high input impedance like a MOSFET and low on state power loss like a BJT. • Further, IGBT is free from second breakdown problem presented in BJT. 13 Cross-Sectional View of an IGBT Metal Silicon Dioxide Metal 14 Cross-Sectional View of an IGBT 15 IGBT • It is an FET integrated with a bipolar transistor in a form of Darlington configuration. 16 IGBT I-V Characteristics 17 IGBT • “IGBT Transistor” has the output switching and conduction characteristics of a bipolar transistor but is voltagecontrolled like a MOSFET. • IGBTs are mainly used in power electronics applications, such as inverters, converters and power supplies, were the demands of the solid state switching device are not fully met by power BJTs and power MOSFETs. 18 Comparison Table 19 Antiparallel diode 20 GTO (Gate Turn-off Thyristor) • GTO can be turned-on by a gate signal, and it can also be turned-off by a gate signal of negative polarity. 21 GTO (Gate Turn-off Thyristor) • Applications of GTO: They are used in – Motor drives – Static VAR compensators (SVCs) – AC/DC power supplies with high power ratings 22 GTO (Gate Turn-off Thyristor) • Compared to a conventional SCR, the device has the following disadvantages – Magnitude of latching, holding currents is more. The latching current of the GTO is several times more as compared to conventional thyristors of the same rating. – On state voltage drop and the associated loss is more. – Due to multicathode structure of GTO, triggering gate current is higher than that required for normal SCR. – Gate drive circuit losses are more. 23 To download this lecture visit http://imtiazhussainkalwar.weebly.com/ END OF LECTURE-9 24