* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.5 Trapezoids and Kites
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometry
Name:
Date:
Per.:
6.5 TRAPEZOIDS AND KITES
Using the list of websites provided (or your own), complete the notes below.
1) Properties of Trapezoids: http://www,coolmath.com/reference/trapezoids.html#the_isosceles_trapezoid
2) Isosceles Trapezoid: http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/isosceles-trapezoid,php
3) Trapezoid: http://w~w.mathopenref,com/trapezoid.html
4) Median of a Trapezoid: http://www,mathopenref.com/trapezoidmedian.html
5) Kite: http://www.mathopenref.com/kite,html
6) Properties of Kites: http://www,cootmath.com/reference/kites,html
7) Textbook Website (link from SchooIWires)
TRAPEZOIDS
Define the following terms and label the ports of each figure shown.
1) Trapezoid
2) Bases of a trapezoid
3) Base angles of a trapezoid
4) Legs of trapezoid
5) Isosceles trapezoid
6) Midsegment of a trapezoid
MD/2-09/Notes 6.5 Trapezoids and Kites
1
Geometry
THEOREMS RELATED TO TRAPEZOIDS. Fill in the missing information using the diagram and your
research.
THEOREM 6.1~T
If a trapezoid is isoscetes, then each
pair of base angles is
THEOREM 6.15
If a trapezoid has a pair of congruent
, then it is an isosceles
t~apezoid,
ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid,
THEOREM 6.10
A trapezoid is isosceles if and only if its
d~agonals are
ABCD is isosceles if and only
A
D
B
C
THEOREM 6,17: ~/IIDSE,GMENT THEOREM FOR TRAPEZOIDS
The midsegment of a trapezoid is parallel
B
C
to each base and its le~th is one half the
M
sum of the lengths of the bases,
PRACTICE
i.
Find the angle measures of ABCD.
A)
MD/2-O9/Notes 6.5 Trapezoids and Kites
2
Geometry
Find the measure of the midsegment RT.
C) w
KITES
Define Kite
List the properties of a kite and mark the diagram to
reflect those properties.
THEOREMS RELATED TO KITES. Fill in the missing information using the diagram and your
research.
C
If a quadrilateral is a kite, then its
diagonals ate
B ~,,~.,~D
A
THEOREM 6.19
C
If a quadrilateral is a kite, then
exactly one pair of opposite angles
ate congruent,
ZA__ ZC, ZB __ ZD
MD/2-O9/Notes 6.5 Trapezoids and Kites
3
Geometry
PRACTICE
Find the length of the sides to the nearest hundredth or the measure of the angles in
kite KITE.
K
c)
E
~,2o
T
STANDARDIZED TEST PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1) MMtIpI¢ Choiv~ h~ the [sosceies trapezoid
ABCD, find
2)MMtiple Choice Find the [engt:la of~ in
{he l:rape~oid beIow
~_ ,iB) 4
g
~+ 1
N
3)Multiple Choice The- mtdsegment of a
trapezoid is 9 cm long. What choice bek)w is
not a possible choice for the lengths of ~he
bases?
(~ 2, 1~5
@, 5 4
.~b 8 10
L
M
4) M#itipie Choice ABCD is a ~,rapez.oi& Find
the length of mic[segmen~
A
13
11
22
Mb/2-O9/Notes 6,5 Trapezoids and Kites
B
4
NAME
D~E
Practice A
For use with pages 356-363
Match the pair of segments or angles with the term, which describes
them in trapezoid PQRS,
1. QR and PS
A. bases
B. legs
2. PQ and RS
R
C. diagonals
D. base angles
3. QS and PR
4. /__Q and/-S
5. AS and !-P
E, opposite angles
P
S
Complete the statement with always, sometimes or never.
6, A trapezoid is ~? a parallelogram.
7. The bases of a trapezoid are ? paralle!.
8. The base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are ~? congruent.
9. The legs of a trapezoid are ? congruent.
Find the angle measures of ABCD.
11. A 91°
)
12.
132o,~x
//108°
D,----..~--~ C
D
~
o/
) --C
~
Find the length of the midsegment ~-T.
15. W
22, Z
!3
)
12
Z
y
Y
Find the length of the sides to the nearest hundredth or the measure of
the angles in kite KITE.
16.
/
17,
K
18.
K~ TE
E~I
T
Copyright @ McDougal Littelt Inc.
All rights reserved.
18
Geometry
Chapter 6 Resource Book
c
DATE
NAME --
Practice B
For use with pages 356=363
Draw a trapezoid JKLM with JK II LM. Match the pair of segments
or angles with the term, which describes them in trapezoid JKLM.
1. JK and ML
2. MJ and KL
4, /-K and/_M
5. JL and KM
A. bases angles
D. diagonals
B. consecutive sides
3. ML and KL
6. Z_M and/-L
C. opposite angles
F. legs
E. bases
Find the angle measures of ABCD.
The midsegment of the trapezoid is RT. Find the value of x.
10,
11,
7
12,
8
24
x
14
x
Find the length of the sides to the nearest hundredth
or the measure of the angles in kite MATH.
13.
14,
A
A
15,
M
H
H
T
Write a two-column or a paragraph proof.
17 Given: ~ is a midsegment of ~XYZ.
XZ-~ YZ
16. Given: DEIIAV,
ADAV ~ AEVA
Prove: DAVE is an isosceles trapezoid.
Prove: XWVY is an isosceles trapezoid.
D
x
,E
z
Geometry
Chapter 6 Resource Book
Copyright@ McDougal Lit[ell Inc.
Al! rights reserved,
DATE
NAME
Practice C
For use with pages 356-363
Decide whether the figure is a trapezoid. If it is, is it an isosceles trapezoid?
2,
1.
Quadrilateral ABCD is a trapezoid with midsegment EF. Use the given
information to answer the following.
4. Ifm/-B= 73°, thenm/-C= ? .
A
5. If mZ_A = 51°andm!-C= 105°,then m/_D = ?
6. Ifm/-A = 48° and m/_C = 112°, then mZ_CFE =? .
7. IfAB=28andDC= 13, thenEF= ? .
8, IfEF= 13 and DC = 6, then AB = ? .
9. IfEF=x+ 5andDC+AB=4x+ 6, thenEF= ?
Find the length of the sides to the nearest hundredth, or the measure
of the angles in kite WEST.
10.
11.
W
12,
E
w
W~S
E~’ T
T
S
13. In an isosceles trapezoid, if one pair of base angles is twice the measure of
the second pair of base angles, what are the measures of the angles?
14. If the midsegment of a trapezoid measures 6 units long, what is tree about the
S
lengths of the bases of the trapezoid?
Write a two-column or a paragraph proof.
15. Given: LORIis a rectangle.
LB ~ DO
AABC ~ ,~CDA
Prove: BIRD is an isosceles trapezoid.
L
B
D
Copyright © McO0ugaI Littell Inc.
All rights reserved.
16. Given: AF~:BC
0
Prove: ABCF is a trapezoid.
O
CF
Geometry
Chapter 6 Resource Book
Geometry
NAME:
WORKSHEET:OtherQttadrilaterals..
PERIOD:
DATE:
Trapezoids and Kites
Trapezoids
A trapezoid is a
with exactly one pair of
be a parallelogram.
By definition, a trapezoid can (always, sometimes, never)
The sides that are parallel are called the
The sides that are not parallel are called the
A trapezoid is isosceles if
Use the trapezoid to complete...
a) the bases are
A
b) the legs are
c) one pair of base angles:
d) the other pair of base angles:
e) Since RA//TP, mZT+ mZR =
f) If TRAP is isosceles, then..,
_=
and
mZ
rnL
=- mZ
_~ mL
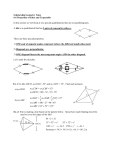
Is it possible for the diagonals of a trapezoid to be congruent? Explain.
The midsegment of a trapezoid is a segment that connects the midpoints of its legs.
The midsegment has two interesting properties...
I
O/
I*
1) it is parallel to each base
2) its length is the average of the lengths of the bases.
Complete the following.
Z
~
a) Sketch in the midsegment of ZOID and include congruency marks.
b) Find the length of the midsegment ifOI= 8 and ZD = 14.
c) Write a general equation for finding the length of the midsegment of any trapezoid ZOID.
Kites
A kite is a
with two pairs of
congruentsides,
but opposite sides are NOT
By definition, a kite can (always, sometimes, never)
be a parallelogram.
Use the kite shown to answer the following.
Do ANY angles appear congruent? Which?
i
Do diagonals appear congruent?
Are the diagonals bisected?
Do the diagonals appear perpendicular?
Does a diagonal appear to bisect an angle?
Properties of KITES
1) The diagonals of a kite are
2) Only one pair of opposite angles is
3) Only one diagonal is
by the other diagonal.
4) Only one diagonal
a pair of opposite angles.
5) Since a kite is a quadrilateral, the sum of the measures of its interior angles is
Sketch a kite by using the properties of its diagonals.
Find the perimeter of the kite below.
Find the perimeter of the isosceles trapezoid.
Geometry
NAME:
REVIEW: Trapezoids, Kites and Other Quads
PERIOD:
DATE:
1) Given: CH =- US.
From just this information, which of the following are
possible classifications of quadrilateral CUSH? (circle all that apply)
C
~U
H
S
Rectangle (non-square) ... Rhombus (non-square) ... Square ...
Trapezoid (not isosceles) ... Isosceles Trapezoid ... Kite
Indicate whether each statement is always, sometimes, or never true.
2) A trapezoid
has two adjacent sides that are congruent.
supplementary.
3) Consecutive angles in a kite are
4) Diagonals of a kite
have opposite reciprocal slopes.
5) Given: NEMO is an isosceles trapezoid where NE//OM.
E
Ifm/_l = 100°,thenmZ2 =
6) What is the length of the midsegment of trapezoid MRLN? Show work. M
16.5
12.3
7) Use the figure to find the length of NL.
L
6
9
NL=
L
8) What is a possible length of each base of a trapezoid whose midsegment is 8.5cm long?
Base 1 =
Base 2 =
Complete the following using the diagram of BRCE that is given.
9) IfmZ.1 = 35° and m/_5 = 55°, then m/-BRC =
R
U
10) IfBU= 15 and RE = 16, then BR =
E
Geometry
NAME:
WORKSHEET: Trapezoids in the Plane
PERIOD:
DATE:
Trapezoids in the Coordinate Plane
If you are given the vertices of a quadrilateral, you may determine whether it is a trapezoid it by
characterizing its sides and/or diagonals. You start by calculating the slope of each side.
If exactly one pair of opposite sides has the same slope, it’s a trapezoid.
If the other sides are congruent (or the diagonals are congruent), then it is an isosceles trapezoid.
Classify quadrilateral MARY with vertices M( -1, 2), A( 4, -3), R( 2, -7), Y( -5, 0)
Geol~eti~y
HOMEWORK: Trapezoids in the Plane
NAME:
Determine whether these quadrilaterals are trapezoids or isosceles trapezoids by:
Calculating the slopes of the sides
a)
Calculating the lengths of diagonals or the lengths of the sides
b)
c)
Classifying the quadrilateral as a trapezoid, isosceles trapezoid, or neither
1) Classify quadrilateral BERT, where B( -3, 5), E( 5, 4), R( 2, M), T(-4, -1)
2) Classify quadrilateral GVNR, where G( -6, -1), V(-2, 3), N( 5, -2), R(-1, -8)