* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lesson2_turf_anat_id
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
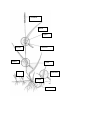
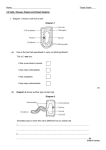
Module 2 – Turfgrass Anatomy and Identification Lesson Title - How do we identify the various turfgrass species and why is identification important? Overview Turfgrass surfaces are used for a variety of recreational and aesthetic purposes. Depending on the application, turfgrass systems have different quality requirements. Proper turfgrass growth, development, and management are essential to achieve healthy turfgrass areas. Turfgrasses are characterized by unique anatomical features which are necessary for identification between the various species. Proper identification allows turfgrass managers to choose the best suited turfgrass species for the site based on climatic adaptations, management strategies, and user needs. Objectives: Consider what determines a quality stand of turfgrass Explain turfgrass growth and development Properly identify turfgrass anatomical features Use anatomical features to identify turfgrass samples Discuss why turfgrass identification is important Classify turfgrasses according to their use Additional Readings: Turgeon, A. J. (2007). Turfgrass Management. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Simon & Schuster. Gardner, D. (2012). Turfgrass Identification. Retrieved from http://buckeyeturf.osu.edu/pdf/01_turfgrass_identification.pdf Landschoot, P. (2012). The Cool-Season Turfgrasses: Basic Structures, Growth, and Development. Retrieved from http://cropsoil.psu.edu/turf/extension/factsheets/pdfs/coolseason.pdf Turgeon, A. J. (2006). Seed Structure and Identification of Cool Season Turfgrasses. Retrieved from http://turfgrass.cas.psu.edu/education/turgeon/Modules/02_GrowthandDevelopment/Se edStructure/SeedStructure_text03.html PP Slide 12 - Do you have any type of animation that shows the stages of growth from seed to mature plant? Quiz: What are some factors that determine a quality stand of turfgrass? - density, texture, uniformity, color, elasticity, rooting, and recuperative capacity Explain the process of turfgrass seedling germination. - - - - - The germination process begins when water is absorbed by the seed. This helps break down starch in the endosperm to simpler carbohydrates for nourishing the embryo. All structural components of the seedling grass plant arise from the embryo. Enlargement of the coleorhizae via cell elongation, accompanied by the emergence of root-hairlike structures from the coleorhizae anchor the embryo to the soil and function in absorbing water. The primary root (radical) pushes through the side of the coleorhizae and penetrates downward through the soil. The coleoptile, a sheath of translucent tissue surrounding the growing point, emerges above the soil surface. Within the emerging coleoptiles, the first leaf elongates and pushes out through a pore at the tip of the coleoptile. Photosynthetic activity begins, and soon the seedling becomes entirely independent of the endosperm for its food supply. The seedling is now considered to be autotrophic. (The seedling is considered heterotrophic when it is entirely dependent on the endosperm for food.) If seeds are buried too deeply in the soil, food reserves in the endosperm may become depleted before the seedling is capable of manufacturing all its complex organic compounds through photosynthesis and associated biochemical processes. Seedling death may result. The growing point of the seedling is enclosed within the coleoptiles. The second leaf also grows through the coleoptiles and within the fold of the first emerging leaf. Eventually the coleoptile withers away, and only leaves are evident above the soil surface. Each succeeding leaf develops from the growing point and upward within the older enclosing leaves. The next seedling structures that form are the roots. Adventitious roots develop from nodes at the base of the new shoot and become the primary root system in mature plants. What are some features used to identify turfgrasses? - Growth habit, vernation, ligule, collar, auricles, leaf tip, leaf surface, inflorescence What are rhizomes and stolons on grass plants? - horizontally growing shoots that grow outward from the parent shoot What does vernation mean? - orientation of a newly emerging leaf What are the two types of vernation on grass plants? - Rolled and folded What are the three types of leaf tips that characterize turfgrasses? - Pointed, rounded, boat-shaped What is the inflorescence? - flowering part of the grass plant that bears seeds Why is turfgrass identification important? - Climatic adaptation, management practices, user needs Please name the structures. Please name the structures – Answer Key Seedhead Blade Ligule Sheath Auricles Midrib Collar Stolon Leaf Bud Crown Rhizome