* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data Mining and Data Warehouse
Operational transformation wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Forecasting wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
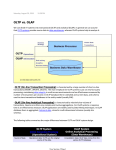
Data Warehousing Data Warehousing • Make the right decisions for your organization – Rapid access to all kinds of information – Research and analyze the past data – Identify and predict future trends • The construction of data warehouse – Involve data cleaning and data integration – Provide on-line analytical processing (OLAP) tools for the interactive analysis of data • W.H. Inmon – A data warehouse is a subject oriented, integrated, timedependent and non-volatile collection of data in support of management’s decision making process Characteristics of Data Warehouse • Subject-oriented – Data warehouse is designed for decision support and around major subject, such as customer and sales – Not all information in the operational database is useful • Integrated – Integrate multiple heterogeneous sources and make it consistent – The data from different sources may use different names for the same entities Characteristics of Data Warehouse • Time dependent – Record the information and the time when it was entered – Data mining can be done from the data in some period of time • Non-volatile – Data in a data warehouse is never updated Data Warehousing • Data warehousing – The process of constructing and using data warehouse • Two types of databases – Operational database • Large database in operation • Built for high speed and large number of users – Data warehouse • Designed for decision support • Contain vast amounts of historical data • Data mart – A department subset of the data warehouse that focuses on selected subjects, and its scope is department-wide OLTP & OLAP System • OLTP (On-Line Transaction Processing) System – The major task of operational database is to perform on-line transaction and query processing • OLAP (On-Line Analytical Processing) System – Data warehouse system serves users on data analysis and decision making Differences ~ OLTP & OLAP • Characteristic – OLTP: operational processing – OLAP: informational processing • Orientation – OLTP: transaction-oriented – OLAP: analysis-oriented • User – OLTP: customer, DBA – OLAP: manager, analyst • Function – OLTP: day-to-day operations – OLAP: information requirement, decision support Differences ~ OLTP & OLAP • DB design – OLTP: ER based, application-oriented – OLAP: star/snowflake, subject-oriented • Data – OLTP: current; guaranteed up-to date – OLAP: historical • Unit of work – OLTP: short, simple query – OLAP: complex query • Access – OLTP: read/write – OLAP: mostly read • DB size – OLTP: 100 MB to GM – OLAP: 100 GB to TB Differences ~ OLTP & OLAP Data Warehousing Relational Data Model Relational Schema Multidimensional Data Model Star Schema or Snowflake Schema Model & Schema for Relational Database Relational Data Model Relational Schema Multidimensional Data Model • Example: AllElectronics creates a sales data warehouse in order to keep records of the store’s sales – Fact Table • sales amount in dollars and number of units sold (measure) – Dimension Tables • time, item, branch, and location • Multidimensional data model views data in the form of a data cube Two Dimensions • 2-D view of sales data for item sold per quarter in the city of Vancouver. The measure is dollars_sold (in thousands) Dimensions Measures Three Dimensions • 3-D view of sales data according to the dimensions time, item and location. The measure is dollars_sold (in thousands) Dimensions Measures Three Dimensions • 3-D data cube representation according to the dimensions time, item and location. The measure is dollars_sold (in thousands) Four Dimensions • 4-D data cube of sales data according to the dimensions supplier, time, item and location. The measure is dollars_sold (in thousands) Schemas for Multidimensional Data Model • Star Schema • Snowflake Schema • Fact Constellation Schema Star Schema Snowflake Schema Snowflake Schema • Some dimension tables are normalized to reduce redundancies and save storage space • Reduce the effectiveness of browsing since more join will be needed to execute a query • This saving of space is negligible in comparison to the magnitude of the fact table • Snowflake schema is not as popular as the start schema in data warehouse design Fact Constellation Schema • Multiple fact tables share dimension tables OLAP Technologies Concept Hierarchies Three-Tier DW Architecture Case Study in Data Warehousing 公司簡介 公司簡介 公司簡介 背景資料 • A公司利用傳統的E-R Model 來建立其關 聯式資料庫系統 • A公司發現此種資料庫系統無法即時地滿 足高階主管對有效資訊的取得與分析, 進而做出決策 – 傳統的E-R Model資料模型的設計對資料的 一致性 (Consistency) 及避免資料的重複 (Duplication) 上有最佳的效率 – 對於Multi-constraint及Multi-join的多維度查 詢除了會拉長查詢的時間外,還會搶奪系統 資源,造成系統負荷過重而產生瓶頸 背景資料 • A公司決定利用多維度資料模型 (Multidimensional Data Model) 所設計的 資料庫系統來解決上述的問題 – 建立資料倉儲 (Data Warehousing) – 一次滿足所有的限制,而不需大量的合併動 作,同時使用者介面也較為和善 建立多維度資料庫的步驟 • 了解作業流程與需求,以作為設計時的基礎知 識,此部份可藉由與客戶的訪談、閱讀交易系 統文件、分析現有作業流程而得知 • 界定Fact Table內要有哪些組成?此部份要注意 到是否能滿足第一步驟所定義的需求 • 找出用戶的思考觀點及每一個思考觀點的層級 關係,也就是Dimension Table • 定義Fact Table的Measure,這些Measure是各個 維度所可能會取用的值 因 果 關 係 圖 因 果 關 係 圖 因果關係圖 因 果 關 係 圖 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 多維度資料庫的建立 • 其餘表格依此類推。 • 最後共產生共20個 Fact Tables及數十個 Dimension Tables 。 • 這些表格為OLAP系統或資料探勘(Data Mining)系統的輸入(Input)。 • 利用這些系統我們才能得到更進一步的 統計及知識的輸出(Output)。 Design of Data Warehouse • How can I design a data warehouse ? – Top-down approach – Bottom-up approach – Combination of both • In general, the warehouse design process consists of the following steps – – – – Choose a business process to model Choose the gain of the business process Choose the dimensions Choose the measures 其它應用實例 其它應用實例 其它應用實例