* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review Basic Topics covered Unit 1 Basic terms of
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
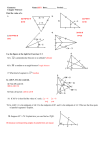
Final Exam Review Basic Topics covered Unit 1 Basic terms of geometry Parallel lines and transversals Angle Measures Triangles and Quadrilaterals and polygons Good definitions Inductive and deductive reasoning Midpoint Unit 2 Constructions Main consturctions – duplicating segments, duplicating angles, perpendicular lines, perpendicular bisectors, angle bisectors and parallel lines Main properties of perpendicular bisectors, perpendicular lines and angle bisectors Using the main constructions to make triangles and quadrilaterals Transformation and Symmetry Know the rules for – translation, reflection and rotation Know reflection symmetry and rotational symmetry Know multiple steps and how to do the rule to ordered pairs Unit 3 Sum of angles of a triangle Exterior angle conjecture Isosceles triangles What makes a triangle and what type will it be Know the conjectures to prove triangles congruent – SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS Know CPCTC Know how to write a proof Unit 4 we have already discussed most of this in the first unit so not much of it will be ne or unknown Angles in a Polygon Exterior angles of a polygon Trapezoids and midsegments Practice problems 1. Which of the following has only one-dimension and extends without end in the opposite directions? (Draw a picture) a. plane b. point c. line d. segment 2. Which of the following has only one endpoint? (Draw a picture) a. plane b. ray c. segment d. line 3. Which of the following angles is most likely to have a measure of 130 ? a. b. c. d. 4. The fewest number of noncollinear points needed to determine a plane is a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. Infinite 5. Which pair of numbers could be the measures of two supplementary angles? a. 25 and 65 b. 180 and 180 c. 90 and 45 d. 120 and 60 6. A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles is called a(n) a. Angle midpoint b. Midpoint ray c. Ray of congruence d. Angle bisector Use the figure at the right for questions 7 and 8 Figure 2 7. What kind of angle is BXC? a. c. Acute Obtuse b. Right d. Straight 8. What kind of angle is CXE? a. Acute b. Right c. Obtuse d. Straight A F X B C E D 9. Finding the fifth number in the following sequence 12, 15, 18, 21, . . . is an example of a. Inductive reasoning b. Deductive reasoning 10. Proving a conjecture in geometry is a. Inductive reasoning b. Deductive reasoning 11. Which of the following cannot be used to prove that lines are parallel? a. Vertical ’s are b. Corresponding ’s are c. Alternate interior ’s are d. Same-side interior ’s are supplementary 12. Refer to Figure 4. Two parallel lines are cut by a transversal. Which pair of angles are supplementary and not linear pairs. a. 5 and 6 Figure 4 b. 3 and 6 7 c. 1 and 2 5 8 d. 3 and 5 6 3 1 4 2 Refer to Figure 5 for questions 13 and 14. Look at picture carefully. A Figure 5 B G C D E F 13. What are the BCD and CEF? a. Alternate interior b. Alternate interior and congruent c. Corresponding d. Corresponding and congruent 14. What are GDC and GAB? a. Alternate interior b. Alternate interior and congruent c. Corresponding d. Corresponding and congruent 15. Find the m B (Show Work) a. 150 b. 45 B A 150 c. 360 c. 120 16. Find the m D (Show Work) a. 90 b. 50 c. 130 d. 180 A D 45 45 B 130 D C 17. What is the midpoint of the segment joining the points (4,-2) and (-8,6)? (Show Work) a. (6,4) b. (6,-4) c. (2,2) d. (-2,2) C 18. M is the midpoint of AB . The coordinates of A are ( -2,3) and the coordinates of M are (1,0), what are the coordinates of B? (Show Work) 1 3 3 3 a. , b. (4,-3) c. (-4,3) d. , 2 2 2 2 19. What is the midpoint of the segment connecting the points (a,b) and (5a,-7b)? (Show Work) a. (3a,-3b) b. (2a,-3b) c. (3a,-4b) d. (-2a,4b) 20. Study the diagram. What is the measure of ADC a. 50˚ b. 80 ˚ c. 100 ˚ d. 130 ˚ 21. Study the figure, what is the value of x (show work) a. 14 b. 21 c. 31 d. 45 22. Study the figure, What are the values of e and f? (Show work) a. m e=112 ˚ and m f=54 ˚ b. m e=126 ˚ and m f=68 ˚ c. m e=54 ˚ and m f=68˚ d. m e=54 ˚ and m f=54 ˚ 23. Study the figure below. Jose believes that all of the statements about this figure must be true. Is Jose Correct for each statement, state yes or no? Explain why or why not for each statement. Statement A: The figure is a quadrilateral. Statement B: The figure is a parallelogram. Statement C: The figure is a rhombus. Statement D: The figure is a rectangle. Statement E: The figure is a square. 1) Which construction is shown in the accompanying diagram? a) The perpendicular bisector of AB b) The midpoint of DF c) The perpendicular bisector of DE d) A perpendicular line to AB from point D 2) The diagram below illustrates the construction of PS parallel to RQ through point P. Which statement justifies this construction? a) m1 m3 c) PS RQ b) m1 m2 d) PR RQ 3) What other term might be used to indicate a perpendicular bisector a) Altitude b) ) Divide into thirds c) Midpoint d) Constructing a Triangle 4) The diagram at the right is a construction involving ABC . Which of the following statements is NOT tue? 1 a) mABD mABC 2 b) mDBC mABC c) mABC 2(mCBD ) d) mABD mCBD mABC 5) What construction is represented by this picture? a) Altitude b) Median c) Midsegment d) Parallel lines 6) The GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION below shows how to: a) Bisecting a line b) Constructing a scalene triangle c) Constructing an isosceles triangle d) Constructing a equilateral triangle. 7) The GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION below shows how to: a) Bisecting a line b) Constructing an equilateral triangle c) Constructing an isosceles triangle d) Constructing a scalene triangle. 8) What construction does this picture represent? a) Perpendicular bisector b) Angle bisector c) Altitude d) Median For questions 9-18, Decide whether each statement is true or false. If the statement is false correct it to be true. 9. A geometric construction uses a protractor and ruler. 10. The shortest distance from a point to a line is the length of the perpendicular segment from the point to the line. 11. Every point on a median in a triangle is equidistant from the sides of an angle. 12. If a point is equidistant from the endpoints of a segment, then it must be the midpoint of the segment. 13. Every point on an angle bisector is equidistant from the sides of the angle. 14. In a triangle, an altitude is shorter than either side of the triangle from the same vertex. 15. In a triangle, an altitude is shorter than the median from the same vertex 16. In a triangle, if a perpendicular bisector of a side and an altitude coincide, then the triangle is isosceles. 17. Exactly one altitude lies outside a triangle 18. The intersection of a perpendicular bisector s of the sides of a triangle lies inside the triangle