* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nerve
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
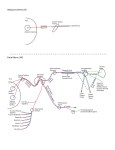
Autonomic nervous systém 1) smooth muscles of internal organs, vessels and skin 2) glands 3) heart Parasympathetic Sympathetic Enteric system Eye Salivatory glands Superior cervical g. Lungs III VII, IX X N. vagus Stellate ganglion Heart Celiac ganglion Liver Stomach Pankreas SMG Inferior mesenteric ganglion Symphatetic trunc Adrenal glands Intestine Rectum Urinary bladder Genitals Nn. erigentes Target organ Sympathetic nerv. syst. (NA) Heart Heart rate and contractility, Arteries Constriction ( blood pressure) Bronchi Dilatation Parasympathetic n.s. (Ach) heart rate Dilatation ( blood press.) Constriction Stomach, intestine peristaltic activity peristaltic activity Intestinal glands secretion secretion Urinary bladder Pupils Releasing of the detrusor Contraction of sphincter Constriction of vessels Ejaculation Secretion of vestibular glands Dilatation (mydriasis) Sweat glands Small amount of sticky secretion Lot of dilute secretion Salivatory glands Small amount of sticky secretion Lot of dilute secretion Genitals Contraction of the detrusor Releasing of the sphincter Dilatation of vessels Erection Narrowing (miosis) Temperature Increased Decreased Methabolism Increased Decreased Cervikothoracolumbal systém (C8-L3) X Craniosacral system (III, VII, IX, X, S2-S4) To the target organ with vessels X with nerves Autonomic ganglia are far from the target organ X close to the target organ Mediator in the target organ noradrenaline x acetylcholine Varikosities on the axons of the postganglionicic fibres Acetylcholine Nikotine receptor Noradrenaline α + ß receptors SYMP Acetylcholin Muscarine receptor Para Preganglial neuron Postganglial neuron Sympathetic nervous system • Paravertebral ganglia – sympathetic trunc • Prevertebral ganglia – in front of aorta abd. Paravertebral ganglia Paravertebral ganglion Prevertebral ganglion GCB WCB Interganglionar branch Cervical ganglia Cervical gangia Stellate ganglion Ansa subclavia Horner´s syndrome Injury of the cervical sympathetic systém • - miosis (narrow pupil) • - ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid) • - enophthalmus (backward displacement of the eyeball) If the conjunctiva is exposed to ipratropium (an anticholinergic agent) by means of metered-dose inhalers or nebulizers, mydriasis as well as acute glaucoma may occur. The BiPAP (bilevel positive-airway-pressure) face mask was found to fit imperfectly and leak slightly to the right. The anisocoria resolved within 24 hours after the patient stopped receiving ipratropium Thoracic ganglia Greater splanchnic nerve Th6-9 Lesser splanchnic nerve Th9-11 Nervus splanchnicus imus Th12 Lumbar ganglia Abdominal aortic plexus Schema of the abdominal aortic plexus, superior and inferior hypogastric plexus Superior and inferior hypogastric plexus Spinal ganglion Paravertebral sympathetic ganglion Prevertebral Pasympathetic ganglion Parasympathetic ganglion + ENTERIC SYSTEM Enteric system • Ganglia and plexuses in the wall of the gut from the cardia to the sphincter ani externus • Myenteric plexus of Auerbach • Submucous plexus of Meissner • 1) enteric neurons in the wall of the gut • 2) efferent centripetal fibres – dendrites of cells in the spinal ganglion and ganglion inferius n. vagi and axons of enteric neurons running to the prevertebral ganglia • 3) afferent centrifugal fibres – from n.vagus, • prevertebral ganglia and pelvic ganglia • 4)enteric glia Myenteric plexus of Auerbach ENTERIC SYSTEM A) intestine – intestine B) duodenum – gall bladder C)stomach - pancreas ESs = submucosous plexus (of Meissner) ESm= myenteric plexus (of Auerbach) Ganglia Trigeminal ganglion (Gasseri) Geniculate ganglion (VII.) Sup. and inf. ganglion of the IX. Sensory ganglia axon Sup. and inf. ganglion of the X dendrit Parasympathetic ganglia Sensory root Sympathetic root Parasympathetic root Efferent braches Afferents Parasympathetic ganglia • • • • Ciliary ganglion Pterygopalatine ganglion Submandibular ganglion Otic ganglion Ciliary ganglion Nasociliary n. Internal carotid pl. E.W.-r.inf. n.III. short.ciliary nerves (cornea) m.dilator pupillae mydriasis m.sphincter pupillae, m. ciliaris Miosis, akomodation Pterygopalatine ganglion Pterygopalatine nn. Superior posterior nasal branches Inferio posterior nasal branches Deep petrosal n. Orbital branches Greater petrosal n. Greater palatine nerve Lesser palatine nerves VII. –ncl. salivatorius sup Glands of the nasal cavity and palate Communicating branch to the lacrimal n. Lacrimal gland Submandibular ganglion Lingual n. Glandular branches for Facial artery pl. Submandibular and sublingual gland chorda tympani Branches in the lingual nerve to the VII. Superior salivatory nucleus Glands in the distal 2/3 of the tongue Otic ganglion Mandibular n. Communcating branch to the Auriculotemporal n. Middle meningeal artery pl. Parotid gland Lesser petrosal n. Communicating branch to the buccal nerve IX. Inferior salivatory nucleus Buccal glands Motor fibres for tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani VII pterygoideus medialis V Cranial nerves Nuclei of cranial nerves Cranial nerves, base of the brain Base of the skull Cranial nerves - II., III., IV., V., VI. Cavernous sinus and cranial nerves III. IV. VI. V/1 V/2 Orbit and cranial nerves IV. 1-n.lacrimalis 2-n.frontalis n. nasociliaris III. II Common annular tendon Muscles of the eyeball - schema of the function and inervation Levator muscle of the upper eyelid Superior rectus Inferior oblique Lateral rectus VI III Medial rectus Superior oblique IV IV Inferior rectus Paralysis of nerves III., IV., VI. • III. – ptosis of the lid, divergent strabismus, diplopia • mydriasis – dilated pupil, loss of light reaction • IV. – rare, diplopia on looking downward (difficulty in descending stairs), slight convergent strabismus • VI. – convergent strabismus, diplopia Alternating hemiplegia media superior Trigeminal nerve Nuclei of the trigeminal nerve Branches of the trigeminal nerve Skin supplied by the trigeminal nerve Ophthalmic nerve Maxillary nerve Mandibular nerve N.VII 1. ncl. salivatorius sup. 2. chorda tympani (VII) do n. lingualis(V3) 3. ggl. submandibulare 4. rr.(V3) 5. ggl. submandibularis, sublingualis N. IX 1. ncl saliv. inf 2.n. tympanicus (IX) do n.petrosusu minor (IX) 3. ggl. oticum 4. n. auriculotemporalis (V3) 5.gl. parotis Mandibular nerve Mandibular nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve N facialis SM ncl. motorius mimic muscles, p.b.of digastricus , SH, platysma, stapedius N. intermedius VM ncl. salivatorius sup. Lacrimal gland, nasal and palatine and lingual glands, Submandibular and sublingual glands SS skin of pinna přes ggl. geniculi do Vs VS anterior 2/3 of the tongue - ggl. geniculi - ncl. tractus solitarii IX (ncl. gustatorius) Facial nerve Paralysis of the facial nerve Paralysis of the facial nerve A – Bells palsy – peripheral facial paralysis) Chilling of the face, middle ear infections, tumors, fractures, meningitis, hemorrhage. Localization of the lesion 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) In pons: colliculus facialis lesioned only motor fibres - ipslateral paralysis of mimic muscles At the emergence of the pons (meningitis) involved of other nerves (VIII. a V.) Internal auditory meatus Involved VIII. nerve nerv – paralysis of VII, deafness, vertigo In facial canal involving the geniculate ganglion (herpes zoster) pain, decreased secretion of tears, hyperacusis, loss of taste in the anterior two thirds of tongue, reduced salivation, paralysis of mimic muscles In facial canal involving the stapedius – hyperacusis, loss of taste in the anterior two thirds of tongue, reduced salivation, paralysis of mimic muscles In facial canal involving the chorda tympani–loss of taste in the anterior two thirds of tongue, reduced salivation, paralysis of mimic muscles Outside the stylomastoid foramen ipsilateral paralysis of mimic muscles Central paralysis of the facial nerve – lesion of cortico-nuclear connections Stroke Contralateral paralysis of mimic muscles with hemiparesis of limbs Taste and salivation are not affected Temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve are spared Cortical motor centers for mimic muscles around the eye are bilateral Central and Peripheral Facial Weakness Central Peripheral Hemispasm Voluntary Central Facial Weakness That Is Greater Than Mimetic (Involuntary) Central Facial Weakness Axial computed tomography of the brain revealed a left hemispheric infarct involving cortical and subcortical structures (Panel C). Because voluntary central facial weakness is greater than mimetic central facial weakness, the cerebral cortex is functionally more damaged than are subcortical structures. Mimetic (Involuntary) Central Facial Weakness That Is Greater Than Voluntary Central Facial Weakness MRI revealed a deep-seated right hemispheric infarct Nervus vestibulocochlearis • Pars vestibularis N. utriculoampullaris N. saccularis N. ampullaris posterior • Pars cochlearis VII A P Fundus meati acustici interni Lesion: deafness, vertigo, instability, nystagmus Nervus vestibulocochlearis Glossopharyngeal, Vagus and Accessory Nerves IX, X, IX Ncl ambiguus – SM IX a X – muscles of the soft palate, pharynx, larynx and esophagus 1-IX 2–X 3 - XII 4 – r.cranialis XI 5 - C1 6 – r.spinalis XI Ncl. dorsalis n. vagi – VM –parasympaticus IX, X Upper part – ncl. salivatorius inf.-.parotide gland Ncl. solitarius VS – IX, X, and VII Upper part – ncl. gustatorius Ncl. spinalis n.V. – SS from the pinna and external auditory meatus, posterior 1/3 of the tongue, tonsilla palatina and the soft palate Nervus glossopharyngeus SM –muscles of the soft palate and pharynx VM – parotid gland (Jacobsons anastomosis), cavum tympani SS +VS- pharynx, tonsills, posterior 1/3 of the tongue, auditory tube cavum tympani Taste – posterior 1/3 of the tongue Lesions: Dysphagia Loss of the gag reflex Loss of the taste in posterior 1/3 of the tongue Loss of the sensation of posterior1/3 of the tongue, pharynx and tonsills Deviation of the uvula to the well side Tachycardia (in some lesions) Neuralgie n. IX. ! Nervus vagus SM – muscles of the pharynx, laryngx (ncl. ambiguus) VM – parasympaticus fot the gut, respiratory systém, heart and big vessels.(ncl. dorsalis n.X) SS –external acoustic meatus, part of the pinna (ncl.Vs) VS – from organs (ncl. solitarius) Taste - from the area around the epiglottis (ncl. gustatorius) LESIONS Aphony – loss of voice, dysphony Dysphagia Paralysis of the soft palate - rhinolalie Tachykardia Loss of the okulokardial reflex Irritation: Laryngospasmus, esophagospasmus, pylorospasmus, bradykardia, zástava, nausea, vomitus, singultus, cough, dyspnoe Nervus vagus branches N. laryngeus reccurens N. vagus sin. r. cardiacus thoracicus dx. n. laryngeus reccurens sin. r. cardiacus thoracicus sin. rr. bronchiales truncus vagalis ant. truncus vagalis post. r. hepaticus rr. coeliaci rr. renales rr. gastrici ant. rr. gastrici post. striated muscles parasympathetic Sensory ( mainly visceral sensory fibres) Nervus accessorius X. X. ramus. externus XI. XI. rr.craniales M.sternocleidomastiodeus (SCM) C1 M. trapezius (TR) C2 C3 XI. C4 C5 Ramus internus XI. Muscles of the soft palate and larynx rr.spinales C6 LESIONS: R. internus : paralysis of the soft palate and dysphony R. externus: Difficulty in rotating head to the uneffected side or raising chin (SCM), squareness of shoulders (TR) IRRITATION or CENTRAL PARALYSIS: Torticollis spastica Nervus hypoglossus Intraglossal and extraglossal muscles Lesion: On protrusion the tongue deviates to the side of lesion (peripherial paralysis) or to the side opposite to lesion (central, supranuclear paralysis) Test 1 N.lingualis 2 N.glossopharyngeus 3 N.hypoglossus 4 N.laryngeus superior 5 N.laryngeus reccurens Sources • • • • • • • Borovanský, Anatomie 2 Petrovický, Anatomie 3 Petrovický, unpublished schemas Martin, Neuroanatomy Netter, Atlas of Anatomy Kahle,Frotscher, Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol.3 Chusid, Correlative Neuroanatomy and Functional neurology • http://Content.nejm.org.-NEJM—Bells Palsy • http://Image –chalenge.nejm.org-NEJM:Image Challenge Archive