* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Middlemen and Distribution Channels
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
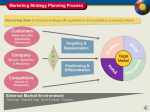
Distribution Sanjeev Varshney Middlemen and Distribution Channels • A middleman is a firm that renders services related directly to the sale and/or purchase of a product as it flows from producer to consumer. – Merchant middlemen take title to products. – Agent middlemen do not take title to products, but arrange the transfer of title. – Middlemen serve as purchasing agents for their customers and as sales specialists for their suppliers. Channel Members • • • • • Distributors or Stockists Carrying & Forwarding agent Wholesalers Dealers/Retailers Brokers Classification of Channel Members Title of Goods Transferred Titles of Goods Not Transferred Redistributors Distributors Carrying & Forwarding Agent Selling to End Consumers Retailer Agent Role of the Marketing Channel (manufacturers viewpoint) • Offers manpower and physical facilities • Provides personal selling, advertising and display to aid in selling • Interprets consumer demand and transfers this information back • Breaks the bulk • Offers storage • Shares risk of the manufacturer • Information provider of all other sought Role of Channel (consumers view point) • Product decision • Brand decision – Consideration set formation – Information search – Evaluation of alternatives • Purchase – – – – Form utility Time utility Place utility Possession utility Functions to be performed • • • • • Prospecting Promoting Bulk breaking & assortment Service Feedback Information Flows © 2007 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin Designing a Distribution Channel Specify Select the role of type of distribution distribuwithin the tion marketing channel mix Determine appropriate intensity of distribution Choose specific channel members WELLDESIGNED DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Copyright © 1997 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Consumer Decision Process & the Role of Channel Decision Process The role the channel can play Picking/Impulse Displaying the brand ensuring visibility Variety seeking Brand enters the consideration set through the process of recognition (merchandising & display) Habit Supplement the buyers evaluation through testimonial based POP advertising Sub-contracting Increase the credibility by acquiring technical skills Extended problem solving Brand enters the consideration set and also help in information search and evaluation by increasing the credibility by acquiring technical knowledge Framework for Designing the Channel Objective Variables Dimensions of the Channel Objective, which is likely to be influenced Consumer Role of the channel in decision making Positioning Type of outlet Company norms Market orientation Minimum standards Middlemen service norms (push vs pull) Exercise • A company is planning to launch a new product. There are no substitutes available in the market. What should be the distribution objective • A company is entering into a already crowded market but with some enhanced features. What should be the distribution objective • A company is entering into a product which is in growth stage. Company has developed a new cheaper production technology than the competitor and thereby plans to launch the product at a price lower than the competitor. What should be the distribution objective. Major Channels of Distribution • For distribution of consumer goods, five different types of channels are widely used. • Business goods are normally distributed through four major types of channels. • There are only two common channels of distribution for services. • Some producers are not content to use only a single distribution channel and use multiple channels. • Multiple channels can aggravate middlemen and cause conflicts in the channels. Major Distribution Channels PRODUCERS OF CONSUMER GOODS Agents Merchant wholesalers Retailers Retailers Agents Merchant wholesalers Retailers ULTIMATE CONSUMERS Retailers Major Distribution Channels PRODUCERS OF BUSINESS GOODS Merchant wholesalers (industrial distributors) Merchant wholesalers (industrial distributors) Resellers BUSINESS USERS Agents Agents Merchant wholesalers (industrial distributors) Major Distribution Channels PRODUCERS OF SERVICES Agents ULTIMATE CONSUMERS OR BUSINESS USERS Multiple Distribution Channels • Some firms choose to use two or more channels of distribution • They are used when: – the same product is sold to business & consumer markets – the producer has unrelated products – the buyers are of different sizes – geographic concentration differs across parts of the market Vertical Marketing Systems (VMS) • Has become the dominant form of channel • High degree of coordination and control – Corporate VMS - common ownership of successive channel levels – Contractual VMS - contracts between channel members – Administered VMS - market power of one or more members, or willing cooperation of channel members Factors Affecting Choice of Channels • Market Considerations – Type of market – Number of potential customers – Geographic concentration of the market – Order size • Product Considerations – Unit Value – Perishability – Technical nature Factors Affecting Choice of Channels (Con’t.) • Middlemen Considerations – Services provided by middlemen – Availability of desired middlemen – Producer’s and middleman’s policies • Company Considerations – Desire for channel control – Services provided by seller – Ability of management – Financial resources Marketing Channels & Customer Value • Product benefits (Quality, assortment & form) • Service Benefits (after sales service, availability & delivery, transaction services) • Image benefits • Company benefits • Cost efficiency • Competitive advantage Determining Intensity of Distribution • A firm must decide on the appropriate intensity of distribution for its product. • Intensity is actually a continuum, but three categories are normally used: – Intensive – Selective – Exclusive Conflict and Control in Channels • Channel conflict exists when one channel member perceives another to be acting in a way that prevents the first member from achieving its distribution objectives. – Horizontal Conflict • Middlemen of the same type • Different types of middlemen on the same level – Vertical Conflict • Producer versus wholesaler • Producer versus retailer Who Controls Channels? • Sources of power in distribution channels – Expertise – Rewards – Sanctions • A channel viewed as a partnership – Collaborative planning – Relationship marketing Some of the criteria's to appraise Channel members • • • • Sales Performance (against targets) Servicing Financial Discipline Inventory Maintenance (no more a very imp criteria) • Personal Commitment & involvement • Adherence to norms (infrastructure and people) and reporting structure Channel Evaluation: Concept • Includes both – Financial Performance measures – Contribution to consumers demand Dimensions of channel performance measures • Effectiveness – Delivery (how the channel meet demands) – Stimulation (how well it stimulates latent demand) • Efficiency – Productivity (measure of physical efficiency) – Profitability (measure of financial efficiency) • Equity – Service to problem ridden market or disadvantged market Profitability Analysis NMC = Volume X [ End user price X (1-%channel cost)-COG]-Marketing Expenses • Direct channels have higher margin per unit but incurred higher marketing expenses • Indirect channels have a lower margin per unit but lower marketing expenses Supply Chains Streamline Distribution • Reduce number of transactions • Increase value for consumers • More efficient and effective © 2007 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin Supply Chain Management Affects Marketing • Fulfilling delivery promises • Meeting customer expectations • Reliant on an efficient supply chain © 2007 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin