* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 牛顿环和劈尖
Survey
Document related concepts
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
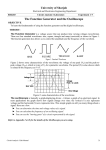
EXPERIMENT 2: NAME T h e Us a g e o f t h e O s c i l l o s c o p e STUDENT ID Scores ROOM:1101 DATE: TABLE NUMBER: 1. The Purpose of this Experiment (1) To know the structure and principle of the oscilloscope. (2) To know how to use the oscilloscope. (3) To be able to measure the voltage, period and frequency of the electrical signal, and to measure the phase shift between two electrical signals. 2. Equipments An oscilloscope, a signal source, two probes 3. Experiment Principles (1) What Can You Do With the Oscilloscope? The oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device - it draws a graph of an electrical signal. In most applications the graph shows how signals change over time: the vertical (Y) axis represents voltage and the horizontal (X) axis represents time. (2) How Does an Oscilloscope Work? To better understand the oscilloscope controls, you need to know a little more about how the oscilloscopes display a signal. When you connect an oscilloscope probe to a circuit, the voltage signal travels through the probe to the vertical system of the oscilloscope. Figure 1 is a simple block diagram that shows how an oscilloscope displays a measured signal. Depending on how you set the vertical scale (VOLTS/DIV control), an attenuator reduces the signal voltage or an amplifier increases the signal voltage. Next, the signal travels directly to the vertical deflection plates of the cathode ray tube (CRT). Voltage applied to these deflection plates causes a glowing dot to move. (An electron beam hitting phosphor inside the CRT creates the glowing dot.) A positive voltage causes the dot to move up while a negative voltage causes the dot to move down. oscilloscope 示波器 / probe 探头 / vertical 垂直 / horizontal 水平 /axis 轴 / voltage 电压 / attenuator 衰减器 / amplifier 放大器 / deflection 偏转 / CRT 阴极射线管 / phosphor 荧光体 1/4 The Usage of The Oscilloscope or Figure 1 Oscilloscope Block Diagram The signal also travels to the trigger system to start or trigger a "horizontal sweep." Horizontal sweep is a term referring to the action of the horizontal system causing the glowing dot to move across the screen. Triggering the horizontal system causes the horizontal time base to move the glowing dot across the screen from left to right within a specific time interval. Many sweeps in rapid sequence cause the movement of the glowing dot to blend into a solid line. At higher speeds, the dot may sweep across the screen up to 100 millions times each second. Together, the horizontal sweeping action and the vertical deflection action trace a graph of the signal on the screen. The trigger is necessary to stabilize a repeating signal. It ensures that the sweep begins at the same point of a repeating signal. In conclusion, to use an oscilloscope, you need to adjust three basic settings to accommodate an incoming signal: The attenuation or amplification of the signal. Use the VOLTS/DIV control to adjust the amplitude of the signal before it is applied to the vertical deflection plates. The time base. Use the SEC/DIV control to set the amount of time per division represented horizontally across the screen. trigger 触发 / sweep 扫描 / accommodate 适应 / amplitude 幅度 / generator 发生器 / 2/4 The Usage of The Oscilloscope The triggering of the oscilloscope. Use the trigger level to stabilize a repeating signal, as well as triggering on a single event. In addition, adjusting the focus and intensity controls enables you to create a sharp, visible display. 4. Measurements and Results You will learn some basic measurement techniques in this section. The two most basic measurements you can make are voltage and time measurements. Every other measurement is based on one of these two fundamental techniques. (1) Voltage Measurements(电压测量) There are three voltages in the voltage measurements area of the signal source. You can take voltage measurements by connecting CH1 to voltage 1, 2 or 3 and connecting the little clip to . Adjust the VOLTS/DIV to let the signal cover most of the screen vertically. By counting the number of divisions which a waveform spans on the oscilloscope's vertical scale, you can measure the voltage. Table 1.Voltage measurements of the three voltages from the board of the signal source Voltage VOLTS/DIV Divisions to the zero voltage equation Voltage1 (DC) Voltage2 (DC) Voltage VOLTS/DIV Divisions(Peak-to-peak) Peak-to-peak voltage equation Voltage3 (AC) Note: DIV means the major division. There are 5 minor divisions in each major division (2) Period and Frequency Measurements(频率测量) You take time measurements by connecting signal 1, 2 or 3 to CH1 and connecting the little clip to . Time measurements include measuring the period and frequency. Like voltage 3/4 The Usage of The Oscilloscope measurements, time measurements are more accurate when you adjust SEC/DIV to let the signal cover a large area of the screen. Table 2.The results for frequency measurements (All the three signals are sin wave) SEC/DIV Divisions Period(ms) Frequency(Hz) Signal 1 Signal 2 Signal 3 (3) Phase Shift Measurements(相位差测量) Phase shift describes the difference in time between two identical periodic signals. So we need two channels(CH1 and CH2)to measure the phase shift. The two signals may be displayed by alternate or chop mode. You need to connect A to CH1 and B (C, D) to CH2 respectively. For YB4320B, please make sure the two buttons, CH1 and CH2, are pushed down. Table 3. The results for phase shift measurements Divisions between two Divisions of one signals period Phase shift between Phase shift (π) A and B A and C A and D 5. Questions How to measure the voltage of a mixing electrical signal? For example, U A B sin t . 4/4





![1. Higher Electricity Questions [pps 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000880994_1-e0ea32a764888f59c0d1abf8ef2ca31b-150x150.png)