* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download procedure for blood pressure monitoring
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
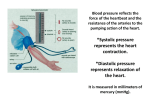
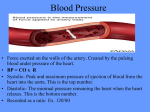
CLINICAL PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change To accurately perform and obtain a blood pressure measurement in a community setting Planned Review Date 2016 Named Responsible Officer:- Approved by Date Quality and Governance Service Quality, Patient Experience and Risk Group December 2013 Section:- CP25 Target Audience Multidisciplinary UNLESS THIS VERSION HAS BEEN TAKEN DIRECTLY FROM TRUST WEB SITE THERE IS NO ASSURANCE THIS IS THE CORRECT VERSION PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING CONTROL RECORD Title Purpose Author Equality Assessment Subject Experts Document Librarian Groups consulted with:Infection Control Approved Date approved by Quality, Patient Experience and Risk Group Method of Distribution Archived Access Procedure for Blood Pressure Monitoring To accurately perform and obtain a measurement in a community setting Quality and Governance Service (QGS) Integrated into procedure Lorraine Adams QGS Clinical Policies and Procedures Group 2nd Review 13.11.13 December 2013 Email Date Via QGS VERSION CONTROL RECORD Version Number Author Version 1 L Adams blood Yes Intranet:- Staff Zone Location:- Datix Librarian Status N Changes / Comments New Status – Revised PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 2/12 pressure No PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING INTRODUCTION To ensure the effective, co-ordinated management of blood pressure monitoring undertaken by health professionals who have been trained and assessed to be competent when delegated this procedure. TARGET GROUP This procedure is performed by all health professionals who are required to carry out this procedure as part of their role. TRAINING All staff in the Trust are required to comply with mandatory training as specified in the Trusts Mandatory Training Matrix. Clinical Staff are also required to comply with service specific mandatory training as specified within their service training matrix. Blood pressure monitoring is a core competency of a registered health professional. Health care assistant, nursing auxiliaries and assistant practitioners need to have been trained and have their competence assessed by a registered nurse. A record of this must be kept in their personal file. Assistant Practitioners and Nursing Auxiliaries are required to undertake training in the use of the Omron Sphygmomanometer (or equivalent). A blood pressure competency must be completed and updated every 2 years. A copy should be kept within their portfolio and personal file. REFERRAL Accurate patient information regarding the indication for blood pressure (BP) monitoring(please refer to indications) and relevant patient diagnosis is required from the referring clinician to enable the registered nurse to appropriately delegate blood pressure monitoring to a non- registered practitioner. RELATED POLICIES Please refer to relevant Trust policies and procedures INDICATIONS Patients who have been assessed by a registered health professional and have been identified as requiring a blood pressure measurement. Where medication requiring blood pressure monitoring Patients who have the potential of Autonomic Dysreflexia Screening patients who may have hypertension/hypotension As indicated for initial nursing assessment As indicated following nursing reassessment PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 3/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING CAUTIONS Oscillometric blood pressure devices may not be accurate in those with weak or thready pulse. Patients with Atrial Fibrillation should have blood pressure taken using a aneroid sphygmomanometer In patients with heart beats below 50 beats/minutes, even if the rhythm is regular, some of the semi-automatic devices are unable to reduce their deflation rate sufficiently so that too rapid a fall in cuff pressure results in underestimation of systolic blood pressure and overestimation of diastolic blood pressure Patients who have had trauma to the upper arm, previous mastectomy, Arteriovenous fistula or a forearm amputation should not have blood pressure measured from the effected side or those at risk of lymphedema In pregnancy diastolic blood pressure is best measured using the disappearance of the Korotkoff V sounds.( Consider using aneroid monitoring device). If the use of an aneroid sphygmomanometer is indicated the registered nurse or health professional needs to consider the appropriateness of delegating this role to an Assistant Practitioner and /or Nursing Auxiliary or Nurse Practitioner. PREPARATION OF EQUIPMENT The accuracy of the blood pressure reading obtained is highly dependent upon proper use of the equipment provided Blood pressure monitoring equipment must be recalibrated annually by Electronic Biomedical Equipment (EBME) Department at Wirral University Teaching Hospital Trust. It is the responsibility of the team leader/ case load manager to have a system in place to monitor and maintain quality assurance with this standard. Clean blood pressure machine and cuff with Trust approved cleaning wipe. Use a single patient use cuff cover when a patient has a multi resistant organism The circumference of the upper arm must be measured at the widest point in order to determine which size cuff be used. See table below:Arm Circumference Less than 23cm Cuff Size Small Adult 23cm to 33cm 33cm to 50cm Standard Adult Large Adult 51cm to 53cm Adult Thigh Cuff PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 4/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING CONSENT Valid consent must be given voluntarily by an appropriately informed person prior to any procedure or intervention. No one can give consent on behalf of another adult who is deemed to lack capacity regardless of whether the impairment is temporary or permanent. However such patients can be treated if it is deemed to be within their best interest. This must be recorded within the patient’s health records with a clear rationale stated at all times. Refer to Trust Patient Information and Consent Policy for further information and guidance or the Clinical Protocol for Assessing Mental Capacity and Best Interests. EQUIPMENT – Organisational recommended blood pressure device Various cuff size Tape measure Relevant documentation Spare batteries single patient use cuff cover (if required) Trust approved cleaning wipe aneroid sphygmomanometer (if indicated) Diagnostic and Screening Standards to Promote and Maintain Patient Safety Description of how each step in the process is undertaken a. How the Screening/Diagnostic procedure is requested In line with individual doctors surgeries. Requests are made Via fax with patient history and the length of time the patient requires their blood pressure monitoring(ensure this is a safe haven fax machine) b. How the clinician treating the patient is informed of the results (including timescales) The General practitioner will receive the results the same day in written format via (safe haven fax). If the patient’s blood pressure is 180/110mmHg or above or their pulse is less than 50 beats per minute. The doctor needs to be contacted immediately via telephone; this should be documented within the patient’s health records along with recommendations from the doctor. The results still need faxing to the surgery The patient is informed of the results by the person performing the c. How the patient is informed of the Additional comments:- Individual surgeries have specific ways of working. Ensure you are aware of these. In the event of fax down time, paper request forms and patient information can be collected from individual doctor surgeries. Urgent results are returned back to the patient’s clinician immediately via telephone. However this must be explained to receptionist staff that it is important to speak to doctor directly in order for them to triage the telephone call. Patient informed at time of procedure. PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 5/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING results (including timescales) d. Taking action on the result of diagnostic /screening tests (including timescales) : documentation of the result procedure interpretation of the result how patient is followed up or referred following a screening Which staff are authorised to request this test? By the referring clinician. For the GP or requesting clinician to action the results Filed within patients health records along with treatment and course Patient should be aware of treatment plan if indicated and the GP should action any further treatment or changes, depending on results Please ensure any allergies are kept up-to-date in records to reduce risks to patients By the referring clinician All Trust staff who have a clinical rationale as to why they are requesting the proposed procedure PROCEDURE Prior to procedure, advise patient not to eat, take alcohol, smoke or exercise for 30 minutes before their blood pressure is measured, as these factors may affect the accuracy of the blood pressure reading. ACTION Verbally confirm the identity of the patient by asking for their full name and date of birth. If client unable to confirm, check identity with family/carer Introduce yourself as a staff member and any colleagues involved at the contact Wear identity badge which includes name status and designation Ensure verbal consent for the presence of any other third party is obtained Explain procedure to patient including risks and benefits and gain valid consent Decontaminate hands Ask patient to remove any tight arm clothing. Assist the patient if required, ensuring privacy and dignity at all times RATIONALE To avoid mistaken identity To promote mutual respect and put client at ease For patients to know who they are seeing and to promote mutual respect Students for example, as the client has the choice to refuse Enables patient to make an informed decision to proceed with blood pressure monitoring To reduce the risk of transfer of transient microorganisms on the healthcare workers hands Allows the cuff to be applied in the correct position thus reducing the potential for error. PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 6/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING Check skin condition of the upper arm Request the patient to empty their bladder if they need to. If patients arm is:Swollen/oedematous or has any breaks do not continue, seek advice. If necessary clean arm to prevent cross infection Can effect blood pressure reading(NICE, 2006) The patient should be seated in a temperate environment and relaxed for at least 5 minutes prior to procedure. Their legs should be uncrossed and flat on the floor Whilst patient is seated measure the circumference of the upper arm at the widest point and record in the health care record Select appropriate cuff from measurements obtained(NICE, 2011) To minimize the effects of the environment to ensure an accurate reading is obtained (NICE, 2006) Support the patients arm out-stretched at heart level and check the brachial pulse, rhythm and pace. If the arm is above or below heart level and not relaxed the reading may be effected (NICE 2006) This is to ensure that the most appropriate equipment is used e.g. a patient with arterial fibrillation should have blood pressure taken with aneroid sphygmomanometer(NICE,2011) To obtain an accurate blood pressure measurement Apply the cuff and measure blood pressure, following the procedure for the use of the monitoring device. Patient should not talk during the procedure Allows the correct sized cuff to be used Using the wrong sized cuff can affect the reading obtained Note the reading in the patients records To maintain an accurate record of readings Repeat procedure for other arm (If indicated) Blood pressure readings can differ between arms (NICE 2006). The arm with the highest reading should be used for all subsequent readings (BHS 2006). Performing sitting and standing BP monitoring (If indicated or requested) Ask the patient to Stand (If able)for 1-3 minutes(BHS 2006) and then take a further blood pressure measurement with the arm supported, from the arm that the highest reading obtained Document in patient’s health care records(see appendix 1) Decontaminate reusable equipment using Trust approved cleaning wipe. Blood pressure readings can differ with the patient sitting or standing older people can suffer from ‘postural hypotension’(blood pressure dropping when they stand Decontamination of medical equipment is essential for the effective delivery of patient care. PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 7/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING On completion of procedure, decontaminate hands. To remove any accumulation of transient micro-organisms Document blood pressure reading within health records Inform General Practitioner by fax on the day the measurements were obtained(see appendix 2) Inform General practitioner by telephone and fax if reading is above 180/110mmHG(see appendix 2) Inform General Practitioner by telephone and fax if pulse rate is less than 50 beats/ per minute As per trust record keeping policy Patient’s GP to make timely clinical decisions and adapt the patient's treatment, if required. May indicate that the patient has accelerated(malignant) hypertension(NICE,2006) Blood pressure measurements may not be accurate(BHS 2006) WHERE TO GET ADVICE FROM Team leader/line manager INCIDENT REPORTING Clinical incidents or near misses must be reported via the Trust’s Datix incident reporting system. SAFEGUARDING In any situation where staff may consider the patient to be a vulnerable adult, they need to follow the Trust Safeguarding Adult Policy and discuss with their line manager and document outcomes. REFERRALS Any referrals to health professionals, therapists or other specialist services must be followed up and all professional advice or guidance documented in the patients health records. EQUALITY ASSESSMENT During the development of this procedure the Trust has considered the clinical needs of Each protected characteristic (age, disability, gender, gender reassignment, pregnancy and maternity, race, religion or belief, sexual orientation). There is no evidence of exclusion of these named groups. If staff become aware of any clinical exclusions that impact on the delivery of care a Trust Incident form would need to be completed and an appropriate action plan put in place. PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 8/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING REFERENCES – British Hypertension Society (2006): Blood Pressure Measurement. Fact file. http://www.bhsoc.org/files/6813/4398/9702/BHS_BP_Measurement_Factfile_2006.pdf Nursing and Midwifery Council (2010): Advice on delegation for NMC registrants. www.nmc-org The Royal Marsden Hospital Manual of Clinical Nursing Procedures. Eighth Edition.(2011) Edited by Lisa Dougherty and Sara Lister. PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 9/12 APPENDIX 1 RISK ASSESSMENT FOR SCREENING/DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES Name of Screening/Diagnostic Procedure: Date risk assessed: Risk assessed by: Likelihood that process Criteria will fail Low Medium High a. Process for requesting the screening/diagnostic procedure low b. Process for informing the clinician treating the patient of the result low c. Process for informing the patient of the result low d/e. Process for action from a diagnostic test or following-up or referring the patient after a screening test low Identify risks from the ‘process’ of conducting the test if relevant Risk identified in process Mitigation/Controls Staff need to ensure that they receive enough information from the referrer to provide care for Patients. Also they are aware of GP surgeries processes and if unsure clarify these with the GP surgeries. This is to ensure patients receive a timely response to their needs and avoid delayed treatment/monitoring or lost results Staff need to ensure that they follow individual GP surgeries processes and if unsure clarify these with GP surgeries. This is to ensure that results are not delayed and results that are urgent are acted upon in a timely manner and patient is kept full informed regarding their treatment. Patient is made aware of the process and is told the reading after monitoring and advised that the doctor will be informed of results. All actions should be documented within the patient’s health records to ensure continuity of care Practitioner should inform patient directly of treatment or further diagnostics required giving patient enough time to ask question Staff should be made aware of risks of cross infection and follow this procedure to protect patients and themselves. Auxiliary Nurse must be deemed competent and this is the responsibility of the person delegating to ensure they are aware of the process. Staff should clarify this prior to obtaining blood pressure reading so that the procedure is documented within the notes so all parties are aware of the process. Patient should be made aware of the results and how the GP will be informed and will contact patient if treatment or if further monitoring required Any treatments need to be documented with in the patient’s records this includes medication, strength dose and length the prescription is for . Any allergies need to be kept up to date within records. Reduce the risks to patient and ensure the process for individual surgeries is followed PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING Appendix 2 Blood Pressure Monitoring Record Date Time Blood Pressure Left Arm Blood Pressure Right Arm Blood Pressure Standing Any Further Measurements Print Name Signature Designation Date Time Blood Pressure Left Arm Blood Pressure Right Arm Blood Pressure Standing Any Further Measurements Print Name Signature Designation PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 11/12 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING Appendix 2 BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING COMMUNICATION RECORD Patient Details Patient Name: Address & Postcode: Date of Birth: Contact Number: NHS No: GP: Referral Details Referred By Referred To: Designation Date: Contact No: Time: Fax No Fax No: Blood Pressure Measurements Date Time Left are blood pressure Right arm Blood pressure Standing blood pressure Any further measurements Print Name Signature Designation Additional Comments…………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………… PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING 12/12