* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EgyptOverview
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
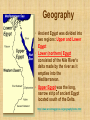
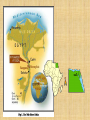
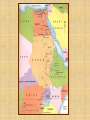
Ancient Egypt: an Overview Timeline • Old Kingdom 2686 BC – 2181 BC (Age of the Pyramids) • Middle Kingdom 2040 BC – 1728 BC • New Kingdom (Age of Conquest) 1570 BC – 1085 BC 1 Three Kingdoms of Ancient Egypt OLD KINGDOM Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods. Egyptians built pyramids at Giza. Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom. MIDDLE KINGDOM Large drainage project created arable farmland. Traders had contacts with Middle East and Crete. NEW KINGDOM Powerful pharaohs created a large empire that reached the Euphrates River. Hatshepsut encouraged trade. Corruption and rebellions were common. Ramses II expanded Egyptian rule to Syria. Hyksos invaded and occupied the delta region. Egyptian power declined. Geography • Egypt is located in northeastern Africa • The Nile River runs the length of the country flowing south to north • The river begins in the mountains of Africa and empties into the Mediterranean Sea • The climate is hot and dry, Egypt is part of the Sahara Desert http://www.worldcountries.info/Maps/GoogleMap-Egypt.php http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/geography/explore/ter.html Geography • Ancient Egypt was divided into two regions: Upper and Lower Egypt • Lower (northern) Egypt consisted of the Nile River's delta made by the river as it empties into the Mediterranean. • Upper Egypt was the long, narrow strip of ancient Egypt located south of the Delta. http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/geography/home.html The Nile River • The Nile was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt • It made life possible in the otherwise barren desert of Egypt. • It is the longest river in the world (over 4,000 miles). • It served as a source of food for the people of ancient Egypt • It was the major source of water for bathing and drinking • The Nile was crucial for farming Blue Nile White Nile White & Blue Nile Meet in Sudan Floodplain Floodplain • The low strip of fertile land located on either side of the Nile River • The river flooded during the annual inundation • When the inundation subsided, it left the earth soaked and overlaid with a fresh layer of black silt. • Most of the farming occurred here Nile Delta • Located in northern Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and empties into the Mediterranean Sea • 240 km of coastline, 106 km in length • Rich agricultural region • Most fertile soil in Africa Facts About the Nile River Length 4,184 miles 2 Sources Lake Victoria, Uganda (White Nile); Lake Tana, Ethiopia (Blue Nile) Mediterranean Sea, off Egypt Mouth Countries Egypt, Sudan, Uganda, Ethiopia, Flows Through Zaire, Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi Name Origin Greek word Nelios, which means "River Valley" Bordered on the south, east and west by the Sahara Desert, and on the north by the sea, ancient Egypt was protected from outside influences. Great Sahara Desert Religion Belief that many gods and goddesses ruled the world and the afterlife Amon-Re: sun god Osiris: god of the underworld and of the Nile • The pharaoh was believed to be a god as well as a ruler Falcon Headed Sun God Religion • Belief in eternal life after death. Relied on the Book of the Dead to help them through the underworld. • Practiced mummification, the preservation of the body for use in the next life. Book of the Dead Collection of spells, hymns, and prayers intended to secure a safe passage to the underworld for the deceased Writing Making paper from papyrus What are hieroglyphs? • Hieroglyphs is the picture writing used in ancient Egypt. The word hieroglyphs is made up of two Greek words - hieros, which means sacred, and glyphe, which means carving. • The Egyptian hieroglyphic writing system consists of hundreds of picture signs (about 800) The signs can be divided into two classes, phonograms and ideograms Phonograms represent sounds (much as alphabet letters do) Ideograms are signs that represent whole words or concepts. Pyramids The Great Sphinx Egyptian goddess Isis, tomb painting, ca. 1360 BC. 2 Social Classes PHARAOH Earthly leader; considered a god HIGH PRIESTS AND PRIESTESSES Served gods and goddesses NOBLES Fought pharaoh’s wars MERCHANTS, SCRIBES, AND ARTISANS Made furniture, jewelry, and fabrics for pharaohs and nobles, and provided for other needs PEASANT FARMERS AND SLAVES Worked in the fields and served the pharaoh