* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mathematics 9 Unit #3: Shape and Space Sub
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
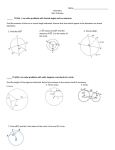
Page 1 Mathematics 9 Unit #3: Shape and Space Sub-Unit #3: Circle Geometry Lesson 1 Topic Triangles 2 Tangents 3 Chords 4 Angles 5 Situational Problems Quiz #5 “I Can” Recall that the interior angles of a triangle have a sum of 180° Solve for an interior angle of a triangle, given the other two Explain properties of side length of isosceles triangles Explain properties of angle sizes of isosceles triangles Explain properties of side length of equilateral triangles Explain properties of angle sizes of isosceles triangles Use Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the hypotenuse of a right triangle, given both legs Use Pythagorean Theorem to solve for a leg of a right triangle, given the hypotenuse and one leg Describe the relationship between tangents and the radius of a circle. Construct tangents by applying the relationship between the radius of a circle and the tangents Use triangle properties to solve for an unknown quantity Describe the relationship between a chord, its perpendicular bisector and the center of a circle of a circle Use triangle properties to solve for an unknown quantity Understand the relationship between inscribed angles and central angles Understand the relationship between inscribed angles subtended by the same arc Find the diameter of a circle using an inscribed angle of 90⁰ Use triangle properties to solve for an unknown quantity Solve situational problems using properties of circles and triangles Demonstrate your understanding of circle properties Lesson #1 – Triangles In any triangle the sum of the interior angles is 180 . This means if you have the measure of two angles, implicitly you have the measure of the third. Ex) Solve for the unknown angle: Another special property for right angle triangles is the Pythagorean Theorem that states that the sum of the squares of the legs is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. A right angle triangle is a special triangle that has one 90⁰ angle. The two sides straddling the 90⁰ angle are called “legs” while the side opposite the angle is called the hypotenuse. Ex2) Label the legs and the hypotenuse of this triangle: The Pythagorean States: the Sum of the squares of the legs equals the square of the hypotenuse: Page 2 For the following triangles, state the Pythagorean Theorem: To solve for an unknown side, determine the hypotenuse and the legs, plug in the two given values and solve for the third, using your rules for solving an equation: Ex3) Solve for the unknown side in each of the following: a) b) Page 3 c) Page 4 Assignment: Lesson #2 – Tangents Using the circle to the right: 1. Draw any chord on the circle using a ruler. DO NOT PICK UP THE RULER! 2. Move your ruler away from the line slowly. Look at the two points that the ruler intersects the circle. When you hit a point where the ruler is only touching the line once, draw another line. The tangent is a line that intersects the circle at only one point, no matter how much it is extended. The point of tangency is that point at which a tangent intersects a circle. Use the circle below: 1. Sketch a tangent anywhere on this circle. 2. Draw a radius from the center, O, of the circle to the tangent you have drawn 3. Measure the angle between the radius and the tangent. Compare with your neighbor. What is the angle between the radius and the tangent? Page 5 tangent for your nearest neightbor? What is the angle between the radius and the CIRCLE PROPERTY #1 A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the same point of tangency. Use this property to solve the following; assume O to be the center of every circle: Ex1) Solve for Ex2) Solve for x. Page 6 Ex3) Solve for the indicated length; round any necessary answers to one decimal place Page 7 Assignment: Page 388-390 # 3-7, 12, 14 Lesson #3 – Chords A chord is any line that intersects a circle twice. Sketch chords on the following circles. Draw a chord on the piece of paper on the next page and remove it from the booklet. Fold the paper so that the two edges of the chord coincide with each other. In the space below, write your observations: What is special about the fold line? What is this called? Measure the angle between your fold line and your chord. What about your neighbors? Measure the length of the line from the fold line to the outside edge of the circle on both sides of the fold line (2 measurements). What do you notice about these lengths? What does your neighbor notice? The line of symmetry is called a _____________________ _________________. A line bisects another line when it goes through the midpoint of the line (____________ ______ ______ ____________). Therefore a ____________________ _________________ is a line that goes through the midpoint of a chord and is perpendicular to the chord. This leads us to the circle properties CIRCLE PROPERTY #2 The perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord; that is, the perpendicular divides the chord into two equal parts. Using the diagram to the right as a reference: Page 8 When , then **If you know a line from the center of the circle is perpendicular to a chord, then it also bisects the chord.** Page 9 Page 10 CIRCLE PROPERTY #3 The perpendicular bisector of a chord in a circle passes through the center of the circle. Ie: When center of the circle. and , then SR passes through O, the **If a line is perpendicular to a chord and bisects the chord, then the line goes through the center of the circle** CIRCLE PROPERTY #4 A line that joins the center of a circle and the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular to the chord. Ie: When O is the center of a circle and , then **If a line goes through the center of the circle and the midpoint of a chord, then it is perpendicular to the chord. SUMMARY: These three circle properties are like “buy two get one free”. If you are given two bits of information you are expected to deduce the third, as they are a package deal that will always go together. You will be looking for ways to apply them as well as your knowledge of the relationship between diameter and radius and the Pythagorean Theorem. Page 11 Ex1) Determine the values of and using circle properties. Page 12 Ex 2) From the diagram below solve for the length of the chord CD. Assignment: Page 397-399 # 3-7 Lesson #4 – Angles A section of the circumference of a circle is called an arc. There are two types of arcs, major and minor. The _________ arc is the minor arc. The _________ arc is the major arc. The angle formed by joining the endpoints of an arc to the center of the circle is called a CENTRAL ANGLE. In the diagram below, is a central angle. Page 13 The angle formed by joining the enpoinsts of an arc to a point on the circle is an INSCRIBED ANGLE. In the diagram below, , is an inscribed angle. Below are 2 pictures of inscribed angles and central angles. Use your protractor to measure the angles on these and the diagram to the left. Look for a pattern between inscribed angles an central angles. The measure of the central angle tends to be _________________ the measure of the inscribed angle; or the measure of the inscribed angle tends to be _________________ the measure of the central angle. CIRCLE PROPERTY #5 In a circle, the measure of a central angle subtended by an arc is twice the measure of an inscribed angle subtended by the same arc. ( ) or ( ) **Central angles are twice the size of the inscribed angle based on the same arc. CIRCLE PROPERTY #6 In a circle, all inscribed angles subtended by the same arc are all congruent. **All inscribed angles are equal if based off the same arc CIRCLE PROPERTY #7 All inscribed angles subtended by a semicircle are right angles. Since , then it follows that Page 14 **If an inscribed angle is subtended by the diameter, then the angle is a right angle or 90⁰, since the central angle is 180⁰. Page 15 Ex1) Triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle with the center O. Determine the values of , , and . and . Page 16 Ex2) Rectangle ABCD has its vertices on a circle with a radius of 8.5 cm, as pictured to the right. The width of the rectangle is 10.0 cm. What is its length? Give the answer to the nearest tenth of a cm. Assignment: Page 410-411 # 3-6; 11 Lesson #5 – Situational Problems There are many situational problems that can be solved using the circle properties explained throughout this unit. The hardest part of solving these problems is determining which property or properties you must use. The most important key to solving situational problems is knowing the properties and the terms involved in the properties. The net key to solving situation problems is drawing a diagram and understanding which values you are looking for. Luckily, in grade 9 you will be given the diagrams! Page 17 Ex1) A small aircraft, A, is cruising at an altitude of 1.5 km. The radius of the Earth is approximately 6400 km. How far is the plane from the horizon at point B? Calculate his distance to the nearest km. Page 18 Ex 2) A radar station, R, tracks all ships in a circle with a radius of 50.0 km. A ship enters this radar zone ant the station tracks it from 62.5 km, until the ship passes out of range. What is the closest distance the ship comes to the radar station? Assignment: Page 418-419 # 2, 3, 8, 10,