* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PULSE MODULATION
Pulse-Doppler radar wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Air traffic control radar beacon system wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Broadcast television systems wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-wave radar wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Active electronically scanned array wikipedia , lookup
405-line television system wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
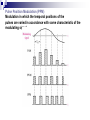
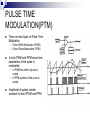
PULSE MODULATION Three different sampling methods of PAM 4.2 Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) Modulation in which the amplitude of pulses is varied in accordance with the modulating signal Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Modulation in which the duration of pulses is varied accordance with the modulating signal in Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) Modulation in which the temporal positions of the pulses are varied in accordance with some characteristic of the modulating signal. SAMPLING Process of converting a continuous time signal to an equivalent discrete time signal. Continuous time signal x(t) is applied at input of multiplexer. Other input of multiplexer is train of impulse. At the output of multiplexer we get the sampled version of x(t) DIFFERENCE PAM Amplitude of pulse is proportional to amplitude of modulating signal. Band width of transmitting channel depends on width of pulse. Instantaneous power of transmitter varies. Noise interference is high. Complex system. Similar to A.M. PWM Width of pulse is proportional to amplitude of modulating signal. Band width of transmitting channel depends on rise time of the pulse. Instantaneous power of transmitter varies. Noise interference is minimum. Simple to implement. Similar to F.M. PPM Relative position of pulse is proportional to amplitude of modulating signal. Band width of transmitting channel depends on rise time of the pulse. Instantaneous power remains constant. Noise interference is minimum. Simple to implement. Similar to P.M. •Flat Top PAM The top of pulses of this PAM is flat. Noise interference at the top of transmitted pulse can be easily removed. Due to this it is widely used. Better than Natural PAM Because in case of Natural PAM, the varying top signal is when received at receiver, it becomes quite difficult to determine shape of top of pulse due to noise (which is always present). Thus errors are introduced in the receiving signals due to wich we prefer a flat top PAM. •Flat Top PAM cont. Sampled and hold circuit consist of 2 flat switches and a capacitor. The sampling switch is closed for a short duration by a short pulse applied to gate G1 of transistor. When the sampling switch is opened the capacitor hold the charge. The discharge switch is then closed by a pulse applied to the gate G2 pf the other transistor. During this period the capacitor is charged up to a voltage equal to the instantaneous value of input signal x(t) Due to this capacitor discharge to zero volts. Hence the output sampled and hold circuit consist of Flat Top Samples. Fig. shows sampled and hold circuit to Produce FLAT TOP sampled P.A.M. PULSE TIME MODULATION(PTM) There are two types of Pulse Time Modulation Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Pulse Phase Modulation (PPM) In both PWM and PPM some time parameters of the pulse is modulated. In PWM the width of pulse is varied. In PPM position of the pulse is varied. Amplitude of pulses remain constant for both PWM and PPM