* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1 Notes
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
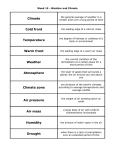
Climates of the World Section 1 2.5 relate major climate and vegetation regions of the world • The sun, the brightest star in our sky, is a major factor in creating Earth’s climates. The sun, composed of hydrogen, helium, and other gases, rotates on an axis at about the same angle as the earth’s axis. Only a tiny fraction of the power generated by the sun reaches the earth. Sun video Climate and Weather •Weather is the condition of the atmosphere in a certain place at a specific time. • The climate of an area is its longterm typical weather pattern. • The climate of an area is determined by many things; the most important is the earth’s position in relation to the sun. 2.6 describe factors that influence climate regions Weather & climate Video Earth’s Tilt and Rotation • Earth is currently tilted at an angle of about 23½°. Because of the tilt of this axis, not all places on Earth receive the same amount of direct sunlight at the same time. Earth’s Revolution • Earth travels in an orbit around the sun, completing one trip about every 365 days. • The seasons are caused by the earth’s revolution around the sun and the earth’s tilt. • The Equator divides Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. When one hemisphere experiences winter, the other experiences summer. Tilt video The Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn • The line of latitude at 23½°N is called the Tropic of Cancer–the northernmost latitude on the earth to receive the sun’s direct rays. • The line of latitude at 23½°S is called the Tropic of Capricorn–the southernmost latitude to receive the sun’s direct rays. The Poles • The North Pole and the South Pole are located at either end of the earth’s axis. • Each Pole receives continuous indirect sunlight six months each year. • While one receives continuous sunlight, the other receives little to no sunlight. South pole video The Greenhouse Effect • Part of the sun’s radiation passes through Earth’s atmosphere. • Like the glass in a greenhouse, the atmosphere keeps the heat from escaping back into space too quickly. • Humans have altered Earth’s atmosphere by burning fuels that release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse video