* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download blood typing - WordPress.com
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
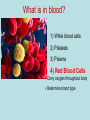
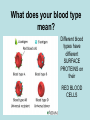
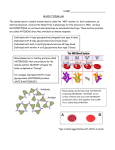
Blood Typing Biology Powerpoint #3 Mr. Velekei Vocabulary 18. 19. 20. 21. Agglutination Antibody Antigen Glycoprotein What is in blood? 1) White blood cells 2) Platelets 3) Plasma 4) Red Blood Cells • Carry oxygen throughout body • Determine blood type Blood Typing Genotypes Up to this point, we have talked about only 2 alleles for any gene (for example A or a) In human blood types, there are 3 alleles: A, B and O This is called multiple alleles Blood Typing Genotypes Some rules in blood typing: I is dominant to i A is Co-Dominant to B There are 6 possible genotypes, and 4 phenotypes IAIA and IAi IBIB and IBi IAIB ii = blood type A = blood type B = blood type AB = blood type O What does your blood type mean? Different blood types have different SURFACE PROTEINS on their RED BLOOD CELLS Glycoproteins on the surface of cells help identify “self” The pattern of sugars that are attached is determined by a gene Type A An A allele tells the cell to put “A” glycoproteins on its surface Type B An B allele tells the cell to put different “B” glycoproteins on its surface Type O An O allele tells the cell NOT to put A or B glycoproteins on its surface Type AB A cell with BOTH an A and a B allele has BOTH A and B glycoproteins on its surface ANTIBODIES are specialized proteins that are part of your immune system. They react to, and attempt to destroy, ‘foreign’ invaders. Usually determined by their glycoproteins. Glycoproteins on the surface of cells that cause an immune reaction are called ANTIGENS How Antigens & Antibodies Interact If you are blood type “A”, you have: “A” Antigens AND “B” Antibodies If you add ANTI-A (antibody A) to cells with “A” glycoproteins on their surface, it causes them to clump together AGGLUTINATION = ________________________ How Antigens & Antibodies Interact Adding ANTI-A antibodies to cells with B glycoproteins on their surface causes NO REACTION BLOOD TYPES NO YES NO Will ANTI-A react? YES BLOOD TYPES NO NO YES Will ANTI-B react? YES Genetics of Blood type phenogenotype type A B AB O antigen on RBC antibodies in blood donation status IA IA or IA i type A antigens on surface of RBC anti-B antibodies __ IB IB or IB i type B antigens on surface of RBC anti-A antibodies __ IA IB both type A & type B antigens on surface of RBC no antibodies universal recipient ii no antigens on surface of RBC anti-A & anti-B antibodies universal donor Blood Typing Game http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/landsteiner/landsteiner.html The A,B,O SYSTEM IS NOT THE ONLY ONE Blood can also be Rh+ (positive) or Rh-(negative) Rh Factor The Rh factor describes another surface protein on the RBC. It is named after the Rhesus monkey, where it was initially identified If your blood does contain the Rh protein, your blood is said to be Rh positive (Rh+) If your blood does NOT contain the Rh protein, your blood is said to be Rh negative (Rh-) Rh Factor Similar to ABO blood types, an Rhperson may have the Rh antibody. Therefore, Rh+ individuals can give blood only to other Rh+, but Rhcan give blood to both Rh+ and RhSo, O- is the ultimate donor! BLOOD TYPES YES Will ANTI-Rh react? NO You can determine the blood type of a cell by seeing which ANTIBODY it reacts with Add 1 drop of person’s blood to each well Add 10uL ANTI-A serum to A well Add 10uL of ANTI-B serum to B well Add 10uL of ANTI-Rh to Rh well You are looking for blood agglutination Type A will clump in well A Type B will clump in well B Type AB will clump in both well A & B Type O will NOT clump in A or B Rh+ will clump in Rh well