* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applied Bio Ch. 14.2 Evidence ppt notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
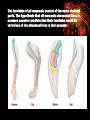
Evidence for Evolution Concept 14.2 pp 299-304 Fossil Record • Fossils- preserved remains of organisms from the past- extinct. • Most- sedimentary rocks• Chronological collection of fossil remains • Each rock layer represents a particular time period. • Older fossils are found at the bottom. • Prokaryotes- oldest form of lifefound in rocks believed to be 3.5 billion yrs old. Sedimentary Rock Layers Terms • An extinct species- a species that no longer exists. • Paleontologist- a scientist that studies fossils. • Studying fossils of ancestral life- links past and present. Geographical distribution • Patterns of geographical distribution make sense in terms of evolution • Geographic distribution is a clue to how species may have evolved. • Explains why we see related species today in a particular area. • Ex.- Australia- many pouched mammals (marsupials) and few placental animals. Hypothesis_____. Homologous structures. • Definition- the presence of similar structures in different species that share a common ancestor. • Examples- forelimbs of mammals have the same skeletal parts even though the function is completely different. • Human arm, cat forelge, whale flipper, bat wing • These structures have become adapted. The forelimbs of all mammals consist of the same skeletal parts. The hypothesis that all mammals descended from a common ancestor predicts that their forelimbs would be variations of the structural form in that ancestor • Vestigial Structures • Definition- a remnant of a homologous structure that once had an important function in the ancestral species but no longer has a function in modern related species. • Often vestigial structures are reduced in size. • Example – whale hipbones • Hypothesis- whales descended from land organisms that had 4 limbs. • Natural selection favors survival of individuals with genes for reduced versions of these structures. Comparison of Embryonic Development • Closely related organisms have similar stages of development. • All vertebrates evolved from a common ancestor. • Example- pouches on side of throat • Fish-gills • Birds and primates-bones of skull Molecular Biology • DNA sequences • A common genetic code shared by all species. • Unrelated species show more differences in DNA sequence. • If 2 species have genes and protein sequences that match closely then they have a more recent common ancestor. • If 2 species have more differences in DNA and protein sequences then no close common ancestor. Hemoglobin amino acid sequences- Concept Check 14.2 • 1. Why are older fossils generally in deeper rock layers than younger fossils? • 2. How can evolutionary theory explain why Australia is home to relatively few native placental mammals? • 3. What are homologous structures? • 4. What can you infer about species that differ significantly in their DNA sequences? Reviewing Concepts Multiple Choice Choose the letter of the best answer. • 1. Which of the following is an incorrect match? • a. Lyell—suggested physical changes to Earth result from geologic processes occurring over long periods of time. b. Lamarck—proposed that organisms adapt to their environment. c. Darwin—developed the theory of natural selection as a mechanism of change in species. d. Malthus—thought that characteristics acquired during an organism's lifetime can be passed on to the next generation. • 2. Which of the following provides clues about the size and structure of once-living organisms? • a. b. c. d. fossils DNA and proteins from the organisms vestigial structures development of embryos • 3. What statement is not an observation or inference on which Darwin's theory of natural selection is based? • a. Variations among individuals exist in a population. b. Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring. c. Individuals whose inherited characteristics give them advantages in their environment will generally produce more offspring. d. Species living today descended with modification from earlier species. • 4. Artificial selection is similar to natural selection in that both processes • a. b. c. d. were suggested by Darwin. adapt species to their environments. occur over many millions of years. depend on variation among individuals.