* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module IV Session 1 Intro and Management
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
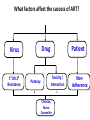
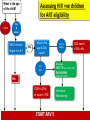
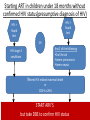
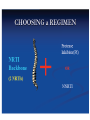
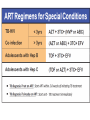
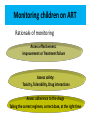
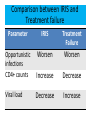
Module IV: Paediatric ART Treatment An Introduction to Antiretroviral Therapy Key questions: • What are ARVs? • Why do we give ARVs to HIV infected children and adolescents? • How do ARVs reduce the replication of HIV? • What are the different ARV drug classes and types? • What factors affect success of ART in children? Why do we give ARVs to HIV infected children and adolescents? To reduce the HIV related morbidity & mortality of children and improve survival and quality of life. What do ARVs do? • Suppress HIV replication and prevent disease progression. • Restore and/or preserve the immune system reducing the risk of opportunistic Infections. • Promote optimal growth and development Why do we learn about the structure and life cycle of the Virus? • Understanding the structure helps us to know structures in the virus that helps it multiply in the human cell • Understanding the Life cycle helps us to know how the virus multiplies, where the ARV drugs work and how they are classified Structure Of Human Immunodeficiency Virus HIV STRUCTURE Envelope Proteins Envelope gp120 Enzymes gp41 2.Reverse Transcriptase Matrix Protein p17 Core Proteins RNA HIV Core protein’s 1.P24 surrounds protein Core converts viral single-stranded RNA into double stranded (DNA) 3.Integrase. Integration of the viral p24 DNA into the host’s chromosomal RT DNA. Integrase 4.Protease splits generated macro Protease proteins into smaller viral proteins which are then incorporated into the new viral particles HIV life cycle shows where the ARVs work INFECTING VIRUS HIV RNA INTEGRASE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE S. S. HIV DNA REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION D. S. HIV DNA HIV mRNA INTEGRATION PR RIBOSOMES HIV LIFE CYCLE HIV precursor proteins O TE AS E HIV RNA ASSEMBLY HIV RNA Insertion in Host Genome HIV LG. PROTEINS NEW VIRUS Steps in HIV life cycle 1. Fusion and entry into human cell. 2. Reverse Transcription RNA-DNA. 3. Integration into host genome 4. Transcription and Translation of virus components 5. Budding and maturation of new virus particles Video of Life cycle What are the different classes of ARVs? • Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTI) • Non- Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTI) • Protease Inhibitors (PI) • Integrase Inhibitors • Fusion Inhibitors (FI) Which three classes are commonly used in Uganda? Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) Single Drugs: • Zidovudine (AZT) • Stavudine (D4T) • Lamuvudine (3TC) • Didanosine (DDI) • Abacavir (ABC) • Tenofovir • Emtricabine • Zaltacibine Fixed Dose Combinations • AZT/3TC/NVP (Douvir N) • AZT/3TC (Combivir or Duovir) • D4T/3TC/NVP (triomune) • D4T/3TC • AZT/3TC/ABC(Trizivir) • ABC/3TC(Epzicom) • Tenofovir/Emtricabine(Truvada) Non Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Nevirapine (NVP) Efavirenz (EFV) Delarvirdine (DLV) Protease Inhibitors lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra/ Aluvia) Ritonavir Lopinavir Atazanavir Darunavir Saquinavir Nelfinavir Indinavir New Classes Entry/ Fuzion Inhibitors • T20/ Fuzeon / Enfuvertide Integrase Inhibitors • Raltegravir Principles of Paediatric Antiretroviral Therapy • Initiate therapy with at least three drugs in a potent regimen • Include at least two new agents when changing a therapy. • Avoid using drugs previously used in a failing regimen (recycling) unless you have done resistance testing • Keep doses at the upper end of dosing range • Check children’s weights and adjust drug dosages at each visit • Maximize adherence to ART • Rationally sequence drugs to preserve future treatment options What factors affect the success of ART? Drug Virus 10 OR 20 Resistance Potency Patient Toxicity / Interaction Clinician, Nurse, Counsellor NonAdherence Activity: Do you know the basics about ARVs? • Let us practice with a T/F quiz competition Management of ART Key questions: • When should HIV+ve children be started on ART? • What 1st line regimens are used to start ART? • When do we substitute drugs in the 1st line regimen? • How do we monitor children on ART? • How do we make a decision to switch from a 1st line to 2nd line regimen? • What 2nd line ARV regimens are used in Uganda? • How can we identify an Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory (IRIS) event? When are children supposed to start ART? 1. Determine eligibility for ART – Clinically – Immunologically 2. Determine the readiness of the child to start ARVs – – – – – – Disclosure if appropriate Adherence counseling Social life and current responsibilities Being in and out of school Family support Availability of trusted treatment supporter (Buddy) 3. Do a Pre-treatment (Baseline) Assessment – – – – – – Full clinical assessment for infections & clinical staging Neuro developmental assessment (include Tanner staging) Weight, length/height, head circumference Do Hb CD4+ count Viral load (where available) 4. Identify and prepare the main parent/caregiver – Educate on giving the child ARVs and continuing with home care – Counsel on caring for and living with an HIV infected child Comparing 2006 and 2010 guidelines- What has changed? 2006 2010 Immune marker Age-specific recommendation to initiate ART <12 m 12 to 35 m CD4 percent All <20% <20% <15% CD4 count/mm3 All <750 cells <350 cells <200 cells TLC/mm3 All <3000 cells <2500 cells <2000 cells Immune marker Age-specific recommendation to initiate ART Clinical criteria <24m 24-59m >5 yrs stage 4 disease <350 cells stage 3 disease CD4 percent All <25% CD4 count/mm3 All <750 cells 36 to 59 m ≥5 yrs Clinical criteria Stage 4 disease Stage 3 disease (for children aged over 12 months with TB, LIP, OHL or low plts, ART initiation may be delayed What is the age of the child? < 2yrs Assessing HIV +ve children for ART eligibility 2yrs & above WHO clinical Stage 3 or 4? NO What is the age & CD4 count? 2 to <5yrs Yes CD4% <25% or count <750 START ARV’S 5yrs & above CD4 count <350 cells 2 to <5yrs CD4% >25% or count >750 5yrs and above CD4 count >350 Continue Monitoring Starting ART in children under 18 months without confirmed HIV status(presumptive diagnosis of HIV) HIV + Rapid test HIV + Rapid test OR Any 2 of the following •Oral thrush •Severe pneumonia •Severe sepsis HIV stage 4 conditions Recent HIV related maternal death or CD4 % <20% START ARV’S but take DBS to confirm HIV status Choosing a Regimen • The first line regimen is the best chance to achieve maximum and sustained viral suppression Examples of Combinations to be avoided • TDF+DDI – Low potency – Interactions • TDF+ABC – Early treatment failure • d4T+ddI – Mitochondrial Toxicity • D4T +AZT – Competition for same site Monitoring children on ART Rationale of monitoring Assess effectiveness: Improvement or Treatment failure Assess safety: Toxicity, Tolerability, Drug interactions Assess adherence to the drugs Taking the correct regimen, correct dose, at the right time How do we monitor children on ART? • Clinical • Laboratory • Psychosocial Clinical monitoring 1st Visit after ART initiation • Review understanding of HIV: disease process and adherence strategies • Observe accurate dosing and administration of drugs by caregiver • Full clinical assessment • Return visit in 2 weeks Monthly clinical monitoring • Interval medical history, symptom check – Wt,Ht, physical exam, nutritional assessment – Side effects/toxicity, IRIS – Assess adherence • Ask for demonstration of dose and administration of medication at each visit • Recalculate dose • Dispense more doses Laboratory monitoring Immunological testing – CD4 counts: done every 6 months or if there are other features suggesting treatment failure Virological testing - Done every 6 – 12 months if available Lab monitoring Lab test for diagnosis and monitoring Baseline ( entry into care) Initiation of 1st or 2nd regimen HIV diagnostic testing . Hb . . . . Every six months . . WBC and differential CD4% or absolute CD4 count As required or symptom directed . . Preg. Test in adols . Chemistry . VL . . OI screening . Psychosocial Monitoring • • • • • Progress at school Relationships with family members, friends Attitude to daily drug taking, adherence Progress of disclosure Development into adolescence – sexual awareness, behavioural issues 34 What is substitution? Substitution is the process of replacing one drug with another. When or why do we substitute drugs in the 1st line regimen? Main reasons for substitution of an ARV drug: – Toxicity – Pregnancy – Development of OI like TB, Hep B., etc – Change in treatment guidelines Examples of substitution Drugs What to substitute with ABC or D4T EFV Reason to change the drug Anaemia (toxicity) pregnancy NVP TB treatment EFV AZT Steven Johnsons syndrome (toxicity) NVP When do we switch from 1st line to a 2nd line regimen? Switch from one ARV regimen to another when there is Treatment Failure Parameters used to assess ARV Treatment Failure include: •Clinical •Immunological •Virological Remember: Always consult and discuss the case with a colleague before you substitute a drug or switch a regimen! Immunological failure or not? • Patient takes D4T+3TC+NVP for 1 year and 6 months. • CD4 was measured at baseline (50 cells/ml), month 6 (143) , month 12 (247) , month 18 (220). • Is this failure or not? • Not enough indications to say it’s failure. • CD4 physiological variation more probable. • Look also at CD4%; less variable. • In case of doubt, and before deciding on treatment switch, do another CD4 test (same machine, same lab) +/- 1 or 2 months later What 2nd line to Use National ART Paediatric Guidelines help us to: • Decide when to start ARVs • Decide on the 1st line regimen to use • Decide the ARV regimen to use in special clinical conditions • Identify a failing regimen • Decide a 2nd line regimen to switch to IRIS (Immune reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome) Definitions • Previously quiescent diseases which become symptomatic or worse after the introduction of HAART (unmasking type) OR • Worsening of symptoms of OI’s that were already under effective treatment (TB, AC,CMV), shortly after starting HAART (paradoxical worsening) How does IRIS come about? • There is a quiescent disease like TB, MAC and a failed immune system. • On starting ART, the immune system begins to recover and mount an attack on these quiescent diseases. • This makes the symptoms of the quiescent disease appear or re-appear if it was previously there Comparison between IRIS and Treatment failure Parameter IRIS Treatment Failure Opportunistic infections CD4+ counts Worsen Worsen Increase Decrease Viral load Decrease Increase Treatment of IRIS • Continue ART (sometimes stop needed due to interactions or patient’s condition too bad) • Treat the IRIS according to the presenting OI with the standard treatment for that condition e.g. TB (if already on Rx , intensification may be required) • Add corticosteroids in case of severe inflammatory response e.g. dyspnoea due to large thoracic LN, or severe CNS (e.g. prednisolone 20-40 mg/day, 2 weeks-1 month) • Use mechanical measures (drainage) • Use of NSAID (ASA) Activity: Case # 1 • John is a one year old, HIV +ve child who was started on AZT+3TC and NVP at 2 months of age. The child has been adherent to his treatment. His CD4+ has fallen from 500 to 150 cells over 6 months. He was well until 2 weeks ago when he developed oral thrush. He has been treated with Ketoconazole with no improvement. Qn1: What is the Treatment stage? Stage 3 Qn2: Would you switch therapy in the child and why? Length on treatment >24 weeks, Adherent to treatment yes Then switch because there is clinical and immunological failure. Qn3: what ARV regimen would you give? ABC +3TC+LPV/r Activity: Case # 2 Na-gundi is a 4 year old girl who has been on AZT+3TC+ NVP for the past 3 months, and she has not missed her drugs. Her mother reports that she has developed symptoms of cough and difficulty in breathing. Her mother also reports that she thinks that Na-gundi gets a bit hot especially in the afternoon and sweats a lot at night. Na-gundi was treated with IV ceftriaxone for 5 days with no improvement. •IRIS – TB • Pneumonia Qn1: What could be the diagnosis in Na-gundi? Sputum ZN Qn2: What other investigations would you do ? CXR Mantoux test Early CD4+ counts Qn 3: Would you switch treatment in this child and why? •No •Duration on treatment= 12 weeks •Adherence good •If she has confirmed TB – IRIS, substitute NVP for Efavirez Practical 3 Mukonogum is an 8 year old boy. He has been on AZT+ 3TC +•Yes NVP for 3onyears He has been - Duration ART >24now. weeks, Adherent-Yes, Clinicaladherent failure- yes , and doingImmunological very wellfailure-Yes until 1 month ago when he developed •ABC+ 3TC + LPV/Rtr skin •Factors rashesforand pneumonia. His CD4 count when he clarification: started Adherence treatment was 200. His CD4 as per last month Tolerability (e.g. side effects) was 300.Pharmacokinetic It was repeated 2 daysrequirements ago and it was 90 issues (food/fasting Drug-drug interactions cells/mm . 1. Potency of current ARTs FromPrior thisART information experience do you think Mukonogum is •Potential for or known resistance his first line regimen? failing on 2. If yes, which regimen are you likely to switch him to? 3. What factors do you need to clarify on before you initiate him on the second line?