* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1- Circulation and Immunity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
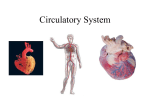
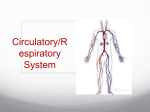
SCIENCE 30 UNIT A: MAINTAINING HEALTH Chapter 1- Circulation and Immunity Mrs. Steinbrenner Name: 1 1.1) Circulatory System Descending aorta • 4 main roles of the circulatory system: – _____________ (gases, nutrients, wastes). chordae tendinae – Regulation (by hormones). (a.k.a. aortic valve) – Protection/Defense (immunity and injury). (a.k.a pulmonary valve) – Distributes ________________. (a.k.a bicuspid or mitral valve) (a.k.a tricuspid) • Divided into 2 parts: – 1. ______________________ (heart, blood septum apex vessels). – 2. Lymphatic system ( lymph vessels and nodes). Ideas about the heart • Historical ideas: – ________: Greek physician (2nd century) • Believed that heart sucked blood from veins, blood flowed like the tides. – ___________________: 15th century • Complete and realistic sketches of the heart. – William Harvey: 17th century • Discovered __________ in heart and veins, 1 way movement of blood. • Calculated cardiac output. • Aided by ___________ discovery of capillaries. A. Cardiac Output • The ___________________ that flows from each side of the heart per minute. • Two factors affect this output: 1. _____________: quantity of blood pumped with each beat of the heart (~ 70mL). 2. Heart rate: # of times heart beats/minute. Cardiac output = ______________________ Applications of Cardiac Output Provides comparison for fitness levels: - ______ heart rate = high stroke volume. - High heart rate = ______ stroke volume. B. The heart • There are 4 chambers in the heart: – Left and Right _________ (receive blood from lungs and body). – Left and Right _______________ (pump blood to lungs and body). • Double sided pump: Left and Right sides of the heart are separated by a muscular wall called the ________________. • The sac that encloses the heart = ______________________. Fluid inside is called the pericardial fluid. 1) The Heart Pumps • There are 2 pumps that work simultaneously; these are synchronized. • Left pump = ____________ blood received. • Right pump = _________________ blood received. 2) Blood Flow- Low oxygen • Blood low in oxygen (from the body) enters the ______________ and is pumped Descending aorta to the right ventricle. • The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated chordae tendinae blood to the ______________________ (a.k.a. aortic valve) (a.k.a pulmonary valve) (a.k.a tricuspid) (a.k.a bicuspid or mitral valve) 2 septum apex and then to the lungs. This blood is then oxygenated. Blood flow- high oxygen • Blood high in oxygen (from the lungs) enters __________________ to the left atrium. • The ________________ pumps blood to the left ventricle, pumped to the aorta, to the arteries and then to the body. • Arteries divide into arterioles and then into capillaries. All gas, nutrient and waste exchange happens using the __________. Blood flow • Capillaries branch into venules, becoming veins, then the _______________ and blood enters the right atrium. • Why is the left ventricle (8-10mm) thicker than the right ( 2-3 mm)? ________________ Vena Cava The largest vein in the body. There are 2 branches of the vena cava: 1. _____________ Vena Cava (receives blood from the diaphragm up). 2. ___________ Vena Cava (receives blood from below the diaphragm). 3) Heart Valves • Valves open and close to let the blood flow through the heart. • 2 types: – ________________ (AV) valves: between atria and ventricles. • Open when atria contract, close when ventricles contract. – __________: between ventricles and arteries. • Open when ventricles contract, close when atria contract. 4) Heartbeat • “lub-dub” sound caused by closing of heart valves. • “lub”= ___valves close (ventricles contract) • “dub”= _____________ valves close (atria contract). • “gurgle” = heart murmur (valves do not close properly). • _________ = ventricular relaxation (“dub”). • ________ = Ventricular contraction (“lub”). 5) Factors affecting heart rate • Many factors affect heart rate including: – ______________________. – Temperature change (↑ temp = ↑ HR). – Cardiovascular exercise (running, swimming, cycling) can decrease heart rate. • A stronger heart is ______ a larger heart but a more elastic/efficient one! 6) Target Heart rate • Once your body reaches 85% of its max. HR, lactic acid is made and pain increases. • To calculate target HR, use: _____________ = target HR Target Heart Rates Health goal % of maximum HR Maintain fitness level 50 -60% Increase fat burning 60-70% Increase cardio 70-80% 3 1.2) Blood Vessels • 3 types of blood vessels in the body: 1. Artery: take blood _______ from the heart. 1. Thick elastic walls that can stretch. 2. Vein: takes blood ____ the heart. 1. Thin walled with valves for 1 way flow. 3. Capillaries: connect arteries and veins. 1. 1 cell thick to allow ___________ into cells. 1)Blood pathway in vessels • Heart --- arteries ---- arterioles ---- capillaries ---- venules ---- veins ---- vena cava --heart. • Arterioles and venules are just smaller versions of arteries and veins. • Arteries always carry _______________ blood (except for pulmonary artery). • Veins always carry ________________ blood (except for pulmonary vein). • Pressure ___________ as you get to the capillaries; builds going back to the heart. 2) Varicose veins • Raised veins due to damaged valves and stretched walls. • Blood _____________________ veins. • Prolonged standing can cause this. 3) Blood Pressure (BP) • The force of blood against the artery walls during ventricular contraction (systole) and during atrial contraction ( diastole). Heart rate = ______________________ _________= 120/80 (average) • ____________ is most important because it determines the pressure on arteries when ventricles are relaxed. • Measured using a sphygmomanometer. a) Factors that affect BP 1. Heart rate (HR): High HR = high BP. 2. Blood vessel size: _________ = high BP. 3. Blood volume: High volume = high BP. 4. Stroke volume: High volume = high BP. b) Regulation of Blood Pressure (BP) • ___________ = difficulty transporting blood to tissues (especially head). • ____________ = weaken artery, ruptures blood vessels. • __________________ (in aorta and carotid arteries) detect changes in BP. Brain receives message and either speeds up (sympathetic) or slows down (parasympathetic) impulses. c) Hypertension: The Silent Killer High blood pressure Caused by increased resistance to blood flow Blood vessels weaken and may rupture Body compensates by increasing support provided by connective tissues Arteries become _____________ During systole, blood pressure increases even more; Further stress and weakening Causes of Hypertension 1. Hereditary 2. _________ Excess salt High fat Silent killer: Symptoms not noticeable until a heart attack or stroke results 4 d) Pressure and Blood flow • As the area that blood flows through increases, the pressure ___________ (because velocity does too). • Blood travels the slowest through the capillaries; allows for all nutrients to be picked up! • Velocity of blood _____________ from arteries --- capillaries --- veins. • 1.3) Blood • Average 70kg person has ____ of blood. • 55% of blood is fluid,45% is blood cells. • __________ = fluid; 90% water and 10% proteins, vitamins, glucose... • There are 3 groups of proteins in plasma: 1. Albumins: draws water back into capillaries 2. Globulins: produces antibodies 3. Fibrinogens: used to clot blood. A. Red Blood cells (_________________) • Make up ________ of blood cells. • Main function = transport __________ (each rbc can have 4 oxygen molecules). • Respiratory pigment hemoglobin allows rbc’s to carry oxygen ( 70x more than without hemoglobin)- gives red color! • Without hemoglobin, life can be maintained for _____; with = 5 minutes. • ______________ shape to maximize SA for gas exchange. • Enucleated = ________________ when mature, allows for more oxygen to be carried. Bone marrow produces rbc’s, can not reproduce without a nucleus. Bone marrow • Erythropoiesis = _________ production ( occurs in bone marrow). • Rbc’s begin as stem cells, divide and shrink- losing nucleus. • Age of rbc’s is monitored by wbc’s; when rbc is _________ days, it releases hemoglobin and is transported from the cell. • Iron (globin) is recycled and used in new rbc’s; heme is converted into _______ pigments (bilirubin). B. White blood cells (__________) • Around ____ of blood. • Responsible for: housekeeping/ defence. • Have a nucleus. • Made in bone barrow; last _____________ days. • Destroy invaders by: – __________________: move towards microbe. Enzymes released digest leukocyte and microbe; fragments = pus. C. Platelets (thrombocytes) • Have no nucleus. • Produced in bone marrow; last ____ days. • Irregularly shaped, very _________ and responsible for blood-clotting reactions. D. Blood Clotting • Maintains homeostasis. • Platelets ___________ when striking a sharp object . • Fibrinogen breaks up into fibrin threads. These seal the cut: prevent bacteria from entering and create framework for ___________ to patch up cut. • A _____________ is a blood clot that seals the vessel = blocks vessel and prevents gas exchange. 5 • • • • • 2 types: Cerebral: clot in brain, causes a __________ Coronary: clot in artery, causes ___________________. Embolus = dislodged blood clot, travels to other organs; life threatening Hemophilia: The ability to produce fibrinogen to form a clot is hindered. • Czar Nicholas II son had hemophilia. 1.4 Cardiovascular diseases and disorders • There are many diseases that affect the heart and blood vessels: – Atherosclerosis ( hardening of arteries due to plaque). – Coronary Heart disease ( ________________ _________ to artery(s) of the heart). – Heart Attack ( no blood flow to coronary artery). – Stroke (no blood flow to brain). – _______________ ( bulging of artery or vein). – Septal Defect ( septum is not completely closed- “___________________”). a) Plaque and cholesterol • Cholesterol that is deposited on the artery is called ___________. • ________ fats are “bad” because they build up in the artery (found in saturated fats). • _________’s are “good” because they take LDL’s away to the liver (found in fish, etc). b) Atherosclerosis c) Problems with the heart • _____________= chest pains that occur when too little oxygen from the coronary arteries reach the heart. • Treatment: – Drugs to reduce plaque in arteries. – Coronary __________ surgery (used in severe cases, grafts a new vein to the heart around the blockage). Heart must be stopped to do this! 1.5 Immune system • Pathogens (an agent that causes disease) enter the body in many ways: – Protozoans (______________): example – malaria. – Fungi ( mold, etc): example – athlete’s foot. – Bacteria (rapidly reproduce; stopped by antibodies): example – __________. – Viruses (infect host cell and reproduce DNA): example- __________, cold virus. 1) Immune response • 2 lines of defence: – 1st line = primarily _________ (skin, mucous). – 2nd line = within the body (______________ produced). • 1st line: Non-specific Immunity – Barriers: skin mucous, cilia. – ____________: wbc’s engulf the foreign invader (packman)- releases pus. – Fever: raises body temperature to 40° destroy bacteria (at _____ all cells die). 6 a. 1st line : Physical Mainly physical ___________ – protective o Acidic secretions (pH of 3 – 5) Respiratory tract (windpipe) – mucus and cilia sweep foreign material away from lung ________________ – acids and protein digesting enzymes destroy microbes Tears, saliva, mucous secretions – ____________ (enzyme) destroys bacterial cell walls b) 2nd line: specific Immunity • Lymphocytes: produced in bone marrow and seed in _________________. • When a foreign antigen (protein) is present, immune system responds. Foreign cell has different antigen markers than body cells; this ______________________. • Complement proteins (in plasma) activated by foreign microbes, _________ to invader and help phagocytes. • 2 Types: ____________________. 1. B cells • Formed and mature in the ____________. • Each b cell produces a single type of antibody. • Plasma cells can produce up to 2000 antibody molecules/second. • Recognize the foreign antigen and start dividing into 2 groups: 1. ____________: provide life-time immunity. 2. _______________: produce antibodies that stick to antigen and disable the invader. 2. T cells • Formed in bone marrow, mature in ________________________. • Recognize foreign protein on cell membrane and divides into 4 types: 1. Memory cells: Provide lifetime immunity. 2. ___________ cells: secrete cytokines that activate B cells and Killer T-cells. 3. Killer T cells: cytotoxic cells = _________ any infected body cells; destroy mutated cells. Responsible for rejection of organs (transplantation). 4. __________________ T cells: shuts down immune response. c. Antibodies • ______ shaped proteins that target foreign invaders. • Specific to the antigen on the invader. • Each antibody has a complementary shape to it’s antigen; each antibody will only attach to a _______________. • Larger molecule is then engulfed by macrophage (phagocytotic wbc’s). • Invaders can’t access the cells and can’t pass through cell membrane- await death. • Body contains ____________ different antibodies Immune response • Bacteria enters----macrophage attacks ----helper T cells release lymphokine ---____________ activated--- antibodies released --- released into circulatory system. • B cells also activate ____________ cells ---- puncture cell membrane or attack cell membrane of infected cell (by virus)--- kill cells. • Once foreign cells destroyed _______________ T-cell stops immune response---- body maintains antibodies to kill antigen--- ________________ clean debris and tissues repair. 2) Vaccinations • Memory T cells can provide immunity to viruses; you never get sick from the same 1 twice. • Vaccinations are a __________________ ______________ of the virus injected, antibodies are produced and immunity is created. 7 3) Autoimmune Disorders Immune system mistakenly attacks body cells o Renegade lymphocytes treat body’s cells as foreign and attack cells (Usually held in check) o Mutated _____________________. o Theory: suppressors secrete a substance that tells macrophage to engulf renegade cells o Examples: Lupus,_____, Type 1 diabetes, AIDS. Causes Weakening of suppressor T cells: Drugs or serious infections Decline with age Some people are born with defective suppressor T cells Treatment ___________________________ drugs Reduce intensity of renegade cells. 8