* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ce_ch14_e
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
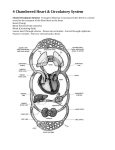
Answers to Continuous Evaluation New Biology — a modern approach 14 The human circulatory system Check your progress 14.1 Why do we need a circulatory system? 14.2 Blood Vessels A. 1. F 2. F 3. T 4. T B. 1. B C. 2. 3. 4. 5. (a) D A C E 1. muscles and elastic fibres 2. lining of wall X: artery Y: vein Z: capillary (b) to withstand the high pressure of blood (c) Valves can be found in Y but not in X. 14.3 The heart 1. (a) A. superior vena cava B. coronary artery C. aorta D. pulmonary artery (b) It carries blood to the heart which supplies the heart with oxygen and nutrients. (c) The blood in C is oxygenated while that in D is deoxygenated. (d) Chamber 1: left atrium/auricle Chamber 3: right atrium/auricle Chamber 2: left ventricle Chamber 4: right ventricle (e) (i) bicuspid valve (ii) tricuspid valve (iii) heart tendon It prevents the valves from being turned inside out. © Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2007 1 New Biology — a modern approach Answers to Continuous Evaluation 2. (a) (b) P: aorta Q: ventricle R: atrium 14.4 Blood circulation in man 1. F 2. 3. 4. T F F 14.5 What is blood? 1. A, B, C, D 2. C, D 3. B 4. D 5. E 6. 7. 8. 9. A A C C 14.6 The functions of mammalian blood 14.7 What is the lymphatic system? 1. C © Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2007 2 New Biology — a modern approach Answers to Continuous Evaluation 2. 3. C A Exam Practice A. Multiple Choice Questions 1. C 2. A 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. C 7. 8. 9. 10. B. D C A A Structured Questions 1. (a) Red blood cells: - without nucleus - biconcave disc-shaped - filled with haemoglobin 2. (Any two) (b) Red blood cells are biconcave disc-shaped. This increases the surface area for diffusion of oxygen. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin which has an affinity for oxygen. (c) Lymphocytes produce antibodies which inactive pathogens. Phagocytes can engulf pathogens like bacteria. (a) The highest blood pressure is recorded in the arteries and the blood pressure fluctuates in the arteries. The blood pressure drops in the capillaries. The blood pressure is the lowest in the veins. (b) The blood pressure fluctuates as a result of alternate contractions and relaxations of (b) 3. White blood cells: - with nucleus - irregular shape - no haemoglobin (d) (a) (b) the heart. High blood pressure at the arterial end forces the fluid out through the capillary walls to body tissues. glucose, amino acids, oxygen (any 2) A - aorta, C - pulmonary veins, E - bicuspid valves, F - heart tendon, H - semilunar valves K - (inferior) vena cava (i) E, H, L (ii) B (iii) C © Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2007 3 Answers to Continuous Evaluation New Biology — a modern approach (iv) K (c) The blood in X has to be pumped to all parts of the body. A thicker muscular wall 5. can create a larger force during contractions which provide a higher pressure for pumping blood. (a) (i) X (ii) Z (iii) Y (iv) X (v) W (b) D - hepatic portal vein D has capillaries at both ends while E has capillaries only at one end. (c) The blood in vessel A contains a higher concentration of CO2 and food but a lower concentration of O2 than that in vessel B. (d) The blood in the renal artery contains more urea, water and oxygen than that in the renal vein. C. 1. STS Connections (a) The blood pressure in the veins is too low to prevent backflow of blood because • the blood in the veins is far away from the effect of the pumping action of the heart. • the blood in the veins has experienced great friction after travelling over a long way (capillary network) which results in the loss of blood pressure. • some fluid is lost from the blood during the formation of tissue fluid. (Any two) (b) The flow of blood in the veins relies on the contraction of skeletal muscles. Loosened muscles do not provide enough power to squeeze blood upward. (c) 1. do regular exercise. 2. control your body weight. 3. avoid long periods of standing (Any two other reasonable answers). 2. (a) to initiate cardiac muscle contraction and start the cardiac cycle. (b) The heart cannot contract properly. If the heart beats arrhythmically, it cannot pump out the blood effectively which may lead to death. (c) The artificial pacemaker is an electronic device which is sensitive to the magnetic field. A strong magnetic field may damage its function and this will put the life of the patients at risk. (d) Contents (3 marks) Organization (1 mark) (Discussion should be related to the ethics of biotechnology application.) © Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2007 4