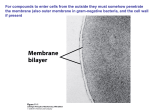
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membranes - buechner
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Name the different types of membranes & their locations in the body. LT9 State names & locations of the ventral cavities’ serous membranes. LT10 MEMBRANES Types of membranes Mucous Serous Synovial Meninges Cutaneous Mucous membranes - location Line interior walls of organs & tubes that open to the outside of the body Digestive tract Respiratory tract Urinary tract Reproductive system Epithelium overlying connective tissue layer Containing goblet cells that secrete mucus Mucous membranes - function Protects interior from invasion (bacteria, viruses) Infection causes increased mucus (runny nose from a cold) Protects walls of stomach & intestine from stomach acid / without it ulcers form Serous membranes Line the ventral body cavities: thoracic & abdominopelvic Parietal Visceral Simple squamous epithelium overlying connective tissue Secretes a watery fluid to keep membranes lubricated Compartmentalizes large thoracic / abdominopelvic & hinders spread of infection Synovial membranes Line joint cavities Composed of connective tissue Secretes synovial fluid into joint cavity to lubricate the ends of the bones Rheumatoid arthritis = inflammation of synovial membrane causing it to grow thicker. Fibrous tissue invades the joint & can become bony restricting movement. Meninges Dorsal cavity membranes Composed of connective tissue Serve as protective coating for the brain & spinal cord Meningitis = serious infection of the meninges Cutaneous membranes Skin! = out covering of body Thin outer layer of stratified squamous epithelium attached to a thicker underlying layer of connective tissue Protection against environmental pathogens & abrasion Names & locations of the ventral cavities’ serous membranes. LT 10 Thorax = pleural & pericardial Lining of thoracic cavity & double back to cover lungs Pleurisy = infection of this membrane Pericardium = sack enclosing heart Pericarditis = infection of this membrane Abdomen = peritoneum & mesentery Mesentery = parietal & visceral come together to support visceral organs Greater omentum – double layered & covers intestines Lesser omentum – runs between stomach & liver Peritonitis – inflammation of peritoneum (happens with appendicitis)