* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current, resistance, and electromotive force
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
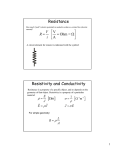
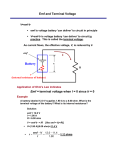
1 Chapter25 Current, resistance and EMF 2 Current • current is the amount of charge flowing through a specific area per unit time. dQ I= , units : 1A = 1C/s (2.1) dt dQ n|q|Avd dt I= = = n|q|Avd , units : 1A = 1C/s (2.2) dt dt n, concentration q, charge of charge carriers vd , drift velocity, the constant average velocity of charge carriers • current density J= I = n|q|vd , A (2.3) Example 25.1 2.1 Resistance • Ohm’s Law ∆V = IR (2.4) • Resistance, unit 1Ω = 1V /A ∆V I L R=ρ A ρ = ρ0 (1 + α(T − T0 )) R= R = R0 (1 + α(T − T0 )) (2.5) (2.6) (2.7) (2.8) ρ is electrical resistivity of materials α is temperature coefficient of resistivity R0 the resistance at reference temperature T0 Good conductor (small resistivity), superconducting For metals, resistance and temperature coefficient of resistivity increases as temperature increasing. 1 2.2 Electrical energy and power • Power unit: Watt, W • Energy unit: 1kW h = 1000W ∗ 3600s = 3.6 × 106 J P = ∆U ∆t (2.9) P = I∆V = I 2 R = ∆V 2 R (2.10) Example A circuit provides a maximum current of 20A at an operating voltage of 120V. (a) how many 75W bulbs can operate with this voltage source? (b) at 12 cents per kilowatt-hour, how much does it cost to operate these bulbs for 8 hours? 2.3 Emf, Electromotive force, ε • Emf is not a force. It describes the influence that makes current flow from low voltage to high voltage. • unit V (Volt) • source of emf: batteries, electric generator, solar cellls, fuel cells • Vab terminal voltage, r internal resistance Vab = ε − Ir Example 25.5 2 (2.11)