* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
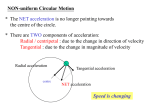
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Review Questions: What are Newton’s first two laws of motion? What does acceleration mean? What happens to objects when they accelerate? What causes objects to accelerate? What would a moving object do if the forces acting on it were balanced? Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) occurs when an object moves at constant speed in a circular pathway. The speed remains constant, but the velocity does not, because the object's direction is always changing (velocity = speed + direction) . Since the direction component of velocity is changing as the object moves in a circle, the object is accelerating. It is called centripetal acceleration (ac), and it measures how quickly the object is changing direction. What causes an object to accelerate??? The unbalanced force (net force) that causes objects to move in a circle is called the centripetal force (FC). The centripetal force is provided by a real force acting on the object, and it pulls or pushes the object toward the center of the circular pathway. The Fc is provided by a real actual force that must be identified for each situation. Fc can be provided by Force of tension (F T), Force of Friction (Ff), Normal Force (FN), or Force of gravity (weight) (Fg). A ball is whirled in a circle on the end of a string. Which direction will the ball go if the string is let go? The direction of the velocity of an object in UCM is always changing and is tangent to the pathway at each moment. Drawing a free body diagram for UCM: Fc always points toward the center of the pathway ac always points toward the center of the pathway velocity is perpendicular to Fc & ac and is tangent to the circular pathway. When object move in circles, they can repeat the same pathway over and over again. One around a circular pathway is called a revolution. The circumference (C = 2πr) is the distance an object travels in one revolution. The period (T) is the time it takes to complete one revolution. The frequency (f) is how much of a revolution is completed per unit time (T = 1/f) and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The velocity can be calculated by dividing the distance (circumference of the circle) by the time (period). So v = 2πr/T v= d t v = 2πr T ac = v2 r Fc = mac How do you calculate the speed of an object moving in Uniform Circular Motion?? Velocity (v) (magnitude only = speed) Acceleration (ac) Centripetal Force (Fc) Practice Problems: 1. A 0.5 kg mass is attached to the end of a 1.5 m string. The mass is whirled in a horizontal circle. The stopper completes each revolution in .5 sec. Find the velocity of the rubber stopper as it moves in a circle. 2. The Barf-with-Bunning ride at Magic Mountain has a radius of 5 m and spins with a period of 3.1 s. What is the speed of the occupants of the ride? What acceleration do they experience? What force does Ben (60 kg) experience as he goes on the ride? (10.1 m/s; 20.4 m/s2; 1224 N) 3. How long does it take for a piece of lettuce to go one time around a salad spinner that has a radius of 0.20 m that is moving at 15 m/s? What is the centripetal force provider? (.08 sec; FN) The Centripetial Force is a center pointing force that causes the object to change direction. Centripetal forces are provided by real forces acting on the object. (FT, Ff, FN, Fg) (The actual force acting on the object that causes it to change direction.) Situation Centripetal Force Provider Object on a string or wire swinging in a circle Object in a circular drum or on a circular track Object going around a curve Object orbiting another object What is the centripetal force provider in each situation? Situation: Observation: What is pushing or pulling the object? (What kind of force is causing the object to change direction?) A ball is tied to a string and twirled in a circle Tetherball on a pole A child swings on amusement park swings A ball rolls around a circular pathway in a wooden hoop A ball rolls around a vertical circular track (like a roller coaster) Salad in a salad spinner Water in a bucket swinging in a circle object on a tray swinging in a circle clothes in a washing machine object on a rotating platform car going around a curve (exit ramp) Children playing on a merry-go-round a satellite orbiting the Earth the moon orbiting the Earth