* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Workshop
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
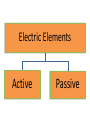
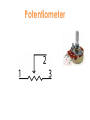
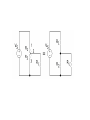
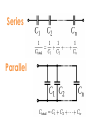
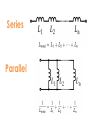
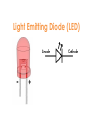
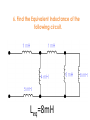
Interactive Engineering Workshop Eng. Mageda Al-Moubarak Eng. Fadia El-ssa Contents • Electric Elements • Instruments Electric Elements Active Passive Active Elements • Active elements are capable of providing an average power greater than zero to external devices, over an infinite period of time. Examples Current source: produces a current in a conductor Voltage source: produces a potential difference between two points. Passive Elements • Passive element is an element of the electrical circuit that Does Not create Power. Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors and diodes are examples of passive elements. Voltage and Current • Voltage: A measure of the work to move a charge. Voltage= Energy/ Charge. • Current: Charge in motion Current= Charge/ Time. • Power = V*I= Energy * Charge = Energy Charge Time Time Resistor • When a voltage V is applied across the terminals of a resistor, a current I will flow through the resistor. • The current is directly proportional to the voltage using ohm’s law I=1*V R Where the slope of the line = 1/R Series Parallel Shorted Resistor Potentiometer Capacitor – Capacitance C, measured in Farads - is an electronic component consisting of a pair of conductors separated by a dielectric (insulator). – When there is a voltage across the conductors, a static electric field develops, that stores finite amount of energy. – Impedance Zc= 1/jωc, Where ω = 2πf. Series Parallel In the capacitor the Current leads the Voltage. Inductor • Inductance L, measured in Henries –Typically an inductor is a conducting wire shaped as a coil. • electric current passing through the inductor creates a magnetic field and thus stores energy. • Impedance ZL= jωL , where ω = 2πf. Series Parallel In the inductor the Voltage leads the Current. CIVIL Diode • A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts electric current in only one direction. • The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction while blocking current in the opposite direction. Light Emitting Diode (LED) Bread Board DMM Power Supply Galvanometer instruments Function Generator Frequency Counter Signal Generator Oscilloscope Power Supply Digital Multi-Meter (DMM) Function Generator Cathode Ray Oscilloscope A. A capacitor can be used like a temporary battery. TRUE B. In an Inductor The Current leads the Voltage. False C. Current is inversely proportional to the voltage. False D. The Impedance of the Capacitor depends on the input’s frequency. TRUE E. A student advised His friend to place the LED as follows False 1. Give 3 ways in which you can have an Equivalent Resistance of 60 KΩ. Given the following resistances, 105 Two 1.2 * Ω 20 K Ω 12 K Ω 50 K Ω potentiometer. 47 K Ω 1KΩ •Two 1.2 * 105 Ω in parallel •20 K Ω and 40 from the 50 K Ω potentiometer in series. •12 K Ω, 47 K Ω, and 1 K Ω in Series. 2.Design a circuit consisting of 2 resistors and a power supply of 9 V, whose Current is 3mA. 3. Using the Following Color Code. What is the value of this resistor? 82000Ω with ±5% 5. How can you discharge a capacitor? Connecting it with a resistor 6. Find the Equivalent Inductance of the following circuit. Leq=8mH A. LED stands for Light Emitting Diode …………………… B. Digital Multi-meter is used to measure Resistance ……………………………, Voltage …………………………, Current and ……………………… C. DC offset Knob is found in an instrument which is Function Generator ………………………… E. To generate a Square Wave. We Should use a(n) Function Generator ………………………………. Given a 10K Potentiometer, and a fixed power supply of 5 V. Draw a circuit to show how you can get 3 V output. 5* R2 = 3V 10K R2= 6KΩ R1=10K-6K=4K Ω