* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Multi-junction solar cell wikipedia , lookup
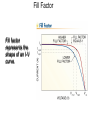
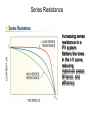
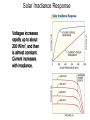
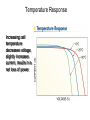
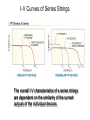
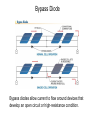
Cells, Modules, and Arrays Photovoltaic Cells Current-Voltage (I-V) Curve Device Response Modules and Arrays Basic Building Blocks The basic building blocks for PV systems include cells, modules, and arrays. Semiconductors Semiconductor materials with special electrical properties can be made by adding small amount of other elements to silicon crystals. Photovoltaic Effect The photovoltaic effect produces free electrons that must travel through conductors in order to recombine with electron voids, or “holes”. PV Material Efficiencies Various PV materials and technologies produce different efficiencies. Monocrystalline Ingots Monocrystalline silicon wafers are sawn from grown cylindrical ingots. Electromagnetic Spectrum Polycrystalline silicon wafers are sawn from cast rectangular ingots. Cell Fabrication Several steps are involved in turning silicon wafers into PV cells. Different PV Cells The different materials, processes, and manufacturing steps produce a range of PV cell types. I-V Curve An I-V curve illustrates the electrical output profile of a PV cell, module, or array. Open-Circuit Voltage Open-circuit voltage is easily measured with a digital multimeter (DMM). Short-Circuit Current Using in-line and clamp-on ammeters are two methods of measuring shortcircuit current. I-V Curve with Power A power against voltage curve clearly shows the maximum power point. Fill Factor Fill factor represents the shape of an I-V curve. Efficiency Efficiency is a measure of how effectively a PV device converts solar power to electrical power. Equivalent Circuit A PV cell can be modeled by a current source in parallel with a diode, with resistance in series and in parallel. Series Resistance Increasing series resistance in a PV system flattens the knee in the I-V curve, reducing maximum power, fill factor, and efficiency. Shunt (Parallel) Resistance Decreasing shunt resistance reduces fill factor and efficiency and lowers maximum voltage, current, and power, but it does not affect short-circuit current. Solar Irradiance Response Voltages increases rapidly up to about 200 W/m2, and then is almost constant. Current increases with irradiance. Temperature Response Increasing cell temperature decreases voltage, slightly increases current, results in a net loss of power. Module Construction Modules are constructed from PV cells surrounded by several layers of protective materials. Arrays of PV Modules An array is a group of PV modules integrated as a single powergenerating unit. Panel from Modules Several modules may be connected together to form a panel, which is installed as a preassembled unit. Junction Box A junction box on the back of a module provides a protected location for electrical connections and diodes. Series Connections of Cells and Modules PV cells or modules are typically connected in series strings to build voltage. I-V Curves of Series Strings The overall I-V characteristics of a series strings are dependent on the similarity of the current outputs of the individual devices. Parallel Connections Strings of PV cells or modules may be connected in parallel to build current. Building an Array Modules are added in series to form strings or panels, which are then combined in parallel to form arrays. I-V Curve for PV Devices in Parallel The overall I-V characteristics of a system of PV devices in parallel are dependent on the similarity of the current outputs of the individual devices. Bypass Diode Bypass diodes allow current to flow around devices that develop an open circuit or high-resistance condition. Breakdown Voltage A bypass diode prevents a large breakdown voltage from allowing a PV device to dissipate a large amount of power. Module Nameplates Module nameplates must include performance ratings for the module and may include other information used to design a PV system. Test Conditions Various test conditions can be used to evaluate module performance and may produce different results.