* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adapting to the Environment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
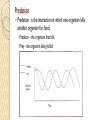
Unit 6 - Change Over Time Adapting to the Environment Adaptation - a behavior or physical characteristic that allow an organism to survive or reproduce in its environment. Environmental Adaptations 15. Behavioral Adaptations 9. Can individual organisms adapt behaviorally? If so, what can cause these changes? Yes! A Behavioral Adaptation is something an animal does - how it acts - usually in response to some type of external stimulus. ◦ Whales migrate to follow the food supply. ◦ Bears hibernate when food sources are depleted (less) each winter. Examples of Some Adaptions Adaptations What is the adaptation? What is this adaptation? 16. Fitness - an organism’s ability to survive and produce offspring. 10. Traits that support successful survival and reproduction in a new environment become _________________ , while those that don’t become _______________ . Plants and animals adapt and change as they respond to their surroundings. 1. What environmental pressures would cause an organism to adapt or change? Drought, loss of habitat, temperature change, flood, volcanic eruption, ? Other examples? 2. Can environmental pressures favor one trait in a species over another? ◦ Yes, amount of fur vs beak size for temperature change. ◦ Other examples? 3. How could that effect a species over time? ◦ Fur may become thicker with colder weather. ◦ Other examples? Many factors influence how organisms change over time. 4. What are the factors that can cause a species to change over time? • Usually the habitat has changed for some reason. Abiotic? Weather, water amount, temperature Biotic? Lack of prey, disease, 5. How do those factors cause changes? Think about your answers to #2 and #3. What examples can you add based on the factors from above? Traits in a Population 6. What might lead to the predominance (greater in number) of certain traits in a population? A change that caused some organisms to survive and reproduce. More fitness! 7. What might lead to the suppression (reduction) of certain traits in a population? A change that causes some organisms to die off and not be able to reproduce. Less fitness! Adapting to the Environment 11. Natural Selection – a process that makes an organism better suited to its environment that becomes common over successive generations in that species ◦ These organisms tend to survive and produce offspring ◦ Offspring inherit these characteristics and pass them on to their offspring over many generations. ◦ Poorly suited characteristics may disappear in the same way. Human Influence on Traits 8. What are some methods humans use to influence certain characteristics of organisms? Artificial Selection (12) – The breeding of plants and animals to produce desirable traits. Organisms with the desired traits, such as size or taste, are artificially mated or crosspollinated with organisms with similar desired traits. Corn has been artificially selected or bred to have more kernels, larger kernels and longer cobs. Human Influence on Traits Selective Breeding (13) – Same as Artificial Selection. Choosing parent organisms with certain traits so that those traits will be passed on to the next generation. Ex., sweet corn, square watermelons, traits in dogs or racing horses, etc. Brain Break FORWARD and BACKWARD CIRCLES 1. Point your arms toward the ceiling. 2. Keep your elbow straight and move your right arm forward creating a large circle. Continue making forward circles with this arm. Now do the same with your other arm except go BACKWARD. Continue with both arms moving at the same time. Make sure you have this pattern working before you continue. 3. While both arms continue to move, lift your right foot off the ground and make a ninety degree angle with your knee. Hold this for a few seconds. 4. Now extend your right knee out to make your leg parallel to the ground. Hold for a few seconds. 5. Stop. 6. Repeat the same process again with your left leg. Cloning Taking DNA from one organism and inserting it into the egg of another organism. This egg is then implanted into a third organism. Dolly the sheep Strawberries Food products Human Influence on Traits Genetic Manipulation (also known as genetic engineering) (14) – Transferring a gene from the DNA of one organism into another in order to produce a desired trait. Ex., cloning, golden rice, insecticide in corn, glow in the dark cats, etc. Artificial Selection Because artificial selection lacks the control of fitness needed to increase fitness, artificial selection can cause problem traits to predominate in a species. For example, Dobermans are a breed of dog that has been bred for a certain appearance. In the process of selecting for this appearance, a genetic defect has increased in frequency in the population. This defect causes narcolepsy, a condition that causes these dogs to uncontrollably fall into deep sleep. Clearly, this condition does not increase the animal's fitness and would be strongly selected against by natural selection. However, since these animals have been subjected to artificial rather than natural selection for generations, the defect has spread in the population. Artificial Selection vs Natural Selection The process of domestication is called artificial selection. Like natural selection, artificial selection acts by allowing differential reproductive success to individuals with different genetically determined traits in order to increase the frequency of desirable traits in the population. However, unlike naturally selected traits, artificially selected traits do not necessarily convey greater fitness. Instead, artificially selected traits are based on what the person breeding the plants and animals desires. These traits, which can range from longer cobs in corn plants to a particular coat color in dogs, are selected for by allowing only individuals that possess the trait to reproduce, while those that lack the trait are prevented from reproducing. Predation Predation is the interaction in which one organism kills another organism for food. ◦ Predator - the organism that kills ◦ Prey - the organism being killed Predator and Prey Effects The effects of predator/prey will change constantly. Look at the graph on page 725 looking at wolves and moose populations. Predators have adaptations that help them hunt more effectively. Prey have adaptations that help them avoid attack. See page 727. Strategies For Animal Survival 1 Animal Video Clip