* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Rules
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
List of works designed with the golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
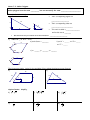
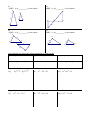
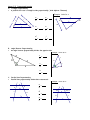
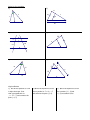
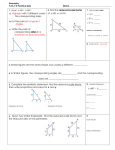
Notes7.1: Solving Ratios and Proportions Ratio: a comparison of two quantities. 3 , 3 to 4, 3:4 4 Proportion: two ratios that are equal to each other. 3 6 4 8 Ex: A scale model of a car is 4 in. long. The actual car is 15 ft long. What is the ratio of the length of the model to the length of the car? Ex: Two cities are 3 1 in. apart on a map with the scale 1 in. = 2 50 mi. Find the actual distance. A. Solving Proportions Fraction bust. Be sure to use FOIL when you are multiplying binomials together Solve for x: 2 3 x 12 1.) 2.) x3 4 2 3 3.) x 1 x 5 2x 3 2x B. Properties of Proportions Complete: 4.) If x 3 , then 7 x ____ 2 7 6.) If a : 2 5 : 3, then 3a ____ 8.) If x y x , then ____ 5 2 y 10.) For the given figure, it is given that: KR = 6, KT = 10, KS = 8 T If 5 3 , then 3x ____ x 2 7.) If x 2 y , then ____ y 9 x 9.) If x y x3 , then ____ 3 4 3 KR KS . Solve for the missing lengths. KT KU RT = ____ K R 5.) SU = ____ KU = ____ S U Notes 7.2: Similar Polygons Similar polygons have the same _________ but not necessarily the same _____________________. Example of similar triangles: B Their corresponding angles are ___________________ 10 6 Y 3 A C 8 X 5 4 Their corresponding sides are _______________________ Z This ratio is called a _______________ and in this case is _______ We show that they are similar with this statement: ___________________ 1.) ABCDE A' B ' C ' D ' E ' b) mA ' _____ , mD _____ a) scale factor = _______ 9 C x 160 mC ' _____ D B 6 c) x = _____, y = ______, z = ______ 100 A E 8y C' y D' 30 2 B' 4 A' E' z The figures are similar. Solve for the variables. (Hint: redraw the diagram as two figures) 2.) 3.) 18 12 12 10 y x x z 8 16 y 9 16 24 Algebra Review: Simplify. 4.) 3 15 5.) 2 8 3 12 6.) 3 5 7.) 3 2 8.) 4 10 2 9.) 5 2 6 2 Notes7.3: Similar Triangles Similar triangles have: ________________ corresponding angles and ______________sides 3 Methods for Proving Triangles Similar: You can conclude that two triangles are similar if: _________: two pairs of corresponding angles are congruent _________: all three pairs of sides are in the same proportion _________: two pairs of sides are the same proportion and their included angles are congruent Are the triangles similar? If so, state the similarity and the postulate you used. Re-draw the triangles in matching positions Mark congruent angles small medium l arg e small medium l arg e Test sides for a constant proportion: Look for these patterns: AA~, SSS~, SAS~ 1.) ABC ~ by _________ or Not Similar F B 35 60 2.) ONP ~ by _________ or Not Similar D O 85 E A N 60 P C M Q 3.) ABC ~ by _________ or Not Similar 4.) ABC ~ by _________ or Not Similar B F E 15 4 4 6 6 F D A 8 B C D 10 C 12 A 5.) QRS ~ by _________ or Not Similar 6.) ABC ~ by _________ or Not Similar R Q B 5 4 Y 10 S 6 8 70 9 X A Y 7.5 70 15 C X 10 Z 6 Z State whether the figures are always, sometimes, or never similar: 7.) two squares 9.) two rectangles 11.) two pentagons 8.) two congruent triangles 12.) two regular octagons 10.) two rhombuses Algebra Review: Factor completely. 13.) 14.) 4 p 4r 3s 2 16 p 2r 3s 4 3x 2 15 x 21 16.) Algebra Review: Solve by factoring. 3x 2 5 x 2 0 17.) 18.) 2 x 2 10 x 28 2 19.) 12 x 7 x 10 2 x3 8 x 2 8 x Notes 7.5: Proportional Lengths A. Triangle Proportionality A parallel slice cuts a triangle’s sides proportionally ( Side-Splitter Theorem) Example: Solve for x a c k j a b , a c a c a , j d k , 12 33 d b 20 x j b B. Angle Bisector Proportionality An angle bisector proportionally divides the opposite side Example: Solve for x: z y x 21 x w 8 14 w z C. Parallel Line Proportionality Parallel lines proportionally divide their transversals Example: Solve for x: a c a b b d d c a c 18 9 24 - x x Solve for the variables: 1.) 2.) 14 24 9 6 x 18 x 4 60 3.) 4.) 20 12 x x 18 21 x+2 5.) 25 6.) 16 3 12 4 x 12 2x 7.5 Algebra Review: 7.) Write the equation of a line in slope intercept form that is perpendicular to y 2 x 5 and contains the point ( -6, 7) 8.) Write the equation of a line that is parallel to 3 x 6 y 5 and contains the point ( 1, 4). 9.) Write the equation of a line that contains ( -2, -3) and ( 4, -9) in standard form.