* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Periodic Table Test Review (3a-3b)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
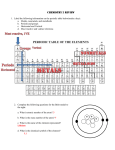
The Periodic Table Test Review (3a-3b) Completion Complete each statement. 1. The ____________________ principle states that a maximum of two electrons may occupy a single atomic orbital, but only if the electrons have opposite spins. 2. The arrangement of electrons in an atom is called the ____________________ of an atom. 3. The group 2A elements are known as ____________________ metals. 4. Elements that have physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals are known as ____________________. Short Answer 5. A student records the following electron configuration for the element Arsenic (As). Evaluate this student’s answer. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p3 6. Explain why it is only possible for two electrons to exist in the same orbital. 7. Use the model of the atom shown to identify the correct element. Write the electron configuration and orbital diagram for this element. 8. Which rule for filling of orbitals by electrons in the element Silicon is being violated in the orbital diagram shown? Justify your answer. 9. Which rule for the filling of orbitals by electrons in the element Magnesium is being violated? Justify your answer. 10. What is the ground state electron configuration of chlorine? 11. Label the blank periodic table with the following terms. A: metalloids B: element with the highest electronegativity C: alkali metals D: lanthanide series E: element with the greatest atomic radius F: noble gases G: halogens 12. Explain the significance of the stair-step line located near the right-hand side of the periodic table 13. Do the figures in this partial periodic table demonstrate the trend in atomic radius, ionic radius, or neither of these? Relate your answer to the structure of atoms across the periodic table. 14. Place these five elements in order of electronegativity, with the highest electronegativity first. 15. State the periodic law. 16. Identify the representative elements from the list given below. Na, Ca, Sc, Co, Ni, Si, N, Se, Cl, Ge 17. Why is argon placed before potassium in the modern periodic table? 18. Why do elements in the same group have similar properties? 19. Why is the size of a sodium ion (Na+) less than that of a sodium atom (Na)? 20. Define ionization energy. 21. Use the periodic table to write the names of the third alkali metal and the first transition metal. Problem 22. Write the ground state electron configuration of sulfur. 23. An element has similar chemical properties as oxygen and selenium. It has an atomic number greater than krypton but less than iodine. Use the periodic table to identify the element. OTHER THINGS TO STUDY: - Chapter 4 Section Reviews - Chapter 4 Vocabulary - Periodic Trends Worksheet - Electron Configuration The Periodic Table Test Review (3a-3b) Answer Section COMPLETION 1. ANS: Pauli exclusion PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 136 OBJ: 5.3.1 Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund's rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation. NAT: B.6 STA: C-3A TOP: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund's rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation. KEY: Pauli exclusion principle MSC: 1 2. ANS: electron configuration PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 135 OBJ: 5.3.1 Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund's rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation. NAT: B.6 STA: C-3D TOP: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund's rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation. KEY: Electron configuration MSC: 1 3. ANS: alkaline earth PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: 4. ANS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 155 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4B Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. Alkaline earth metals MSC: 1 metalloids PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 158 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4A Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. Metalloids MSC: 1 SHORT ANSWER 5. ANS: The “d10” should be preceded by a 3; although the first set of d-block elements are in the fourth period, these electrons are actually contained in the third energy level due to the overlapping of energy levels and orbitals. PTS: 1 STA: C2-1g 6. ANS: DIF: Bloom's Level 6 NAT: UCP.2 | B.1 Electrons have a spin. In any given orbital, only two electrons can exist because one will spin in an “upward” direction while the other one spins in a “downward” direction. A pair of electrons can only exist in an orbital if they are spinning in opposite directions. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 NAT: B.1 STA: C2-1g 7. ANS: The element is Silicon. The electron configuration is 1s2s222p63s23p6. The orbital diagram is shown below. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 5 NAT: UCP.2 | B.1 STA: C-3d 8. ANS: This violates the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons must fill in the orbital with the lowest amount of energy before filling any orbitals with a greater amount of energy. In the diagram shown, electrons are placed in the 3p orbitals before the 3s is filled. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 4 NAT: UCP.2 | B.1 STA: C2-1g 9. ANS: The Pauli exclusion principle is being violated. The Pauli exclusion principle requires that if two electrons occupy the same orbital, they must have opposite spin directions. This is generally shown by having arrows pointing either up or down in the orbital diagrams. Here, the two electrons in the 3s orbital are spinning the same direction, as indicated by the arrows pointing the same direction. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 4 NAT: UCP.2 | B.1 STA: C2-1g 10. ANS: The ground state electron configuration of chlorine is 1s22s22p63s23p5. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 138 OBJ: 5.3.2 Define valence electrons and draw electron-dot structures representing an atom's valence electrons. NAT: B.1 | B.6 STA: C-3D TOP: Define valence electrons and draw electron-dot structures representing an atom's valence electrons. KEY: Valence electrons | Electron configuration MSC: 2 11. ANS: PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 NAT: UCP.2 | B.2 STA: C-4a | C-4c 12. ANS: The stairstep line separates the metals from the nonmetals on the periodic table. Elements that are adjacent to this line are considered metalloids and have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 NAT: UCP.2 | B.2 STA: C-4 13. ANS: These show the atomic radius change. As electrons are added to the outer energy levels of an atom (as one moves across the periodic table), the size of the atom decreases. This is because the additional positive charge in the nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly and no additional shielding effect occurs across the period. PTS: 1 STA: C-4c 14. ANS: B, D, C, E, A DIF: Bloom's Level 4 NAT: UCP.2 | B.1 | B.2 PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 4 NAT: UCP.2 | B.2 STA: C-4c 15. ANS: The periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 153 OBJ: 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. NAT: G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4C TOP: Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. KEY: Periodic table MSC: 1 16. ANS: Na, Ca, N, Si, Se, Cl, Ge PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 154 OBJ: 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. NAT: G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4C TOP: Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. KEY: Metals MSC: 2 17. ANS: In the modern periodic table, the elements are placed in the order of their increasing atomic numbers. The atomic number of argon is 18 while the atomic number of potassium is 19. Therefore, argon is placed before potassium in the modern periodic table. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 153 OBJ: 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. NAT: G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4C TOP: Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. KEY: Atomic number MSC: 2 18. ANS: Elements in the same group have the same electron configuration and number of valence electrons. Valence electrons determine the properties of elements. Therefore, properties of elements in the same group are similar. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 159 OBJ: 6.2.1 Explain why elements in the same group have similar properties. NAT: UCP.1 | B.1 | B.2 STA: C-4C TOP: Explain why elements in the same group have similar properties. KEY: Groups | Electron configuration MSC: 2 19. ANS: The loss of an electron from a sodium atom results in a smaller radius. The electrostatic repulsion between the remaining number of electrons decreases thus allowing them to be pulled closer to the nucleus. Therefore, the size of a sodium ion (Na+) is less than that of a sodium atom (Na). PTS: 1 DIF: 2 REF: Page 165 OBJ: 6.3.2 Relate period and group trends in atomic radii to electron configuration. NAT: UCP.1 | B.1 | B.2 STA: C-4C TOP: Relate period and group trends in atomic radii to electron configuration. KEY: Atomic size | Ionic radius MSC: 2 20. ANS: Ionization energy of an atom is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 167 OBJ: 6.3.1 Compare period and group trends of several properties. NAT: UCP.1 | B.2 STA: C-4C TOP: Compare period and group trends of several properties. KEY: Ionization energy MSC: 1 21. ANS: Potassium is the third alkali metal and scandium is the first transition metal in the periodic table. PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: PROBLEM 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 156 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4B Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. Alkali metals | Transition metals MSC: 1 22. ANS: The ground state electron configuration of sulfur is [Ne]3s23p4. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 REF: Page 138 OBJ: 5.3.2 Define valence electrons and draw electron-dot structures representing an atom's valence electrons. NAT: B.1 | B.6 STA: C-3E TOP: Define valence electrons and draw electron-dot structures representing an atom's valence electrons. KEY: Electron-dot structure | Valence electrons MSC: 3 23. ANS: Tellurium PTS: 1 DIF: 1 REF: Page 157 OBJ: 6.1.1 Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. NAT: G.3 | B.1 | UCP.1 STA: C-4A TOP: Trace the development and identify key features of the periodic table. KEY: Periodic table MSC: 2 NOT: Elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers. Elements in groups have similar properties.