* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angina - History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
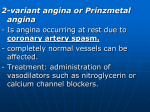
Angina - History Chest Pain - Site classically behind sternum sometimes left chest rarely right chest very rarely back - Radiation left arm commonest right arm sometimes both arms sometimes throat, chin back of neck occasionally epigastrium rarely back rarely sometimes pain reverses - starts in left wrist and radiates back to chest sometimes pain in left arm without chest pain - Character of pain gripping, squeezing, crushing, constricting "like vice/tight band" less convincing: ache, pressure, cramping, heaviness arm pain: lifelessness, deadness, uselessness - Duration of pain angina - lasts 5-10mins once causative factor removed never a few seconds, never hours If it lasts for hours - coronary spasm, MI (prinzmetal's angina, rest angina, unstable angina) Precipitating factors - exertion (most important factor) - mental stress, emotion, cold wind, heavy metal Relieving factors - stopping exertion - glyceryl trinitrate - response in 1-2mins Associated symptoms - 'choking' in the throat (highly suggestive of angina) - 'strangling' and 'suffocation' (also highly suggestive) - breathlessness (transient LVF) - dizziness (could be anxiety - syncope (rare) belching at end of attack Examination May be no abnormal physical signs - Signs of arteriosclerosis retina-arteriolar narrowing and a-v nipping systolic murmur over carotid artery hypertension thickened radial artery arcus senilis (premature arteriosclerosis) xanthelasma (hyperlipidaemia) tortuous brachial artery systolic murmur over abdominal aorta reduced femoral pulse with murmur over vessel absent foot pulses - Signs of hyperlipidaemia xanthelasma arcus senilis xanthomata (tendons, skin extensor surfaces) Differential diagnosis Functional pain (left mammary or inframammary stabbing, or continuous ache, lasts seconds, hours, days. Unrelated to exertion, anxiety symptoms, local tenderness in chest wall) Pleuritic pain (localised to one side. Sharp, stabbing, knife-like. Worse on inspiration and coughing. Associated phlegm -purulent (infection), -blood (embolism). Pleural rub on auscultation) Hiatus hernia (retrosternal burning pain. Worse on bending, lying down, after a heavy meal. Associated with heart burn) Peptic ulcer (epigastric and lower sternal pain, deep gnawing pain, related to meals, relieved by alkalis, may be associated with vomiting which relieves the pain, epigastric tenderness) Pericarditis (retrosternal pain, worse on lying, better on standing or sitting up, worse with inspiration and coughing. May hear pericardial rub) Cervical spondylosis (upper chest pain, involves shoulders and arms, unrelated to exertion. Worse with movements of neck. Often crepitus on moving head) Investigations ECG - during attacks - ST depression or symmetrical T wave inversion. T wave inversion in V1 - V3 indicates critical left anterior descending coronary artery stenosis. May show old MI or left ventricular hypertrophy Exercise ECG contraindicated in unstable angina, recent MI (7days), severe aortic stenosis, severe pulmonary hypertension, significant rhythm disturbances relative contraindications: infirmity and ataxia Positive test - 1mm of J point depression (junction of ST and T wave) (False +ve's : hyperventilation, digoxin and other anti-arrhythmics, hypokalaemia, hypertension, valvular heart disease, left ventricular hypertrophy and pre-excitation syndromes) terminate test if BP falls, VT or if patient becomes pale (peripheral circulatory collapse) relative contraindications for termination: ST depression >4mm, incoordination, paroxysmal rhythm disturbances (other than VT) ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY Assess ventricular function and localise areas of ventricular wall involvement. In angina (no infarction) may be normal Exercise or pharmacological stress echo can detect 'hibernating' myocardium i.e. areas with decreased blood flow. NUCLEAR IMAGING Assess myocardial structure and function. Thallium is injected during exercise - serial x-rays 'Cold spot' that recovers on rest = angina Fixed cold spot = infarction CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY + CARDIAC CATHETERISATION Determine exact coronary anatomy and decide further management Reserved for - angina resistant to medical therapy - strongly +ve exercise test (indicates poor prognosis - unstable angina - persisting angina after MI Mortality from procedure 1 in 1000 Complications : Haemorrhage at site of arterial puncture Emboli - leading to MI Stroke Arrhythmias Coronary artery dissection Infection Treatment General measures - explain and reassure - evaluate risk factors (stop smoking, lose weight, diet) - avoid cold weather, emotion - encourage exercise within limits Drugs - Aspirin - consider Statins - GTN for acute attacks - Prophylactic treatment if regular attacks: ß-blockers (reduce sympathetic tone - negatively inotropic, reduces myocardial contractility/ - negatively chronotropic, decreases heart rate. Reduced Oxygen demand, improve perfusion - longer diastole, more time for coronary blood to flow) contra-indications : asthma, peripheral vascular disease with skin ulceration. 2nd or 3rd degree heart block. Atenolol 50-100mg/day Metoprolol 25-50mg TDS Nitrates: peripheral vasodilation, increases venous return and decreases ventricular volume. Decreased distension of heart wall and decreased Oxygen demand. Sublingual GTN acts for ~30mins ISMN 10-60mg BD slow release ISMN 60-120mg OD adverse effects: headaches, flushing, hypotension, rarely fainting Calcium channel blockers - peripheral arteriolar dilatation - reduced afterload Dihydropyridines (nifedipine) can cause reflex tachycardia, always give with ß-blocker Slow release Nifedipine 10-40mg BD Diltiazem has -ve inotropic and chronotropic effects, careful monitoring if on ß-blockers Verapamil if ß-blockers contraindicated Contraindicated in heart block and heart failure Side-effects - constipation dihydropyridines - headaches, flushing, dizziness, gravitational oedema Potassium Channel Activators - arterial and venous dilation Nicorandil 10-30mg BD side effects : headache, flushing, nausea, vomiting, dizziness Unstable Angina