* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5-HIV-Pharmacotherapy-Update-2016-no
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
HIV vaccine wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of HIV-protease inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
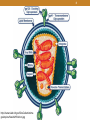
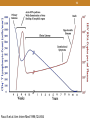
1 HIV Pharmacotherapy Focused Update Drew Lambert, PharmD [email protected] Husson University School of Pharmacy 2 I have no conflicts of interest. • However, I will be using brand names extensively during the presentation 1. Majority of the drugs used are brand-only 2. Easier to say 3 Objectives • Identify and describe new antiretroviral therapies • Review most recent HIV guidelines • Choose an appropriate antiretroviral regimen 4 Definitions • HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus • AIDS – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome • ARV – Antiretroviral • ART – Antiretroviral Therapy • HAART – Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy • NRTI – Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor • NNRTI – Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor • PI – Protease Inhibitor • INSTI – Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor 5 Quick Stats • About 1.2 million infected with HIV in the US • 1 of every 265 people • ~13% undiagnosed (down from ~20% previously) • ~50,000 new cases per year in the US (2013) • ~14,000 deaths per year in the US (2012) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Results of the Expanded HIV Testing Initiative--25 jurisdictions, United States, 2007-2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. Jun 24 2011;60(24):805-810. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/statistics/overview/ataglance.html 6 7 8 http://www.niaid.nih.gov/SiteCollectionIma ges/topics/hivaids/HIVvirion.jpg 9 Pathophysiology • HIV attacks cells expressing the CD4+ receptor (CD4+ or CD4 cells) • T-helper cells • Normal range is 500-1600 cells/mm3 (CD4 count) • 40-70% of total lymphocytes • New viruses bud off from the cell and enter the bloodstream • The number of copies of HIV RNA per mL is known as viral load 10 Fauci A et al. Ann Intern Med 1996;124:654 12 13 HIV vs. AIDS • Patients may be infected with HIV but not have AIDS • Stage 1 – CD4 count ≥500 cells/mm3 or CD4% ≥29 • Stage 2 – CD4 count 200-499 cells/mm3 or CD4% 14-28 • AIDS • Stage 3 – CD4 count <200 or CD4% <14 OR • AIDS defining illness • Only seen with severe immunodeficiency 14 New Drug Approvals All FDA approved drugs: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/education-materials/factsheets/19/58/fda-approved-hiv-medicines 15 Stribild – August 2012 • Elvitegravir 150mg + cobicistat 150mg + emtricitabine 200mg + tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300mg • INSTI based single tablet regimen • Common adverse events • Nausea and diarrhea • Take with food • Take antacids 2 hours before or after Stribild 16 Tivicay – August 2013 • Dolutegravir 50mg daily • Increase to 50mg twice daily when given with UGT1A1 inducers (e.g., rifampin, efavirenz, fosamprenavir, tipranavir) or with INSTI resistance • 2nd generation INSTI • Common adverse effects • Headache, insomnia, fatigue • No food effects • Take 2 hours prior or 6 hours after antacids 17 Triumeq – August 2014 • Dolutegravir 50mg + abacavir 600mg + lamivudine 300mg • Integrase inhibitor based single tablet regimen • 2nd generation INSTI • Only combination with abacavir/lamivudine NRTI backbone 18 Tybost – September 2014 • Cobicistat (cobi) 150mg daily • Pharmacokinetic booster (3A4 inhibitor) approved to be used in combination with • Darunavir 800mg daily • Atazanavir 300mg daily • Elvitegravir 150mg as part of Stribild or Genvoya • Not active against HIV • Inhibits creatinine excretion but does not change GFR 19 Vitetka – September 2014 • Elvitegravir 85mg or 150mg 20 Vitetka – September 2014 • Must be given with ritonavir boosted protease inhibitors • Take with food • Diarrhea is the most common adverse event • Avoid with CYP 3A4 inducers • No data yet on taking it with… 21 Protease inhibitor + booster combinations - January 2015 Prezcobix Evotaz • Atazanavir (Reyataz) • Darunavir (Prezista) 300mg + cobicistat (Tybost) 150mg 800mg + cobicistat (Tybost) 150mg • Both approved for use in combination with other ARV drugs • Previously approved to be boosted with ritonavir • Take with food • Metabolic ADRs (diabetes, fat redistribution, dyslipidemia) 22 Genvoya – November 2015 • Elvitegravir 150mg + cobicistat 150mg + emtricitabine 200mg + tenofovir alafenamide 10mg • INSTI based single tablet regimen • Similar to Stribild • Disoproxil fumarate 300mg • Nausea is most common ADR • Take with food 23 Odefsey – March 2016 • Rilpivirine 25mg + emtricitabine 200mg + tenofovir alafenamide 25mg • NNRTI based single tablet regimen • Similar to Complera • Disoproxil fumarate 300mg • Take with food • Depression, insomnia, headache, nausea are common 24 Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) vs. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) • TDF conversion to tenofovir occurs mainly in the plasma; TAF conversion occurs intracellularly • Plasma levels 91% lower; intracellular levels 4.1x higher • Less serum creatinine increase • Less effects on BMD • Less proteinuria • Less renal dysfunction • Same price • More comparison studies are ongoing Genvoya – A New 4-Drug Combination for HIV. The Medical Letter. 2016;15(1488):19-21. 25 Guidelines (OLD) DRUGS Drug Class & Individual Agent Overview Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors Protease Inhibitors Integrase strand transfer inhibitors 26 2007 1987 CCR-5 Antagonists & Integrase Inhibitors Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors 2003 Fusion Inhibitors 1995 Protease Inhibitors 1996 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors July 12, 2006: Atripla approved 27 NRTIs Generic Abbreviation Brand ABC Ziagen Didanosine* ddI Videx (EC) Emtricitabine FTC Emtriva Lamivudine* 3TC Epivir Tenofovir TDF Viread Stavudine* d4T Zerit Zidovudine* AZT or ZDV Retrovir Abacavir* * – generic (tablet dosage form) 28 Mechanism of Action and notes • Nucleoside/nucleotide analogs • Stop reverse transcriptase because of replacement of 3’ end • Actively compete with endogenous substrates • Mimic different bases • Choose two that mimic different base pairs • Require phosphorylation for activation • Generally renal elimination • Form the backbone for HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) 29 Class Adverse Reactions • Headache • N/V/D • Rash • Lipoatrophy—primarily caused by the thymidine analogs zidovudine and stavudine • Fatty liver • Lactic acidosis 30 Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors • Abacavir (Ziagen, ABC) • 600mg once daily or 300mg BID • Must test for HLA-B*5701 because of possible hypersensitivity reaction • May have higher rates of failure in individuals with an viral load of >100,000 copies/mL • Zidovudine (Retrovir, AZT or ZDV) • 300mg BID • Possible anemias and fatigue • Renal dose adjustments with CrCl <15mL/min • Bone marrow suppression • Fingernail Hyperpigmentation 31 Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors • Emtricitabine (Emtriva, FTC) • 200mg daily • May cause skin discoloration • Generally well tolerated • Active against HBV • Lamivudine (Epivir, 3TC) • 300mg daily • Generally well tolerated • Active against HBV 32 http://www.odermatol.com/wp-content/uploads/figure%201aj.jpg 33 Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors • Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread, TDF) • 300mg daily • NucleoTIDE reverse transcriptase inhibitor • Possible decreases in BMD • Fairly well tolerated • Activity against HBV • May cause renal dysfunction • Dose adjustments needed for CrCL <50mL/min, <30mL/min, and is not recommended with CrCl <10 unless receiving hemodialysis 34 NRTI Combinations • Combivir* • Epivir (lamivudine) and Retrovir (zidovudine) • Epzicom • Epivir (lamivudine) and Ziagen (abacavir) • Trizivir* • Epivir (lamivudine), Retrovir (zidovudine), and Ziagen (abacavir) • Truvada • Emtriva (emtricitabine) and Viread (tenofovir disoproxil) * – generic (tablet dosage form) 35 NNRTIs Generic Abbreviation Brand Delavirdine DLV Rescriptor Nevirapine* NVP Viramune (XR) Efavirenz EFV Sustiva Etravirine** ETV Intelence Rilpivirine** RPV Edurant * – generic ** – second generation NNRTI 36 Mechanism of Action and notes • Inhibit reverse transcriptase directly • Does not require activation • Low genetic barrier to resistance • Single mutation can cause resistance to multiple drugs • Second generation NNRTIs have a higher barrier to resistance • Come in single tablet combinations • Metabolized by and induce CYP 3A4 37 Adverse Reactions • Rash (including SJS) • N/V/D • Increased LFTs • Other drug-specific adverse reactions • Newer NNRTIs are better tolerated 38 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors • Efavirenz (Sustiva, EFV) • 600mg daily • Do not use in moderate to severe hepatic impairment • Pregnancy class D • CNS adverse effects • Depression • Insomnia/abnormal dreams or nightmares • Dizziness • May give a false positive test for marijuana • Generally given at bedtime • Available as a combination tablet 39 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors • Rilpivirine (Edurant, RPV) • 25mg daily • Should be taken with food • Higher barrier to resistance • More virologic failures as compared to efavirenz in patients with a viral load of >100,000 copies/mm3 • Depressive disorders • Contraindicated with CYP 3A4 inducers and PPIs • Only NNRTI to not inhibit or induce CYP enzymes • Available as a combination tablet • Not studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment 40 NNRTI Combinations • Atripla – 600/200/300mg • Sustiva (efavirenz), Emtriva (emtricitabine), Viread (tenofovir) • Sustiva (efavirenz), Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir) • Complera – 200/25/300mg • Emtriva (emtricitabine), Edurant (rilpivirine), Viread (tenofovir) • Edurant (rilpivirine), Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir) • Odefsey – 200/25/25mg • Edurant (rilpivirine), Emtriva (emtricitabine), tenofovir alafenamide 41 PIs Generic Ritonavir Indinavir Abbreviation RTV IDV Brand Norvir Crixivan Nelfinavir Saquinavir Tipranavir Fosamprenavir NFV SQV TPV FPV Viracept Invirase Aptivus Lexiva Lopinavir/r Darunavir Atazanavir LPV/r DRV ATV Kaletra Prezista Reyataz No generics 42 Mechanism of Action and notes • Inhibit HIV protease enzyme, which cleaves polyproteins into mature, active proteins. This results in production of immature, non-infections virus particles. • Occurs post-translation, so PIs are active in acutely and chronically infected cells • High barrier to resistance • Strong CYP 3A4 inhibitors • Many drug interactions • Most require pharmacokinetic “boosting” with ritonavir or cobicistat 43 Acosta, EP. Pharmacokinetic enhancement of protease inhibitors. JAIDS. 2002;29:S11-18. 44 Adverse Effects • Most increase cholesterol and triglycerides • Lipodystrophy • Diabetes and insulin resistance • Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS) • N/V/D • Abdominal pain • Elevated LFTs 45 What is the difference between lipoatrophy and lipodystrophy? • In lipoatrophy, there is wasting of the subcutaneous fat, often accompanied by an increase in triglycerides. This occurs most commonly with the NRTIs, specifically stavudine and didanosine. • In lipodystrophy, there is accumulation of visceral fat. This occurs most commonly with the protease inhibitors. 46 Protease Inhibitors • Ritonavir (Norvir, RTV) • Used to boost other PIs—100mg with each dose of the other protease inhibitor • Available as tablets and capsules—tablets much more palatable • Tingling or numbness of the hands or feet, or around the mouth 47 Protease Inhibitors • Atazanavir (Reyataz, ATV) • 300mg daily boosted, or 400mg daily unboosted • Use boosted regimen when given with tenofovir or in treatment experienced patients • Take with food • Least metabolic side effects of the PI class • Dizziness and lightheadedness • Jaundice • Total bilirubin will likely increase, and can be a marker of adherence • PR prolongation • Interaction with PPIs and acid-decreasing agents 48 Protease Inhibitors • Darunavir (Prezista, DRV) • 800mg daily boosted with ritonavir for treatment naïve patients, 600mg BID boosted for treatment experienced • Take with food • Very high barrier to resistance • Not recommended in severe liver disease • Less metabolic side effects than older PIs • Possible rash on initiation 49 PI Combinations • Evotaz – 300mg/150mg • Reyataz (atazanavir) + Tybost (cobicistat) • Prezcobix – 800mg/150mg • Prezista (darunavir) + Tybost (cobicistat) • Kaletra – 800mg/200mg • Lopinavir/ritonavir • Lopinavir not available separately • NOT single tablet regimens 50 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs) Generic Raltegravir Elvitegravir* Abbreviation RAL EVG Brand Isentress Vitekta Dolutegravir* DTG Tivicay * – Second generation No generics 51 Mechanism of Action and notes • Inhibits HIV integrase, which integrates the viral DNA into the host cell’s DNA • Lower barrier to resistance than the PIs • Adverse Reactions • Generally well tolerated • N/D • Headache • Elevated LFTs 52 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs) • Raltegravir (Isentress, RAL) • 400mg BID • No food requirements • No renal dose adjustments • Not studied in severe hepatic impairment • Metabolized by UGT1A1 mediated glucuronidation • 800mg twice daily with rifampin • Increased total bilirubin • Elevated CK – myopathy and rhabdomyolysis 53 INSTIs Combinations • Stribild - 150/150/300/200mg daily • Elvitegravir/cobicistat/tenofovir/emtricitabine (EVG/cobi/TDF/FTC) • Genvoya - 150/150/10/200mg daily • Elvitegravir/cobicistat/tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (EVG/cobi/TAF/FTC) • Triumeq - 50/600/300mg • Dolutegravir/abacavir/lamivudine (DTG/ABC/3TC) 54 HIV TREATMENT GUIDELINES 55 Treatment Goals • Suppression of HIV viral load • Undetectable - <50 copies/mL or the lower limit of detection (some assays detect a few as 20 copies/mL) • “The goal of ART is to suppress HIV replication to a level where drug-resistance mutations do not emerge.” • Preserve and restore immunologic function • Reduce morbidity and prolong survival • Prevent HIV transmission • Improve quality of life Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 59 Antiretroviral Treatment (ART) • Current standard is minimum of 3 drug regimen • Typically two (or more) classes • Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents convened by the Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) 60 Who and When to Initiate ART • “ART is recommended for all HIV-infected individuals…” • Especially in • History of AIDS-defining illness (including opportunistic • • • • • infections) Pregnancy HIV-associated nephropathy Hepatitis B & C coinfection Low CD4+ counts Acute HIV infection Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf 61 Why initiate ART immediately? • Decreased risk of death • START and TEMPRANO Trials • Higher CD4 count (>500 cells/mm3) • Higher incidence of 1 year viral suppression • Lower viral load = decreased risk of transmission • Public health benefit INSIGHT START Study Group. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(9):795-807. TEMPRANO ANRS Study Group, Danel C, Moh R, et al. A trial of early antiretrovirals and isoniazid preventive therapy in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(9):808-822. 62 Starting HAART <12 months after seroconversion improves immune health • Median CD4 count in uninfected patients is 900 cells/mm3 • 38.4% of patients beginning HAART <12 months after seroconversion achieved this • 28.3% of patients beginning HAART >12 months after seroconversion achieved this • Better overall immune health • Fewer patients progressed to AIDS Okulicz, Jason F., et al. "Influence of the Timing of Antiretroviral Therapy on the Potential for Normalization of Immune Status in Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1–Infected Individuals." JAMA internal medicine 175.1 (2015): 88-99. 65 Recommended Regimens for All Treatment Naïve Patients (6 regimens) NRTI Backbone Combination drug Darunavir/r Emtricitabine + Tenofovir (TDF) Class PI Raltegravir Elvitegravir/cobi* Dolutegravir Emtricitabine + Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) Elvitegravir/cobi* Abacavir + Lamivudine Dolutegravir* INSTI * – Available as a single tablet regimen Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. Recommended Regimens for Treatment Naïve Patients • Stribild ………………. 70 mL/min minimum • Triumeq …………….. 50 mL/min minimum • Genvoya…………… 30 mL/min minimum • Prezista + Norvir + Dose adjust <50mL/min for Truvada only Truvada • Tivicay + Truvada • Isentress + Truvada Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 67 Alternative Regimens for Treatment Naïve Patients NRTI Backbone Combination drug Efavirenz* Rilpivirine* Emtricitabine + Tenofovir (TDF) Class NNRTI Atazanavir/r Atazanavir/cobi** Darunavir/cobi** Abacavir + Lamivudine PI Darunavir/r Darunavir/cobi** * - Available as a single tablet regimen ** - Co-formulated Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. AIDSInfo. Recommendation on Integrase Inhibitor Use in Antiretroviral Treatment-Naive HIV-Infected Individuals from the HHS Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Dec. 30, 2013. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/upload/AdultARV_INSTIRecommendations.pdf. 68 Other Regimens for Treatment Naïve Patients NRTI Backbone Abacavir + Lamivudine Emtricitabine + Tenofovir Lamivudine NONE Combination drug Raltegravir Class INSTI Efavirenz* Atazanavir/r* Atazanavir/cobi* Lopinavir/r NNRTI PI Lopinavir/r Lopinavir/r Darunavir/r + Raltegravir* PI + INSTI * - Viral load <100,000 copies/mL (and CD4+ >200 for DRV/RAL) Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 69 Regimen Notes • Patients receiving any regimen with abacavir must be HLA-B*5701 negative • Patients receiving a regimen with cobicistat and TDF must have a pre-treatment CrCl ≥70 mL/min • Patients must have a viral load <100,000 when initiating Complera (RPV/FTC/TDF) and the 2 other regimens noted in the Other Regimens slide Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 70 Regimen Notes • Emtricitabine/tenofovir (Truvada) and abacavir/lamivudine (Epzicom) are the preferred NRTI backbones • No CCR5 antagonists or fusion inhibitors are Recommended, Alternative, or Other regimens • There are a total of 6 single tablet regimens; 3 are preferred • Genvoya, Triumeq, Stribild • Other 3 are alternatives • Atripla, Complera, Odefsey (anticipated by me) Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 71 Regimen Notes • Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate – use with caution in patients with renal insufficiency • Efavirenz is teratogenic; do not include in regimens for women who may become pregnant • Atazanavir should not be used with >20mg of omeprazole (or equivalent PPI dose). Administer ATV >12 hours after a dose of a PPI Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. 72 Regimen Notes • Rilpivirine is not recommended in patients with a viral load > 100,000 copies/mL • PPIs are contraindicated with RPV • Do not start EVG/cobi/TDF/FTC (Stribild) in patients with CrCl <70mL/min • Change regimen if CrCl falls below 50mL/min • EVG/cobi/TAF/FTC (Genvoya) may be used in all patients with CrCl >30mL/min 73 Choosing a Regimen • Least adverse effects • INSTI-based • Durability • PI-based • Drug interactions • INSTI based (usually) • Single tablet regimen • INSTI- or NNRTI-based 74 Emphasize Benefits of Therapy • Reduces AIDS-related complications • Prolongation of disease-free survival • Viral suppression • Preservation of immune function • Decreased risk of disease transmission • Reduction of HIV-associated nephropathy, cardiovascular disease, malignancies, neurocognitive decline DHHS Guidelines: Adults & Adolescents. Feb 12, 2013 75 Interventions to Improve Adherence • Delivery of prescriptions • Often disadvantaged populations • Automatic refills • Paying for medications • Ryan White programs • PAPs • Other state and federal programs • Dealing with insurance issues to ensure there is not a lapse in therapy 76 XY is a 45 year old patient newly diagnosed with HIV. His CD4+ count is 373 cells/mm3 and viral load is 210,794 copies/mL. He also has CKD with a CrCl of 40mL/min. What is the only first line single tablet regimen recommended for XY? A. Genvoya B. Atripla C. Triumeq D. Stribild E. Complera 77 Which of the following Patients with HIV should begin therapy? A. 16 year old pregnant female with a CD4 count of B. C. D. E. 797 cells/mm3 and a viral load of 7,384 copies/mL 26 year old otherwise healthy male with a CD4 count of 797 cells/mm3 and a viral load of 984 copies/mL 36 year old female with Kaposi’s sarcoma and a CD4 count of 77 cells/mm3 and a viral load of 797,384 copies/mL 51 year old male with diabetes and a CD4 count of 501 cells/mm3 and a viral load of 97,384 copies/mL All of these patients should begin therapy 78 Which set of the following drugs all contain the pharmacokinetic booster cobicistat (Tybost®)? A. Prezista, Stribild, and Tivicay, Vitekta B. Evotaz, Prezista, Tivicay, Vitekta C. Genvoya, Kaletra, Prezcobix, Triumeq D. Evotaz, Genvoya, Prezcobix, Stribild E. Prezcobix, Triumeq, Tivicay, Vitekta 79 Summary & Questions? • Many new therapies are available which give new options to patients seeking alternatives • All patients should be treated regardless of CD4+ count or viral load • Regimens should be individualized based on specific patient parameters • Adherence • Drug interactions • Adverse effects • Durability 80 Resources • AIDSinfo • http://www.aidsinfo.nih.gov • Guidelines and other resources • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) • http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/ • Fact sheets, slide sets, testing and surveillance • World Health Organization • http://www.who.int/topics/hiv_aids/en/ • International data, facts and statistics • Positively Aware • http://positivelyaware.com/ • Annual HIV Drug Guide and other resources