* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System and Heart Circulatory System is composed
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
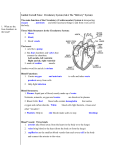
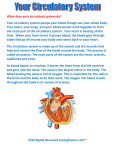
The Circulatory System and Heart Circulatory System is composed of the Cardiovascular System and Lymphatic System o It transports blood and lymph through the body of organisms to distribute nutrients and remove waste o Moves blood to a site where it can be oxygenated & wastes to a site where they can be disposed of. The heart functions as the pump of the circulatory system 1) Systematic Loop: blood circulates into the body’s systems, bringing oxygen to all its organs; collects carbon dioxide and waste; controlled by left side of the heart 2) Pulmonary Loop: the blood circulates to and from a respiratory surface to release carbon dioxide and pick up new oxygen; controlled by the right side of the heart Animals with multiple layers of cells are unable to obtain nutrients by simply exchanging materials with their environment through diffusion, so they need a circulatory system to ensure nutrients reach all cells. This circulatory system needs a heart to power it. Features of the heart the circulatory system depends upon to function: 1) Arteries, capillaries, and respiratory surface 2) Veins, valves, and skeletal muscle contractions 3) Lymphatic System How Organisms without Hearts accomplish Circulation o Unicellular organisms can exchange nutrients directly with their environment by diffusion; the cell surface is the point of exchange with the environment Eg. Bacteria o Plants absorb water and nutrients through their roots. Xylem is vascular tissue that transports water and minerals up from the roots and phloem transports sugar molecules, amino acids, and hormones. They are propelled up the plant by the forces of osmotic potential and water pressure. Eg. Flowers o Animals with gastrovascular cavities have two cell layers. The inner layer has direct access to nutrients by diffusion and the second layer is close enough that the nutrients can diffuse into them also so a circulatory system is not needed. Eg. Hydra Evolutionary Trends of the Heart o Simplest heart is a muscular tube with a rhythmic pump o Fishes contain two chambers in their hearts, one atrium and two ventricles o Amphibians and reptiles have hearts with two atria and one ventricle o Mammals and birds have hearts with two ventricles and two atria o Arthropods and molluscs have an open circulatory system o Earthworms, squids, octopuses, and vertebrates have a closed circulatory system o The evolution of double circulation, a divided ventricle, and a closed system increases the efficiency of the heart Lungs, and the skin of animals that use their skin as respiratory surface, have a dense net of capillaries just under the epithelium. Carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange take place in the capillary vessels, which have alveoli that hold the gases. The respiratory surface (skin or lungs) must remain moist in order for exchange to occur. The skin does not have as much surface area as lungs do so animals that use their skin to obtain oxygen usually have lungs as well. The Circulatory System Depends on Other Systems o Respiratory o Digestive o Excretory Disease Atherosclerosis Aortic Aneurysm Description Plaque builds up in the arteries, causing them to become narrow. Platelets adhere to the inside of the arteries and can cause clotting. When the aorta is damaged it will bulge and eventually tear, causing severe internal bleeding. Cause A diet high in LDL , fat , and calcium. Symptoms Occasional chest pain Weakness could be present at birth or caused by Atherosclerosis, obesity, or high blood pressure. Chest pain, heart murmur, hoarseness, trouble breathing or swallowing. Treatment Avoid smoking, exercise regularly, and eat a balanced diet. The condition cannot be reversed but progression can be slowed or prevented. Medicine may be able to slow the growth of the aneurysm, but surgery might be necessary.