* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adult and Fetal circulation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
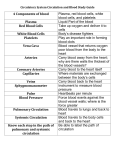
Adult and Fetal circulation Circulation 3. Anastomoses and Collateral Circulation The Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation 1/3 Adult and Fetal circulation circulation the input heart of pumps with the each other. blood beat. into The two closed circuits circuits are arranged –streams, the systemic in series: circulation The output and the of one pulmonary becomes The left side of the heart is the pump for the systemic circulation; bright From which gases tissues. venule. systemic the red, are occur Venules In arteries veins. aorta, supplied oxygen-rich most at capillary Ultimately the cases, carry that by blood carry the deoxygenated blood blood bed pulmonary the ittwo level. from to flows blood all into the Blood organs through flows blood circulation. separate lungs. unloads back of away only the The to one body In from left oxygen the systemic capillary ventricle right –tissues except entering atrium. tissues, and picks ejects and for progressively then merge the the up this exchange alveoli carbon enters left blood to atrium form of a dioxide into of smaller the systemic larger receives nutrients the lungs, aorta. and right side of heart is the pump for the pulmonary circulation; red, ventricle artery deoxygenated plunges into the into pulmonary the blood medial returning arteries surface from that of the carry a lung systemic itoccurs and to the then circulation. right divides and left into Blood lungs. several itthe ejected receives Each from pulmonary all the right dark lobar arteries I. branching delicate oxygenated form freshly heart. Within the oxygenated air the pulmonary arteries sacs blood lung, (the the lung enters become blood veins lobar alveoli). venules flows -divides superior arterioles arteries Gas into and branch four and exchange and progressively pulmonary inferior finally along -the with that veins pulmonary larger exit across the and bronchi. the veins. these medial return capillaries The As capillaries, to aspect largest they that left decrease of venous surround atrium and each newly lung. in tributaries offrom size, the The the Fetal Circulation 2/3 Adult and Fetal circulation Prenatally vessels placenta are (before constricted, to the birth) fetus the therefore, by the umbilical in essentially fetus, vein. Itblood oxygenated, then nonfunctioning nutrient-rich to the (deflated) inferior blood and vena isthe cava carried pulmonary by way venosus (a inferior temporary vena cava, fetal vessel the blood connecting enters the the right umbilical atrium, vein and to then the inferior passes vena through cava). From the foramen ovale into The upper portion lungs. right the aorta extremities The of left atrium, this pumps major atrium moderately which fraction this and and oxygen-rich head pumps from of oxygenated itlungs the there flows itneck), deoxygenated down itare blood through moves to blood towards the down another right flows the to ventricle. into the small upper ispasses retuned left fetal pulmonary From ventricle extremities via the that right arteries and the superior pumps ventricle, head. to vena itthe From into only deflated cava the the afrom aorta. small intoof ductus arteriosus (remaining well connecting the output) in reoxygenation. part the great oxygenated of descending the vessels blood body. the pulmonary The from blood With of aorta head the this throughout passes ascending and kind trunk 35% of into toarrangement the the of aorta the into the prenatal arch umbilical the blood enters of aorta. aorta the life. supplies arteries quickly Only at descending athe point athe and developing small rest lying isvessel, returned volume aorta. ofthe just the brain below About viscera (10% to of the the 65% the of and placenta the emergence fetus of the cardiac the receives inferior for blood Circulatory Changes Occurring After Birth Important placenta (foramen bypass Their the ceases ovale, circulatory developing ductus and remnants adjustments the liver venosus infant’s and inofthe lungs and lungs occur adult ductus close expand atform birth and arteriosus) are (inflate) when cease the the and to that circulation function begin permitted to asof function. they much fetalare blood of The no the more through three blood required. shunts to the fossa ovalis, side ofnonfunctional the interatrial septum, present on the right atrial venosum seen over the inferior surface the liver, and arteriosum ,ligamentum present between the under surface of the arch of aorta and the pulmonary trunk. proceed to Circulation 5. Atherosclerosis and Aneurysms 3/3