* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Improving patient enablement and continuity of care in South Glos
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
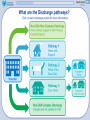
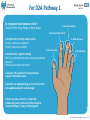
Purpose: To create a culture of patient enablement in hospital, through enhancing professional and organizational interfaces and education. Cathy Yuill Emma Ellis Hazel Lamb Jo Skeets IPECC Project Overview (HE SW) Acute Hospital Patient Enablement Trusted Assessment and Interface Shared DecisionMaking Aim: Create an enhanced culture of patient enablement to maintain functional skills and independence throughout an individual’s acute stay in hospital. Aim: Develop a trusted assessment process and interface between Nursing, Occupational Therapy, Physiotherapy and Social Work. Aim: Improve the interface and continuity of care between hospital and community therapy and Social Care services. Functional Laminate Discharge E-Learning Practice-Based Teaching Health Coaching Enablement E-Learning Practice-Based Enablement Training Purpose: To create a model of practice-based teaching of enablement for Health Care Assistants working on the acute wards. What is enablement? Enablement is supporting people, not by doing things for them, but by working in partnership with them and encouraging them to be as independent as possible. Why Enablement? • Prevent complications associated with deconditioning – the vicious cycle! Muscle Weakness Chest infections Pressure Sores Increase risk of falls Reduced Confidence • Improved patient participation and experience both in hospital and surrounding discharge. Practice Based Enablement Teaching • Piloted on two wards. • Meetings with HCA’s to identify learning needs. • Practice-based teaching on the ward with ‘real’ patients. • Role modelling/Lead by example. • Demonstration of competence. Measurement • Pre- and post-training evaluation • Before and after observation of HCA practice. • Rated against behaviours that promote enablement. • Survey Monkey questionnaire before and after. Summary Results: HCA Enablement Training on 9B 59.64% increase in enabling indicators sustained. Baseline TOTAL (mean average - max 3) In Summary: Enablement Behaviour Increased 0 – No evidence observed. 1 – Evidence observed less than 50% of the time. 2 – Evidence observed 50-75% of the time. 3 – Evidence observed over 75% of the time. Before Training 1.43 After Training 2.57 One Month On 2.29 Percentage Increase 59.64% Feedback From Staff • - I feel much more confident to encourage people (I am less afraid that they will fall). • - I feel confident to explain to the patient about the importance of enablement …. to speak to my colleagues about enablement and the importance of it.” (ward 9B) • “I have learnt that it is important to give patients a chance to do things for themselves, it helps them for when they leave and it builds their confidence” (ward 9A) Health Coaching: ‘Enabling Conversations’ Purpose: Implemented practical training of the health coaching framework, with a focus on Stroke Services. Current Training as part of Health Coaching Pilot • Health Coaching training provided to Therapists, Nurses and HCAs on pilot wards. • 2-day basic training + 2-day accreditation training. • Portfolio development required for accreditation. • Develop a ‘train-the-trainer’ programme using a small group of clinicians who received this Health Coaching training. • Further staff receive health coaching training. When patients see a clinician, their consultation may not be working • Only a third to a half of patients comply with prescribed medications and 10% with lifestyle advice. • Only 60% of patients feel they are sufficiently involved in their care. • Bennett H, Coleman E, Parry C, Bodenheimer, 2010 • KPMG Creating value with patients, carers and communities 2014 • GMC Annual report 2013, • Rhoades DR, Fam Med 2001. • Wolever R, 2013 • Coulter A, 2011 • Not all clinicians are trained in behaviour change. Am I being effective? What is health coaching? Helping patients gain the knowledge, skills, tools and confidence to become active participants in their care, so that they can reach their self-identified health goals Bodenheimer, 2010 Next Steps • Developing a ‘roll-out plan’ to begin to embed a coaching culture within the Trust, using the ‘Train-the-Trainer’ Health Coaching of staff • Developing a process of evaluation (linking with AHSN and UWE re possible research across the stroke pathway) • Linking with the ‘Patient Activation Measure’ • Linking with the STP in BNSSG, with alignment to MECC (Making Every Contact Count) Enablement E-Learning Purpose: Development of an e-learning training programme on patient enablement. This is interactive, and includes photographs and practical video clips. It brings together all enablement information gathered as part of the IPECC project. The Functional Laminate Pilot Ward 32a Purpose: To pilot the development of a Patient Functional Laminate on an acute ward for older people. Feedback from staff and patients • Link therapist reported that communication about patient function between HCA staff and therapy staff has improved. • HCA staff reported the laminates were useful in caring for patients providing they were up to date. • Patients have been agreeable to have their functional information on the whiteboard. One patient consented to the laminate “if it helped”. Another patient commented “if it helps me get out of hospital quicker”. Discharge E-Learning: Home is Best! Purpose: Developed a Discharge E-Learning Training Programme for acute clinical (and applicable to relevant non-clinical) staff © Learning and Development, August 2016 © Learning and Development, August 2016 © Learning and Development, August 2016 © Learning and Development, August 2016 For D2A Pathway 1 Is my patient safe between visits? Count off the 5 key things to think about. 3. Access toileting 2. Access meds & food Consider their mobility and function. Do they need any equipment? Do they have help at home? 4. Wash & dress 1. Access drink 5. Call for help Consider their cognitive ability. Will they understand the need to do these activities at home? Will they remember to do them? Consider if the patient had any previous support with these areas. Consider any safeguarding concerns that need to be addressed prior to discharge. If you have any concerns, contact the community team to discuss if Discharge to Assess Pathway 1 can provide support. © Learning and Development, August 2016 © Learning and Development, August 2016 © Learning and Development, August 2016 Project Risks and Issues • Trust limitations and delays (e.g. winter pressures) • Engagement of staff • Time constraints due to trying to implement in a busy acute hospital • More detailed documentation to support patient enablement • Funding to continue the Health Coaching Co-Delivery training and roll-out of the ‘Enabling Conversations’ training • Roll-out and continuation of each aspect of the project © Learning and Development, August 2016 Any Questions?