* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an Optical Internet?
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
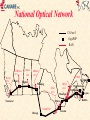
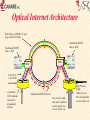
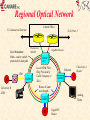
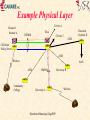
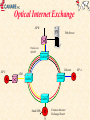
CANARIE Inc “Canada’s National Optical Internet” September 1998 http://www.canet2.net [email protected] http://www.canarie.ca Tel: +1.450.671.8539 CA*net 3 World’s first national optical Internet First Internet network built from the ground up to support Internet first, voice second All existing Internet networks are built on technology originally designed for voice - e.g. SDH/SONET & ATM Consortium members include Nortel, Newbridge, Cambrian, CISCO, Bell, etc Key features: use of individual DWDM wavelengths directly coupled to routers Use intrinsic self healing capabilities of Internet and eliminate SDH/SONET and ATM layers MPLS for layer 3 restoral, protection and traffic engineering National Optical Network CA*net 3 GigaPOP RAN WURCnet OC3 SRnet MRnet DS3 OC12 ACORN BCnet OC3 Calgary Regina RISQ Winnipeg ONet OC48 OC12 Montreal Ottawa Vancouver STAR TAP Chicago Toronto St. John’s Charlottetown Fredericton Teleglobe Halifax What is an Optical Internet? WDM fibers where individual wavelengths are the link layer interconnect directly connected to routers via Optical ADM (Add Drop Mux) or WDM coupler High Performance Router acts as the main switching routing device Bypass or cut-thru connections via dedicated wavelengths SONET or Gigabit Ethernet framing (also 10xGbE) Use intrinsic self healing nature of Internet for redundancy and protection (don’t require SONET/SDH layer) Traffic engineering and network management done via MPLS Network design optimized for unique characteristics of Internet traffic Why build an Optical Internet? Dramatic growth in IP traffic ISPs are already starting to deploy OC-48 IP networks Customers are starting to order OC-12 IP local loops How soon before we need OC-192 or OC-768 IP?? Future trends indicate IP growth will continue IP telephony could be very, very big New Internet 2 and CA*net 2 applications Internet characteristics significantly different than traditional telecommunications traffic If IP is the dominant traffic then optimize network design for IP CA*net 3 will be world’s first network designed from the ground up to carry first and foremost, Internet traffic Relative Load Traffic Growth 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 Data is 23x Voice Traffic Data Data is 5x Voice Traffic Voice 1990 Source:Lightwave April 1998 1995 2000 Year 2005 The real driver for Optical Internet Traditional OC-48 SDH/SONET network costs about $US 4000 - $5000 km per year before overhead, engineering and maintenance 20 year amortization on fiber and installation 5 year amortization on optical amps, regen, SONET Mux, etc Optical Internet with today’s technology costs about $US 500$750 per kilometer per year With low cost regen (e.g.10xGbE), low dispersion fiber, and long range optical amplifiers optical Internet will cost $US 100 - $200 per km per year Optical Internet also has significantly less overhead, engineering and maintenance costs. see Engineering paper http://www.canet2.net for financial analysis Opportunity for Canada World leader in SONET/optical networking - JDS Fitel, Nortel, Cambrian, Positron Fiber Systems, CISCO Canada, PMC Sierra, QNX Over 75% of the world’s Internet traffic is carried on equipment made in Canada CISCO GSR12000 SONET I/F made in Ontario -95% market Nortel Optical Transport made in Montreal - 75% market Newbridge ATM switches made in Ottawa - 50% market JDS Fitel optical components made in Ottawa -85% market Possibility of leveraging our technology and leadership to increase export opportunities and job growth in this area A network for basic research unparalleled anywhere in the world Acceptable Use Policy Same AUP as CA*net 2 Any Canadian organization that is doing high performance meritorious research or applications development that cannot be carried out on the commercial Internet CA*net 3 will only interconnect GigaPOPs One GigaPOP per province plus Ottawa - others may be added GigaPOPs interconnect to regional high speed networks Same Tier A/B/C policy as C2 Allows CA*net 3 to peer with similar international research networks like Abilene, vBNS, etc All institutions must maintain separate commercial Internet connection National IP/WDM Network Edmonton Additional OC-192 WDM Routes for future use Saskatoon 4/BLSR Winnipeg Calgary Ottawa Regina Montreal 4/BLSR Vancouver Charlettown St. John’s 4/BLSR Fredericton - CANARIE Drop Site Chicago 8 Wavelengths per route 4 reserved for traditional SONET 4/BLSR by carrier Teleglobe Toronto Halifax CANARIE OC-192 Route CANARIE OC-48 Route Optical Internet Architecture Both sides of 4/BLSR 1:1 span ring used for IP traffic Traditional SONET Mux or DCS Traditional SONET Mux or DCS WDM WDM 3 0C-48 Tx 2 OC-48 Rx Asymmetric Tx/Rx lambdas that can be dynamically altered Traditional SONET Restoral Low priority traffic that can be buffered or have packet loss in case of fiber cut High Priority Traffic Cannot exceed 50% of bandwidth in case of fiber cut Layer 3 Restoral IP network is intrinsically self healing via routing protocols By cranking down timers on interface cards and keep alive message time-out we can achieve same restoral speed as SONET Biggest delay is re-calculation and announcement of changes in routing tables across the network MPLS promises to simply the problem maintain a set of attributes for restoral and optimization may provide a consistent management interface over all transport services WDM, SONET/SDH, ATM, Frame Relay, etc Layer 3 restoral allows for more intelligent restoral can use a hybrid mix of restoral and protection circuits Can use QoS to prioritize customers and services Only UDP packets (e.g telephony) require fast restoral allows simultaneous use of both working and protection circuits Regional Optical Network Central Office To Commercial Internet Dual Redundant Paths - can be switch protected or dual path To CA*net 3 Packet over SONET ATM OADM University B ATM GigaBit Ethernet OADM OXC? Local WDM Fiber Ring Provided by Cable Company or Telco Ethernet University A Router OADM Reuse of same wavelength Analog Video OADM GigaPOP Router Example Physical Layer Research Institute A CA*net 2 DWDM Research Institute B Telco CA*net 3 ATM CSI Route Policy Server ATM Wireless RAN ATM Community College DWDM University A Distributed Municipal GigaPOP University B Wireless Example IP Layer AS ##1 AS ##2 CA*net 2 Institutional GigaPOP Regional GigaPOP Telco CA*net 3 PNNI X.x.x.x/ iBGP CSI Route Policy Server X.x.x.x/ iBGP RAN X.x.x.x/ eBGP OSPF Wireless OSPF University B OSPF X.x.x.x/ X.x.x.x/ Intermediate Cache Community College X.x.x.x/ University A Wireless High School or CAP site BGP Confederation ### AS ##3 Distributed GigaPOP Daughter Cache x.x.x.x/ Optical Internet Exchange ISP B Web Server Packet over SONET OADM ISP C Ethernet ATM OADM OADM OADM Small ISPs Common Internet Exchange Router ISP A Optical Internet Exchange Logical Diagram ISP B Web Farm ISP C ISP A Common Internet Exchange Router Small ISPs Gigabit Ethernet Framing Gigabit Ethernet Framing advantages frame size = packet size therefore packet switching and SAR more efficient and easier to implement data format consistent with LAN format with no translation low cost tributary service - do not need to terminate link on a router or SONET DCS equipment new 10xGigabit Ethernet will equal OC-192 standard SNMP MIBs, but not accessible by out of band interoperable standard from many vendors No scrambling sync or packet loss Gigabit Ethernet Framing disadvantages not very efficient with 8B/10B block coding new 10xGigabit Ethernet may use more efficient coding No standard out of band management or monitoring But some WDM suppliers provide this SONET Framing SONET framing advantages well established jitter specifications out of band management systems can be used in SONET networks for fast restoral and protection very high efficiency - over 98% SONET framing disadvantages no interoperable standard SAR processing more complex as there can be multiple packets per frame, or packets can cross frame boundaries tributary services require SONET mux services no well established carrier network management protocols for fault detection and location, especially on long haul when SONET used in independent links Future Optical Internet Integrated Transport Services Different Protocol Stacks Integrated to provide different size bandwidth pipes and CoS ATM/IP Network IP SONET Network ADM ADM IP/ATM Network OXC IP SONET Network HDWDM OC-3084 ADM OXC ADM OXC OADM OADM IP Optical Network IP over ATM QoS & VPNs up to OC3 IP Sonet OC3, OC12, OC48 IP Optical Greater than OC-48 Future Optical Internet MPLS as common management layer ATM VCs ATM VCs SONET LSP SONET LSP DWDM LSP IP over ATM QoS & VPNs up to OC3 IP Sonet OC3, OC12 IP Optical OC-48, OC-192