* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangle Inequality Theorem
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Systolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
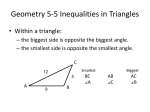
Triangle Inequalities 1 Triangle Inequality The smallest side is across from the smallest angle. A is thesmallest angle, BC is thesmallest side. The largest angle is across from the largest side. B is the largest angle, AC is the largest side. B 89 54 C 37 A 2 Triangle Inequality – examples… For the triangle, list the angles in order from least to greatest measure. B A AB is the smallest side C smallest angle. C 5 cm BC is thelargest side Ais the largest angle. Angles in order from least to greatest C , B, A 3 Checkpoint: Use Inequalities in a Triangle If one side of a triangle is longer than the other side, then the angle opposite the longest side A is _______ larger than the angle opposite the shorter side. B 8 5 C AB BC , so m ___ C m ___ A . Use Inequalities in a Triangle B If one angle of a triangle is larger than another angle, then the side opposite the larger angle 50o A is _______ longer than the side mA opposite the smaller angle. 30o C m C, so ____ BC ____ AB . Use Inequalities in a Triangle Example 1 Write measurements in order from least to greatest Write measurements of the triangle in order from least to greatest. a. C b. 36o B 57o E 22 87o A 13 F D 12 Solution a. m ____ ____ A C m B m ____ BC AB AC ____ Use Inequalities in a Triangle Example 1 Write measurements in order from least to greatest Write measurements of the triangle in order from least to greatest. a. C b. 36o B 57o E 22 87o A 13 F D 12 Solution b. m ____ ____ F E m D m ____ DF EF ____ DE Use Inequalities in a Triangle Checkpoint. Write the measurements of the triangle in order from least to greatest. B 99o 1. A 34o 47o C mA m C m B BC AB AC Use Inequalities in a Triangle Checkpoint. Write the measurements of the triangle in order from least to greatest. Q 80o 2. P 45o 55o R mP mR mQ QR PQ PR Triangle Inequality – examples… For the triangle, list the sides in order from shortest to longest measure. (7x + 8) ° + (7x + 6 ) ° + (8x – 10 ) ° = 180° B (8x-10)◦ 22 x + 4 = 180 ° 22x = 176 m<C = 7x + 8 = 64 ° X=8 m<A = 7x + 6 = 62 ° 54 ° m<B = 8x – 10 = 54 ° A B is the smallest angle AC shortest side. 62 ° (7x+6)◦ 64 ° C (7x+8)◦ C is the largest angle AB is thelongest side. Sides in order from smallest to longest AC , BC , AB 10 Use Inequalities in a Triangle Triangle Inequality Theorem The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is A greater than the length of the third side. ___ AB ___ BC AC AC ___ BC ___ AB ___ BC AB AC ___ B C Triangle Inequality Theorem: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side. B a+b>c a c a+c>b b+c>a A C b Example: Determine if it is possible to draw a triangle with side measures 12, 11, and 17. 12 + 11 > 17 Yes Therefore a triangle can be drawn. 11 + 17 > 12 Yes 12 + 17 > 11 Yes 12 Finding the range of the third side: Since the third side cannot be larger than the other two added together, we find the maximum value by adding the two sides. Since the third side and the smallest side cannot be larger than the other side, we find the minimum value by subtracting the two sides. Example: Given a triangle with sides of length 3 and 8, find the range of possible values for the third side. The maximum value (if x is the largest The minimum value (if x is not that largest side of the triangle) 3+8>x side of the ∆) 8–3>x 11 > x 5> x Range of the third side is 5 < x < 11. 13 Use Inequalities in a Triangle Example 2 Find possible side lengths A triangle has one side of length 14 and another of length 10. Describe the possible lengths of the third side. Solution Let x represent the length of the third side. Draw diagrams to help visualize the small and large values of x. Then use the Triangle Inequality Theorem to write and solve inequalities. Small values of x 14 x 10 x 10 __ 14 __ x __ 4 Large values of x x 10 14 __ 14 __ x 10 __ 24 24 x , or x __ The length of the third side must be _______________________________. greater than 4 and less than 24 Use Inequalities in a Triangle Checkpoint. Complete the following exercise 3. A triangle has one side 23 meters and another of 17 meters. Describe the possible lengths of the third side. Small values of x Large values of x 23 x x 17 x 17 23 x6 17 23 17 23 x 40 x , or x 40 The length of the third side must be greater than 6 meters or less than 40 meters Use Inequalities in a Triangle Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two non adjacent interior angles. 3 2 1 m1 m2 m3 Use Inequalities in a Triangle Example 3 Relate exterior and interior angles Solution B and C are nonadjacen t interior angles to 1. B So, by the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem, m1 60 70 m1 130 70 1 A o 60 o C Use Inequalities in a Triangle Checkpoint. Complete the following exercise Find the measure of angle 1. B 38 1 o C 112 A o m1 150 o