* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.4 Asexual Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
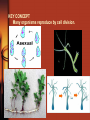
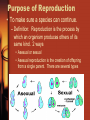
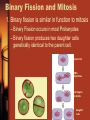
5.4 Asexual Reproduction Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division Mr. Shilala DAHS KEY CONCEPT Many organisms reproduce by cell division. Purpose of Reproduction • To make sure a species can continue. – Definition: Reproduction is the process by which an organism produces others of its same kind. 2 ways • Asexual or sexual • Asexual reproduction is the creation of offspring from a single parent. There are several types Binary Fission and Mitosis 1. Binary fission is similar in function to mitosis – Binary Fission occurs in most Prokaryotes – Binary fission produces two daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell. parent cell DNA duplicates cell begins to divide daughter cells Binary Fission and Mitosis • Prokaryotes have no nucleus but do have DNA – DNA in the shape of single circular chromosome – Chromosome copied and attached to cell wall – When cell is twice as large membrane pinches inward – cytokinesis – Cell wall forms Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction • Environment determines what form of reproduction is most advantageous. – Advantages of Asexual reproduction • Favorable in environments that don’t change much. • Can be more efficient – Disadvantages • In environments that do change, identical offspring respond the same to changes in environment • Extinction can occur if genetic variation is needed – Sexual reproduction • Increases genetic diversity • 1 or more individual may survive change • Asexual reproduction itself is not more efficient, rather the associated costs of sexual reproduction are greater – Example • Two organisms each have 10 offspring • 1 reproduces asexually – All 10 can have offspring of their own • The other 1 reproduces sexually – 5 males and 5 females are produced – Only females can bear offspring – Must attract a mate » Involves energy, signals, and behaviors Some eukaryotes reproduce through mitosis. • Budding – Forms a new organism from a small projection growing on the surface of the parent. – Very common in plants Hydra bud Yeast • Fragmentation – Splitting of the parent into pieces that each grow into a new organism. – Sea Stars and Flatworms • Vegetative reproduction – Forms a new plant from the modification of a stem or underground structure on the parent plant – Sometimes referred to as cloning – Strawberries and potatoes • Regeneration – The ability to restore lost or damaged tissues, organs or limbs. – It is a common feature in invertebrates, like worms and starfish.