* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SIMM (single in-line memory module)
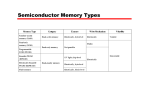
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
1 WHAT IS RAM? RAM is our working memory storage. All the data, which the PC uses and works with during operation, are stored here. Data are stored on drives, typically the hard drive. However, for the CPU to work with those data, they must be read into the working memory storage, which is made up of RAM chips. 2 RAM TYPES The traditional RAM type is DRAM (dynamic RAM). The other type is SRAM (static RAM). SRAM continues to remember its content, while DRAM must be refreshed every few milliseconds. DRAM consists of micro capacitors, while SRAM consists of off/on switches. SRAM can respond much faster than DRAM. DRAM is by far the cheapest to build. 3 DRAM TYPES FPM (Fast Page Mode) ECC (Error Correcting Code) EDO (Extended Data Output) SDRAM (Synchron Data RAM) 4 SD RAM DDR SDRAM (double data rate SDRAM) is synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM) that can theoretically improve memory clock speed to at least 200 MHz*. It activates output on both the rising and falling edge of the system clock rather than on just the rising edge, potentially doubling output. It's expected that a number of Socket 7 chipset makers will support this form of SDRAM. 5 RDRAM Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory (RDRAM) is a memory subsystem that promises to transfer up to 1.6 billion bytes per second. Rambus is intended to replace the current main memory technology of dynamic random access memory (DRAM). These are having much faster data transfer rates 6 RAM SPEEDS RAM speed is measured in ns (nano seconds). The fewer ns, the faster is the RAM 7 RAM MODULES RAM is installed on SIMM or DIMM modules SIMM (single in-line memory module) DIMM (Dual in-line memory module) 8 SIMM A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a module containing one or several random access memory (RAM) chips on a small circuit board with pins that connect to the computermotherboard. SIMMs typically come with a 32 data bit. The memory chips on a SIMM are typically dynamic RAM (DRAM) chips. SIMM were common from the early 1980s to the late 1990s. 9 DIMM A DIMM (dual in-line memory module) is a double SIMM (single in-line memory module). Like a SIMM, it's a module containing one or several random access memory ( RAM ) chips on a small circuit board with pins that connect it to the computer motherboard . A DIMM has a 168-pin connector and supports 64bit data transfer. It is considered likely that future computers will standardize on the DIMM. SIMM and DIMM are very similar, except that DIMM have electrical contacts on each side of the module, while the contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant. 10 RIMM RIMM = RDRAM In-line Memory Module. RIMMs are obsolete, and were only used by very few Intel Pentium 3 based motherboards, and early Pentium 4 motherboards. Its performance was good, But they were over 3 times the cost of similar SD Ram (DIMM) ram sticks. 11 BIOS A special kind of program is required to enable the CPU to talk to other devices A ROM chip stores these programs These programs are collectively known as the Basic Input/Output Service (BIOS) Programs stored on ROM chips are known as firmware Programs stored on erasable media are called software 12 BIOS (BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT SYSTEM) BIOS (basic input/output system) is the program a personal computer's microprocessor uses to get the computer system started after you turn it on. It also manages data flow between the computer's operating system and attached devices such as the hard disk , video adapter, keyboard , mouse , and printer . BIOS is theoretically always the intermediary between the microprocessor and I/O device control information and data flow 13 CMOS CMOS RAM, CMOS is short for Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor. CMOS is an on-board semiconductor chip powered by a CMOS battery inside computers that stores information such as the system time and date and the system hardware settings for your computer. 14 FLASH ROM Flash ROM is a new type of ROM chip developed by Intel It can be reprogrammed without the chip being removed Running a small command line program combined with an update file can change or update the BIOS 15 POST (POWER-ON SELF-TEST) When power is turned on, POST is the diagnostic testing sequence that a computer's basic input/output system runs to determine if the computer keyboard random access memory, disk drives, and other hardware are working properly. If the necessary hardware is detected and found to be operating properly, the computer begins to boot. If the hardware is not detected or is found not to be operating properly, the BIOS issues an error message which may be text on the display screen and/or a series of coded beeps, depending on the nature of the problem. 16 PORTS The term port can refer to either physical or virtual connection points. Physical network ports allow connecting cables to computers, routers, modems and other peripheral devices. 17 SERIAL PORT (COM PORT) A serial port enables external modems to connect to a PC or network router via a serial cable. The term "serial" signifies that data sent in one direction always travels over a single wire within the cable. It is in RS-232 standard. These serial ports and cables are the same used for PC keyboards and other computer peripheral devices 18 LPT PORT A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers for connecting peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface. It is also known as a printer port LPT (line print terminal) is the usual designation for a parallel port connection to a printer or other device on a personal computer. Most PCs come with one or two LPT connections designated as LPT1 and LPT2. 19 USB PORT (UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS) A USB port is a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronic devices to be connected via cables to a computer USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, an industry standard for short-distance digital data communications. USB allows data to be transferred between devices. USB ports can also supply electric power across the cable to devices without their own power source. 20 EISA (EXTENDED INDUSTRY STANDARD ARCHITECTURE) EISA is a standard bus (computer interconnection) architecture that extends the ISA standard to a 32-bit interface. 21 VESA VESA Local Bus (sometimes called the VESA VL bus) is a standard interface between your computer and its expansion slot that provides faster data flow between the devices controlled by the expansion cards and your computer's microprocessor. 22 ACCELERATED GRAPHICS PORT (AGP) Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is an interface specification that enables 3-D graphics to display quickly on ordinary personal computers. AGP is designed to convey 3-D images (for example, from Web sites or CD-ROMs) much more quickly and smoothly than is possible today on any computer other than an expensive graphics workstation. It is especially useful in conjunction with gaming, threedimensional (3D) video, and sophisticated scientific/engineering graphics programs. 23 PC CARD A PC Card (previously known as a PCMCIA card) is a credit card size memory or I/O device that fits into a personal computer, usually a notebook or laptop computer. Probably the most common use of a PC Card is the telecommunications modem for notebook computers. There are 16-binary digit and 32-bit (CardBus) varieties of PC Cards. Another type of PC card is theZV port Card. 24 25