* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
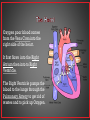
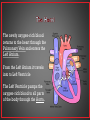
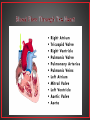
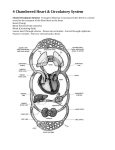
• The human circulatory system consists of the heart, a series of blood vessels, and the blood that flows through them. • The circulatory system helps transport fluids throughout the body which helps it obtain oxygen, nutrients and to remove wastes. • Distributes and delivers materials around an organism • Supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients so that they can perform • Carries hormones to appropriate destinations in body • Maintains body temperature • Protects the body from infection • Has ability to clot – when tissue is broken – internally and externally • There are 3 types of blood vessels • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries • Blood vessels that carries blood away from the heart. • Have thick elastic walls made of connective tissue and smooth muscle • Blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart. • Veins have one-way valves that keep blood moving towards the heart • The flow of blood in veins is also helped by skeletal muscles. • Microscopic blood vessel that connects arteries and veins • Walls of the capillaries are only one cell thick • Nutrients and oxygen diffuse into body cells through the thin capillary walls • Waste materials and carbon dioxide diffuse from body cells to the capillaries • Every minute your heart beats 70 – 80 times • Every minute your heart pumps 5 liters ( 2 ½ bottles of soda) of blood • The heart is made up of four chambers. • The two upper chambers are the Atria (Atrium single), which receive blood. • The two lower chambers are the Ventricles, which pump blood out. Oxygen poor blood comes from the Vena Cava into the right side of the heart. It first flows into the Right Atrium then into to Right Ventricle. The Right Ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs through the Pulmonary Artery to get rid of wastes and to pick up Oxygen. The newly oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart through the Pulmonary Vein and enters the Left Atrium. From the Left Atrium it travels into to Left Ventricle The Left Ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body through the Aorta. • Pulmonary – circulation of blood between heart and lungs. • Systemic – circulation of blood between heart and all of the systems of the body. • Fatty deposits build up on the arterial walls. • Eating foods high in cholesterol and saturated fats can cause these deposits to form. • This can occur in any artery in the body. If it occurs in a coronary artery it can cause a heart attack. • To fix this problem, open heart surgery may be needed. • Also known as High Blood Pressure • Places extra strain on the heart • The heart must work harder to keep blood flowing • Can be caused by Atherosclerosis • Results when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently • Can be caused when heart muscle tissue is weakened by disease • Can be caused when heart valves do not work properly. • When the heart cannot pump blood, fluids collect in the arms, legs, and lungs. • Symptoms = shortness of breath and tired 1. Blood carries oxygen from your lungs to all your body cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses from your body cells into your blood. Your blood carries carbon dioxide to your lungs to be exhaled. 2. Blood carries waste products from your cells to your kidneys to be removed 3. Blood transports nutrients and other substances to your body cells. 4. Cells and molecules in blood fight infections and help heal wounds • Blood is made of a mixture of plasma, cells, and cell fragments • Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood. • Plasma makes up more than half of the volume of blood • Nutrients, minerals, and oxygen are dissolved in plasma and carried to cells • Wastes from cells are also carried in plasma •Formed in the bone marrow • Disk shaped cells with no nuclei • Contain hemoglobin •Hemoglobin carries oxygen •Hemoglobin makes your blood red • Red blood cells survive for about 120 days • Most numerous of the blood cells • Fight bacteria, viruses, and other invaders of your body • Irregularly shaped cell fragments that help clot blood. • Platelets have a life span of 5-9 days