* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4991_Chapter_10_Fall..
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
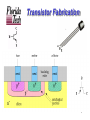
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
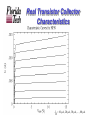
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
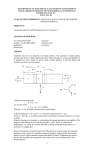
ECE 4991 Electrical and Electronic Circuits Chapter 10 Where We Are • Chapter 2 - The basic concepts and practice at analyzing simple electric circuits with sources and resistors • Chapter 3 – More harder networks to analyze and the notion of equivalent circuits • Chapter 4 – Capacitors and inductors added to the mix • Chapter 5 – Analyzing transient situations in complex passive networks • Chapter 8 – New subject – the wonders of operational amplifiers as system elements • Chapter 9 – Introduction to semiconductors – the basics and diodes – more network analysis • Chapter 10 – Bipolar junction transistors and how they work – now you can build your own op amp 2 What’s Important in Chapter 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Definitions How bipolar transistors work Building a transistor Transistor basics Collector characteristics Load lines and operating points 3 1. Definitions • • • • • • Bipolar transistor • Emitter • Base • Collector • NPN, PNP • • Gain () Cutoff region Active linear region Saturation region Breakdown region Load lines Operating points 4 2. How Bipolar Transistors Work • Transistors are made by creating a PNP (or NPN) “sandwich” • Carriers are “emitted” by the emitter and “collected” by the collector • The base controls how much gets through 5 Transistor Operation • A small amount of base current can control a large amount of collector current • Gain = IC / IB = 6 Transistor Operation in Silicon 7 3. Building a Transistor 8 Transistor Fabrication 9 4. Transistor Basics RC + RB VCC + VBB Typical NPN transistor schematic 10 There are four operating regions for a transistor RC + RB VCC + VBB 1. 2. 3. 4. Cutoff Region – Both junctions reversebiased – Very little base or collector current Active Linear Region – BE junction forward biased, CB junction reverse-biased – amplifying mode Saturation Region – Both junctions forward biased – low VCE – switch mode Breakdown Region – Determines the operating limits of the device 11 5. Collector Characteristics RC + RB VCC + VBB “Collector characteristic” is a plot of collector current versus collectoremitter voltage for different base currents 12 Collector Characteristics “Collector characteristic” is a plot of collector current versus collectoremitter voltage for different base currents 13 Real Transistor Collector Characteristics I = 10 µA, 20 µA, 30 µA, ... , 80 14 µA B 6. Load Lines and Operating Points I = 10 µA, 20 µA, 30 µA, ... , 80 15 µA B Consider this schematic… RC + RB VCC + VBB • • VCC = 15V, RC = 1000, VBB = 3V Design a circuit that operates around the center of the active region collector characteristics 16 First, generate a load line, then set the operating point RC + RB VCC + VBB • • • • • • VCC = 15V, RC = 1000 , VBB = 3V What is IC @ VCE = 0? What is VCE @ IC = 0? Generate load line Pick desired IB Set RB to get it I = 10 µA, 20 µA, 30 µA, ... , 80 µA B 17 Practice with Bipolars 18 Practice with Bipolars 19 Practice with Bipolars 20 Practice with Bipolars 21 Practice with Bipolars 22 Practice with Bipolars 23