* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Expt4
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
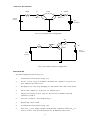
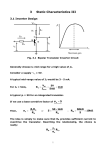
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY COURSE NO.: EEE 212 EXPT. NO. 04 NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT: STUDY OF N-P-N CE AND CB TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS. OBJECTIVE To determine the CE and CB characteristics of a transistor. MATERIALS REQUIRED n-p-n transistor (C829) resistors 2k,1k,500,100 multimeter bread board one piece one piece each two pieces THEORY Transistor has two p-n junctions (see figure below). One junction is called emitter junction and other is called collector junction. When transistor is used as an amplifier, it is operated in active mode. In active mode, emitter junction is forward biased and collector junction is reverse biased. JnE JnC p E iE nC nE JpE iC n p n C C iB B B E Emitter current is given by IE = InE + IpE we can also write IE = IC + IB = [(1 + )/]IC Where = IC /IB is called common emitter current gain. In good transistor IC>>IB i.e. >>1. IC can also be expressed as IC = IE . where = /(1+) . is called common base current gain. For good transistor, is close to unity. Proper dc biasing of a transistor is a prerequisite for proper operation as an amplifier. The purpose of the biasing is to fix the IC (dc) and VCE (dc) . But IC is a function of temperature, VBE and . It is always desirable to design a biasing circuit where IC is insensitive to change in . When E-B junction is forward biased and C-B junction is reverse biased, the transistor operates in active mode. For saturation mode of operation, both junction are forwardbiased. Cut-off region operation requires that both E-B and C-B junctions be reverse biased. The inverted active operation occurs when E-b is reverse-biased and C-B is forward biased. 1 CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS 100 IE C829 IC 500 VEE (0-5V) VCC (0-20V) Fig. 1(a) Common base configeration IC 1k IB 2k C829 VCC (0-20V) VBB (0-5V) Fig. 1(b) Common-emitter configuration PROCEDURE For CB Configuration refer to Fig. 1(a) 1. Construct the circuit shown in Fig. 1(a) 2. Set VCC to 10V. vary VEE so that IE is around 2 mA. Adjust VCC to get VCB as zero. Measure the value of VBE 3. Keeping VCB=0, vary IE by changing VEE and measure the value of VBE and IE 4. Set IE=3mA. Adjust VCC to get VCB=1V. Repeat step 3. 5. Adjust VEE so that IE is zero. Vary VCC from zero to a suitable value and measure VCB and IC. 6. Vary VEE so that IE = 1mA. Repeat step 5. 7. Repeat step 5 for IE=2mA. 8. Assemble the circuit shown in Fig. 1(b). 9. First set VCC=10V. Apply voltage to B-E junction. Adjust the value of VCC so that VCE is zero. Vary VBB and measure VBE for different values of IB. 2 10. Repeat the above experiment for VCE=1Volt. 11. Vary VBB so that IB is about 10A. Vary VCE in steps of 2.5 volts and measure VCE and IC. 12. Repeat the experiment for IB=20A and 30A. REPORT 1. (a) Plot output and input characteristics of the n-p-n CB transistors. (b) Indicate active, linear/saturation and cut-off regions of the characteristics. 2. (a) Plot output and input characteristics of CE transistor. (b) Calculate the early voltage from the output characteristic. (c) Discuss the effect of changing on the output characteristics. (d) Discuss the effect of changing VCE on the input characteristics 3. What are the role of the 2K and 1K fixed resistors in the circuits? 4. Plot (=Ic/IB) as a function of IC for VCE=7.5V. 3