* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3. Celestial Sphere Mark
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
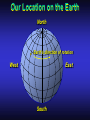
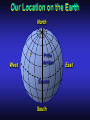
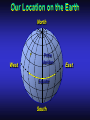
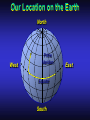
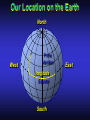
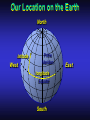
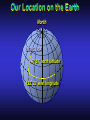
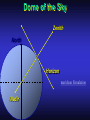
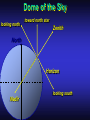
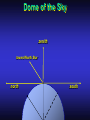
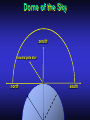
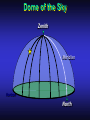
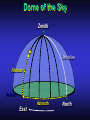
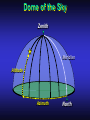
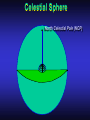
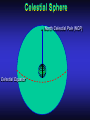
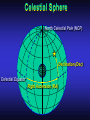
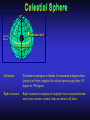
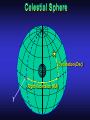
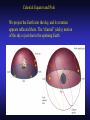
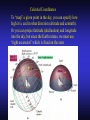
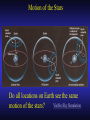
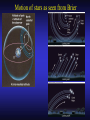
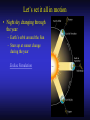
Our Location on the Earth Our Location on the Earth North West East South Our Location on the Earth North you are here West East South Our Location on the Earth North West East South Our Location on the Earth North Earth’s direction of rotation West East South Our Location on the Earth North West East South Our Location on the Earth North West East Equator South Our Location on the Earth North West Prime Meridian Equator South East Our Location on the Earth North West Prime Meridian Equator South East Our Location on the Earth North West Prime Meridian Equator South East Our Location on the Earth North West Prime Meridian longitude Equator South East Our Location on the Earth North latitude West Prime Meridian longitude Equator South East Our Location on the Earth North MTHS, WA 47o 57’ north latitude 122o 23’ west longitude Our Location on the Earth North Brier, WA The Earth turns to the east Our Location on the Earth North Brier, WA Our Location on the Earth North Brier, WA Our Location on the Earth North Brier, WA Our Location on the Earth North Brier, WA Dome of the Sky Zenith North Horizon meridoan Simulation Nadir Dome of the Sky looking north toward north star Zenith North Horizon looking south Nadir Dome of the Sky zenith toward North Star north south Dome of the Sky zenith toward pole star north south Dome of the Sky Dome of the Sky Dome of the Sky Zenith Meridian Horizon North Dome of the Sky Zenith Meridian Altitude Horizon Azimuth East North Dome of the Sky Zenith Meridian Altitude Azimuth North Dome of the Sky Zenith Meridian Altitude Azimuth North Zenith The point directly above the observer Horizon All those points that lie 90 degrees down from the zenith Nadir The point directly below the observer Meridian A vertical circle defined by the path that starts at the zenith and crosses the horizon at a point directly north Altitude The number of degrees along the vertical circle between the object and the horizon Azimuth The number of degrees east of north between the northern horizon and that point where the altitude line crosses the horizon Celestial Sphere Celestial Sphere Celestial Sphere Celestial Sphere North Celestial Pole (NCP) Celestial Sphere North Celestial Pole (NCP) Celestial Sphere North Celestial Pole (NCP) Celestial Equator Celestial Sphere North Celestial Pole (NCP) Celestial Equator Celestial Sphere North Celestial Pole (NCP) Declination (Dec) Celestial Equator Right Ascension (RA) Celestial Sphere NCP Declination (Dec) Celestial Equator Right Ascension (RA) Declination Declination is analogous to latitude. It is measured in degrees above (positive) or below (negative) the celestial equator going from –90 degrees to +90 degrees Right Ascension Right Ascension is analogous to longitude, but it is measured in time units: hours, minutes, seconds, from zero hours to 24 hours Celestial Sphere Declination (Dec) Right Ascension (RA) One of the two points on the Celestial Sphere where the Ecliptic and the Celestial Equator cross one another, The First Point of Aries, which is actually in Pisces, defines the zero-point for Right Ascension. Declination (Dec) Right Ascension (RA) When the Sun reaches the First Point of Aries, as it does once each year, an equinox occurs. In the northern hemisphere, this is the Vernal Equinox, the first day of Spring. The First Point of Aries is not a fixed point in space: it moves along the Ecliptic at a rate of roughly one degree every seventy years. When the Equinox was first observed, thousands of years ago, the First Point actually lay in the constellation of Aries. Due to the effect of precession, the First Point of Aries crossed into the neighboring constellation of Pisces in about 70 BCE. It has taken about 2,000 years to cross Pisces, and it will soon cross into the next zodiacal constellation, Aquarius, in about the year 2600. Following its journey along the Ecliptic, it will return to its starting point in Aries once again in about 23,000 years. The Sky from Here From the ground, the sky looks like a big dome above us. Both the “zenith” and horizon are locally defined. Celestial Equator and Pole We project the Earth into the sky, and its rotation appears reflected there. The “diurnal” (daily) motion of the sky is just due to the spinning Earth. Celestial Coordinates To “map” a given point in the sky, you can specify how high it is, and in what direction (altitude and azimuth). Or you can project latitude (declination) and longitude into the sky, but since the Earth rotates, we must use “right ascension” which is fixed on the stars. Let’s set it all in motion • Diurnal Motion – The rotation of the Earth – This causes the stars to change during a night – They rise in the East and set in the West – Or rise in the SE and set in the SW Motion of the Stars Do all locations on Earth see the same Visible Sky Simulation motion of the stars? Motion of stars as seen from Brier Let’s set it all in motion • Night sky changing through the year – Earth’s orbit around the Sun – Stars up at sunset change during the year Zodiac Simulation Let’s set it all in motion Usefulness of the Constellations • We can use the constellations to orient ourselves in the sky • Polaris - The north star – in Brier our latitude is 48 degrees north – Therefore Polaris is 48 degrees above the horizon – This means you can always know your latitude in the northern hemisphere by knowing were Polaris is • Let’s look to the Northern Sky Northern Sky Usefulness of the Constellations • The constellations can also tell you the time of year by looking to the east around the time of Sunset. • Let’s look at the what you might see in the Summer or Winter Winter Triangle Summer Triangle Chart of the Sky Note how the Sun appears to go North and South as the year progresses. The zero point of Right Ascension occurs at the Spring crossing of the Equator (vernal equinox). The solstices occur at the maximum N/S excursions.