* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy pt. 2
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
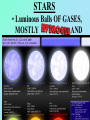
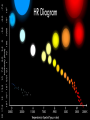
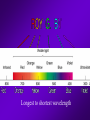
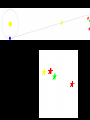
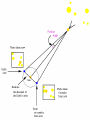
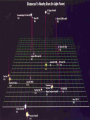
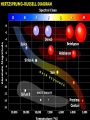
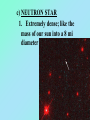
STARS • Luminous Balls OF GASES, MOSTLY AND held together by own gravity • Are all stars the same color? • NO! • Color- determined by surface temperature. • 1. Blue- young and hottest • Ex. Rigel (above 30,000 degrees Celsius • 2. White - usually old and hot o Ex. Sirius (10,000 C) 3. Yellow – Average (5000-6000 C ) temperature and middle age o • Ex. The sun •4 – Red- coolest and growing old •Ex. Betelgeuse less than 3,500 C o Ultraviolet shortest Infrared ^ longest Electromagnetic Spectrum All radiant energy that travels the speed of light in waves Composition, temperature and motion Spectroscope • Attaches to an optical telescope – Analyzes light from the stars Bright line spectrum • Separates visible light by its different wavelengths • Each element is then identified by its own spectrum • Shows direction, movement and composition Spectrum___ D. Classification • 1. H. R. diagram (Hertzsprung – Russell) • 2. Classifies by surface temperature and absolute magnitude. • 3. Main sequence stars- stars of similar composition and size – A. “average” stars • 4. Outside of main sequence 1) Red super giants and red giants 2) Blue Giants. 3) White Dwarfs Betelgeuse Longest to shortest wavelength DOPPLER EFFECT **THE APPARENT SHIFT IN WAVELENGTH DUE TO A MOVING OBJECT Red shift- moving away Blue shift- moving toward DISTANCE LIGHT TRAVELS IN ONE YEAR • 6,000,000,000,000 MILES (186,000 mi/sec) or • 300,000 km/s • AU: Astronomical unit • Distance from Earth to Sun • 149,597,870,700 m or just 1 AU • Distance is measured by using PARALLAX• THE APPARENT SHIFT IN MOTION over time • Ex. • Hold out one arm and give a thumbs up • Close one eye and cover the Red Star • Now switch eyes • That apparent change is parallax! • 2. Apparent Brightness (Magnitude) – A. The brightness we see from earth – B. Depends on size, distance and surface temperature. C. Star’s Brightness • 1. Luminosity or absolute magnitude. – A. Actual brightness of the star – B. found by using the distance and apparent magnitude. OPTICAL TELESCOPES 1. REFRACTING TELESCOPE **uses lenses to bend light to a focus point person 2. Reflecting Telescope – Uses mirrors – Concave mirror reflects light to a flat mirror – Ex. Hubble Space Telescope • Hale telescope 3. Catadioptric Telescope – Uses mirrors – AND Lenses – Ex. Celestron 8 Problems with Optical telescopes • Light pollution EM (electromagnetic) spectrum Jansky 1905-1950 • Discovered radio waves in space 1931 Reber- 1911-2002 • Built the first radio telescope (1937) Collects radio waves from space Can be used at anytime or weather VLA in New Mexico ASTRONOMICAL INSTRUMENTS Radio Telescopes • Operate in the radio frequency portion of the EM spectrum where they can detect and collect data on radio sources. • Used anytime, no light pollution or weather problems Scientific Terms a (testable) proposed explanation for a phenomenon a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with scientific method Alvarez "Big Bang hypothesis “Meteor-impact” theory" describes some aspects of the universe or phenomenon “gravity” E. Life Cycle Of Stars • STEP 1. Begins as a nebula- a cloud of dust and gas. (mostly H and He) • STEP 2. Protostar- gravity forms a ballshaped pocket and temperature increases. STEP 3. Nuclear fusion • 4 hydrogen fuse to make helium plus energy • Occurs in the core • Must be 10 mil – degrees C STEP 4. Main Sequence Star • Must have enough mass to have nuclear fusion for its energy STEP 5. RED GIANTS a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse c)No more H(very little), He turns into C More energy HHe and HeC, gravity cant hold on ahhh! STEP 6. Supernova or white dwarf • a) white dwarf- small, hot, older star no shell, only core left to cool – 1. Ex. Sirius or the Sun (some day) • b) supernova- gigantic explosion of a large mass star like Betelgeuse • Chinese recorded one in 1054 AD Supernova Feb.24, 1987 170,000LY c) NEUTRON STAR 1. Extremely dense; like the mass of our sun into a 8 mi diameter • d) Black hole• 1. An object so dense that not even light can escape its surface QuasarsVery powerful source of energy most distant objects in space • Pulsars– a neutron star that spins rapidly and sends out radio waves GALAXIES 3 TYPES • SPIRAL- 2-4 arms – EX. ANDROMEDA • IRREGULAR – – EX. MAGELLANIC CLOUDS • ELLIPTICAL